
AMD K6-2
Encyclopedia
The K6-2 was an x86 microprocessor
introduced by AMD
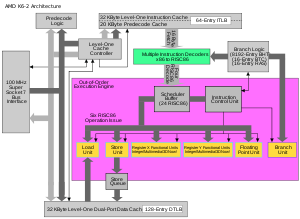
on May 28, 1998, and available in speeds ranging from 266 to 550 MHz. An enhancement of the original K6, the K6-2 introduced AMD's 3D-Now! SIMD instruction set, featured a larger 64 KiB
Level 1 cache
(32 KiB instruction and 32 KiB data), and an upgraded system-bus interface called Super Socket 7
, which was backward compatible with older Socket 7
motherboard
s. It was manufactured using a 0.25 micrometre
process, ran at 2.2 volt
s, and had 9.3 million transistor
s.
 The K6-2 was designed as a competitor to Intel's flagship processor, the significantly more expensive Pentium II
The K6-2 was designed as a competitor to Intel's flagship processor, the significantly more expensive Pentium II
. Performance of the two chips was similar: the previous K6-2
tended to be faster for general-purpose computing, while the Intel part was faster in x87 floating-point applications. To battle the Pentium 2's dominance on floating point calculations the K6-2 was the first CPU to introduce a floating point SIMD
instruction set (dubbed 3DNow!
by AMD), which significantly boosted performance. However programs needed to be specifically tailored for the new instructions and despite beating Intel's SSE
instruction set to market, 3DNow achieved only limited popularity.
Super Socket 7, which increased the processor bus from 66 MHz to 100 MHz, allowed the K6-2 to withstand the effects of ever-increasing CPU multipliers fairly gracefully and in later life it remained surprisingly competitive. Nearly all K6-2s were designed to use 100 MHz Super Socket 7
mainboards, allowing the system-bus to keep pace with the K6-2's clock-frequency.
The K6-2 was a very financially successful chip and enabled AMD to earn the revenue it would need to introduce the forthcoming Athlon
. The introductory K6-2 300 was by far the best-selling variant. It rapidly established an excellent reputation in the marketplace and offered a favorable price/performance ratio versus Intel's Celeron
300A. The Celeron offered superior floating-point performance, but the K6-2 offered faster system RAM access (courtesy of the Super 7 mainboard), as well as 3DNow graphics extensions.
As the market moved on, AMD released a long series of faster K6-2 parts, the best-selling ones being the 350, 400, 450, and 500. By the time the 450 and the 500 were mainstream parts, the K6-2 family had already moved to the budget PC segment, where it still competed successfully against Intel's Celeron.
process (essentially a K6-III+ with half the L2 cache). The K6-2+ was specifically designed as a low-power mobile CPU.


Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
introduced by AMD
Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. or AMD is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Sunnyvale, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for commercial and consumer markets...
on May 28, 1998, and available in speeds ranging from 266 to 550 MHz. An enhancement of the original K6, the K6-2 introduced AMD's 3D-Now! SIMD instruction set, featured a larger 64 KiB
Binary prefix
In computing, a binary prefix is a specifier or mnemonic that is prepended to the units of digital information, the bit and the byte, to indicate multiplication by a power of 2...
Level 1 cache
CPU cache
A CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
(32 KiB instruction and 32 KiB data), and an upgraded system-bus interface called Super Socket 7
Super Socket 7
The Super Socket 7, also referred to as Super 7, is an extension of the Socket 7 ZIF socket specification. It features a 100 MHz front-side bus, support for AGP, and a SPGA package. Super Socket was used by AMD K6-2 and K6-III processors, and some of the final Cyrix M-II processors...
, which was backward compatible with older Socket 7
Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others.Socket 7 was...
motherboard
Motherboard
In personal computers, a motherboard is the central printed circuit board in many modern computers and holds many of the crucial components of the system, providing connectors for other peripherals. The motherboard is sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system board, or, on Apple...
s. It was manufactured using a 0.25 micrometre
Micrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
process, ran at 2.2 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s, and had 9.3 million transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s.
History

Pentium II
The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million...
. Performance of the two chips was similar: the previous K6-2
AMD K6-2
The K6-2 was an x86 microprocessor introduced by AMD on May 28, 1998, and available in speeds ranging from 266 to 550 MHz. An enhancement of the original K6, the K6-2 introduced AMD's 3D-Now! SIMD instruction set, featured a larger 64 KiB Level 1 cache , and an upgraded system-bus interface...
tended to be faster for general-purpose computing, while the Intel part was faster in x87 floating-point applications. To battle the Pentium 2's dominance on floating point calculations the K6-2 was the first CPU to introduce a floating point SIMD
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data , is a class of parallel computers in Flynn's taxonomy. It describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data simultaneously...
instruction set (dubbed 3DNow!
3DNow!
3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
by AMD), which significantly boosted performance. However programs needed to be specifically tailored for the new instructions and despite beating Intel's SSE
Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
instruction set to market, 3DNow achieved only limited popularity.
Super Socket 7, which increased the processor bus from 66 MHz to 100 MHz, allowed the K6-2 to withstand the effects of ever-increasing CPU multipliers fairly gracefully and in later life it remained surprisingly competitive. Nearly all K6-2s were designed to use 100 MHz Super Socket 7
Super Socket 7
The Super Socket 7, also referred to as Super 7, is an extension of the Socket 7 ZIF socket specification. It features a 100 MHz front-side bus, support for AGP, and a SPGA package. Super Socket was used by AMD K6-2 and K6-III processors, and some of the final Cyrix M-II processors...
mainboards, allowing the system-bus to keep pace with the K6-2's clock-frequency.
The K6-2 was a very financially successful chip and enabled AMD to earn the revenue it would need to introduce the forthcoming Athlon
Athlon
Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices . The original Athlon was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and, in a first, retained the initial performance lead it had over Intel's competing processors...
. The introductory K6-2 300 was by far the best-selling variant. It rapidly established an excellent reputation in the marketplace and offered a favorable price/performance ratio versus Intel's Celeron
Celeron
Celeron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers....
300A. The Celeron offered superior floating-point performance, but the K6-2 offered faster system RAM access (courtesy of the Super 7 mainboard), as well as 3DNow graphics extensions.
As the market moved on, AMD released a long series of faster K6-2 parts, the best-selling ones being the 350, 400, 450, and 500. By the time the 450 and the 500 were mainstream parts, the K6-2 family had already moved to the budget PC segment, where it still competed successfully against Intel's Celeron.
K6-2+
Despite the name, the little-known K6-2+ was based on the AMD K6-III+ design (model 13) with 128 KiB of integrated L2 cache and built on a 0.18 micrometreMicrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
process (essentially a K6-III+ with half the L2 cache). The K6-2+ was specifically designed as a low-power mobile CPU.
K6-2 (Chomper, 250 nm)


- CPUIDCPUIDThe CPUID opcode is a processor supplementary instruction for the x86 architecture. It was introduced by Intel in 1993 when it introduced the Pentium and SL-Enhanced 486 processors....
: Family 5, Model 8, Stepping 0 - L1-Cache: 32 + 32 KiB (Data + Instructions)
- MMX, 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
- 9.3 million transistors
- Super Socket 7Super Socket 7The Super Socket 7, also referred to as Super 7, is an extension of the Socket 7 ZIF socket specification. It features a 100 MHz front-side bus, support for AGP, and a SPGA package. Super Socket was used by AMD K6-2 and K6-III processors, and some of the final Cyrix M-II processors...
- Front side busFront side busA front-side bus is a computer communication interface often used in computers during the 1990s and 2000s.It typically carries data between the central processing unit and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge....
: 66, 100 MHz - VCore: 2.2V
- First release: May 28, 1998
- Manufacturing process: 0.25 µm
- Clockrate: 233, 266, 300, 333 & 350 MHz
K6-2 (Chomper Extended (CXT), 250 nm)
- CPUID: Family 5, Model 8, Stepping 12
- L1-Cache: 32 + 32 KiB (Data + Instructions)
- MMX, 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
- Super Socket 7Super Socket 7The Super Socket 7, also referred to as Super 7, is an extension of the Socket 7 ZIF socket specification. It features a 100 MHz front-side bus, support for AGP, and a SPGA package. Super Socket was used by AMD K6-2 and K6-III processors, and some of the final Cyrix M-II processors...
- Front side busFront side busA front-side bus is a computer communication interface often used in computers during the 1990s and 2000s.It typically carries data between the central processing unit and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge....
: 66, 95, 97, 100 MHz - VCore: 2.0(mobile)/2.2/2.3/2.4V
- First release: November 16, 1998
- Manufacturing process: 0.25 µm
- Clockrate: 266, 300, 333, 350, 366, 380, 400, 427.5, 450, 475, 500, 533 & 550 MHz

