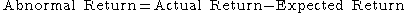Abnormal returns
Encyclopedia
In finance, an abnormal return is the difference between the actual return
of a security
and the expected return
. Abnormal returns are sometimes triggered by "events." Events can include merger
s, dividend
announcements, company earning announcements, interest rate increases, lawsuit
s, etc. all which can contribute to an abnormal return. Events in finance can typically be classified as occurrences or information that has not already been priced by the market
.
trading, abnormal returns are the differences between a single stock or portfolio's performance and the expected return over a set period of time. Usually a broad index, such as the S&P 500
or a national index like the Nikkei 225
, is used as a benchmark to determine the expected return. For example if a stock increased by 5% because of some news which affected the stock price, but the average market only increased by 3% and the stock has a beta of 1, then the abnormal return was 2% (5% - 3% = 2%). If the market average performs better (after adjusting for beta) than the individual stock then the abnormal return will be negative.
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
of a security
Security (finance)
A security is generally a fungible, negotiable financial instrument representing financial value. Securities are broadly categorized into:* debt securities ,* equity securities, e.g., common stocks; and,...
and the expected return
Expected return
The expected return is the weighted-average outcome in gambling, probability theory, economics or finance.It isthe average of a probability distribution of possible returns, calculated by using the following formula:...
. Abnormal returns are sometimes triggered by "events." Events can include merger
Mergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions refers to the aspect of corporate strategy, corporate finance and management dealing with the buying, selling, dividing and combining of different companies and similar entities that can help an enterprise grow rapidly in its sector or location of origin, or a new field or...
s, dividend
Dividend
Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholder members. It is the portion of corporate profits paid out to stockholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, that money can be put to two uses: it can either be re-invested in the business , or it can be distributed to...
announcements, company earning announcements, interest rate increases, lawsuit
Lawsuit
A lawsuit or "suit in law" is a civil action brought in a court of law in which a plaintiff, a party who claims to have incurred loss as a result of a defendant's actions, demands a legal or equitable remedy. The defendant is required to respond to the plaintiff's complaint...
s, etc. all which can contribute to an abnormal return. Events in finance can typically be classified as occurrences or information that has not already been priced by the market
Financial market
In economics, a financial market is a mechanism that allows people and entities to buy and sell financial securities , commodities , and other fungible items of value at low transaction costs and at prices that reflect supply and demand.Both general markets and...
.
Stock market
In stock marketStock market
A stock market or equity market is a public entity for the trading of company stock and derivatives at an agreed price; these are securities listed on a stock exchange as well as those only traded privately.The size of the world stock market was estimated at about $36.6 trillion...
trading, abnormal returns are the differences between a single stock or portfolio's performance and the expected return over a set period of time. Usually a broad index, such as the S&P 500
S&P 500
The S&P 500 is a free-float capitalization-weighted index published since 1957 of the prices of 500 large-cap common stocks actively traded in the United States. The stocks included in the S&P 500 are those of large publicly held companies that trade on either of the two largest American stock...
or a national index like the Nikkei 225
Nikkei 225
The , more commonly called the Nikkei, the Nikkei index, or the Nikkei Stock Average , is a stock market index for the Tokyo Stock Exchange . It has been calculated daily by the Nihon Keizai Shimbun newspaper since 1950. It is a price-weighted average , and the components are reviewed once a year...
, is used as a benchmark to determine the expected return. For example if a stock increased by 5% because of some news which affected the stock price, but the average market only increased by 3% and the stock has a beta of 1, then the abnormal return was 2% (5% - 3% = 2%). If the market average performs better (after adjusting for beta) than the individual stock then the abnormal return will be negative.