
56-bit encryption
Encyclopedia
In computing, 56-bit encryption refers to a key size
of fifty-six bit
s, or seven byte
s, for symmetric encryption. While stronger than 40-bit encryption, this still represents a relatively low level of security in the context of a brute force attack
.
until control was transferred to the Department of Commerce in 1996.
56-bit refers to the size of a symmetric key used to encrypt data, with the number of unique possible permutations being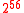 (72,057,594,037,927,936). 56-bit encryption has its roots in DES
(72,057,594,037,927,936). 56-bit encryption has its roots in DES
, which was the official standard of the US National Bureau of Standards from 1976, and later also the RC5
algorithm. US government regulations required any users of stronger 56-bit symmetric keys to submit to key recovery though algorithms like CDMF
, effectively reducing the key strength to 40-bit, and thereby allowing organisations such as the NSA to brute-force this encryption. Furthermore, from 1996 software products exported
from the United States were not permitted to use stronger than 56-bit encryption, requiring different software editions for the US and export markets.
The advent of commerce on the Internet and faster computers raised concerns about the security of electronic transactions
initially with 40-bit, and subsequently also with 56-bit encryption. Although regulations over the use of 56-bit encryption were lifted in 1998, in July of that year a successful brute-force attack was demonstrated against 56-bit encryption with a single desktop computer in just 56 hours. In 1999, all restrictions on key length were lifted, except for exports to terrorist countries.
56-bit DES encryption is now obsolete, having been replaced as a standard in 2002 by the 128-bit (and stronger) Advanced Encryption Standard
.
Key size
In cryptography, key size or key length is the size measured in bits of the key used in a cryptographic algorithm . An algorithm's key length is distinct from its cryptographic security, which is a logarithmic measure of the fastest known computational attack on the algorithm, also measured in bits...
of fifty-six bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s, or seven byte
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information in computing and telecommunications that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, a byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the basic addressable element in many computer...
s, for symmetric encryption. While stronger than 40-bit encryption, this still represents a relatively low level of security in the context of a brute force attack
Brute force attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack, or exhaustive key search, is a strategy that can, in theory, be used against any encrypted data. Such an attack might be utilized when it is not possible to take advantage of other weaknesses in an encryption system that would make the task easier...
.
Descrption
The US government traditionally regulated encryption for reasons of national security, law enforcement and foreign policy. Encryption was regulated from 1976 by the Arms Export Control ActArms Export Control Act
The Arms Export Control Act of 1976 gives the President of the United States the authority to control the import and export of defense articles and defense services. It requires governments that receive weapons from the United States to use them for legitimate self-defense...
until control was transferred to the Department of Commerce in 1996.
56-bit refers to the size of a symmetric key used to encrypt data, with the number of unique possible permutations being
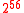 (72,057,594,037,927,936). 56-bit encryption has its roots in DES
(72,057,594,037,927,936). 56-bit encryption has its roots in DESData Encryption Standard
The Data Encryption Standard is a block cipher that uses shared secret encryption. It was selected by the National Bureau of Standards as an official Federal Information Processing Standard for the United States in 1976 and which has subsequently enjoyed widespread use internationally. It is...
, which was the official standard of the US National Bureau of Standards from 1976, and later also the RC5
RC5
In cryptography, RC5 is a block cipher notable for its simplicity. Designed by Ronald Rivest in 1994, RC stands for "Rivest Cipher", or alternatively, "Ron's Code"...
algorithm. US government regulations required any users of stronger 56-bit symmetric keys to submit to key recovery though algorithms like CDMF
CDMF
In cryptography, CDMF is an algorithm developed at IBM in 1992 to reduce the security strength of the 56-bit DES cipher to that of 40-bit encryption, at the time a requirement of U.S. restrictions on export of cryptography. Rather than a separate cipher from DES, CDMF constitutes a key generation...
, effectively reducing the key strength to 40-bit, and thereby allowing organisations such as the NSA to brute-force this encryption. Furthermore, from 1996 software products exported
Export of cryptography
The export of cryptography in the United States is the transfer from the United States to another country of devices and technology related to cryptography....
from the United States were not permitted to use stronger than 56-bit encryption, requiring different software editions for the US and export markets.
The advent of commerce on the Internet and faster computers raised concerns about the security of electronic transactions
Electronic commerce
Electronic commerce, commonly known as e-commerce, eCommerce or e-comm, refers to the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. However, the term may refer to more than just buying and selling products online...
initially with 40-bit, and subsequently also with 56-bit encryption. Although regulations over the use of 56-bit encryption were lifted in 1998, in July of that year a successful brute-force attack was demonstrated against 56-bit encryption with a single desktop computer in just 56 hours. In 1999, all restrictions on key length were lifted, except for exports to terrorist countries.
56-bit DES encryption is now obsolete, having been replaced as a standard in 2002 by the 128-bit (and stronger) Advanced Encryption Standard
Advanced Encryption Standard
Advanced Encryption Standard is a specification for the encryption of electronic data. It has been adopted by the U.S. government and is now used worldwide. It supersedes DES...
.

