
S&P 500
Encyclopedia


Stock market index
A stock market index is a method of measuring a section of the stock market. Many indices are cited by news or financial services firms and are used as benchmarks, to measure the performance of portfolios such as mutual funds....
published since 1957 of the prices of 500 large-cap
Market capitalization
Market capitalization is a measurement of the value of the ownership interest that shareholders hold in a business enterprise. It is equal to the share price times the number of shares outstanding of a publicly traded company...
common stock
Common stock
Common stock is a form of corporate equity ownership, a type of security. It is called "common" to distinguish it from preferred stock. In the event of bankruptcy, common stock investors receive their funds after preferred stock holders, bondholders, creditors, etc...
s actively traded in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. The stocks included in the S&P 500 are those of large publicly held companies
Corporation
A corporation is created under the laws of a state as a separate legal entity that has privileges and liabilities that are distinct from those of its members. There are many different forms of corporations, most of which are used to conduct business. Early corporations were established by charter...
that trade on either of the two largest American
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
stock market exchanges: the New York Stock Exchange
New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange is a stock exchange located at 11 Wall Street in Lower Manhattan, New York City, USA. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed companies at 13.39 trillion as of Dec 2010...
and the NASDAQ
NASDAQ
The NASDAQ Stock Market, also known as the NASDAQ, is an American stock exchange. "NASDAQ" originally stood for "National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations". It is the second-largest stock exchange by market capitalization in the world, after the New York Stock Exchange. As of...
.
The index focus is U.S.-based companies although there are a few companies with headquarters in and/or incorporated in other countries.
After the Dow Jones Industrial Average
Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average , also called the Industrial Average, the Dow Jones, the Dow 30, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index, and one of several indices created by Wall Street Journal editor and Dow Jones & Company co-founder Charles Dow...
, the S&P 500 is one of the most commonly followed equity indices, is considered a bellwether
Bellwether
A bellwether is any entity in a given arena that serves to create or influence trends or to presage future happenings.The term is derived from the Middle English bellewether and refers to the practice of placing a bell around the neck of a castrated ram leading his flock of sheep.The movements of...
for the American economy, and is included in the Index of Leading Indicators
Index of Leading Indicators
The Conference Board Leading Economic Index is an American economic leading indicator intended to forecast future economic activity. It is calculated by The Conference Board, a non-governmental organization, which determines the value of the index from the values of ten key variables. These...
. Many mutual funds
Index fund
An index fund or index tracker is a collective investment scheme that aims to replicate the movements of an index of a specific financial market, or a set of rules of ownership that are held constant, regardless of market conditions.-Tracking:Tracking can be achieved by trying to hold all of the...
, exchange-traded fund
Exchange-traded fund
An exchange-traded fund is an investment fund traded on stock exchanges, much like stocks. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, commodities, or bonds, and trades close to its net asset value over the course of the trading day. Most ETFs track an index, such as the S&P 500 or MSCI EAFE...
s, and other funds such as pension fund
Pension fund
A pension fund is any plan, fund, or scheme which provides retirement income.Pension funds are important shareholders of listed and private companies. They are especially important to the stock market where large institutional investors dominate. The largest 300 pension funds collectively hold...
s, are designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 index. Hundreds of billions of US dollars have been invested in this fashion.
The index is the best known of the many indices owned and maintained by Standard & Poor's
Standard & Poor's
Standard & Poor's is a United States-based financial services company. It is a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks and bonds. It is well known for its stock-market indices, the US-based S&P 500, the Australian S&P/ASX 200, the Canadian...
, a division of McGraw-Hill
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., is a publicly traded corporation headquartered in Rockefeller Center in New York City. Its primary areas of business are financial, education, publishing, broadcasting, and business services...
. S&P 500 refers not only to the index, but also to the 500 companies that have their common stock included in the index. The ticker symbol
Ticker symbol
A stock symbol or ticker symbol is a short abbreviation used to uniquely identify publicly traded shares of a particular stock on a particular stock market. A stock symbol may consist of letters, numbers or a combination of both. "Ticker symbol" refers to the symbols that were printed on the ticker...
for the S&P 500 index varies. Some examples of the symbol are ^GSPC,.INX, and $SPX. The stocks included in the S&P 500 index are also part of the broader S&P 1500
S&P 1500
The S&P 1500, or S&P 1500 Composite Index, is a stock market index of US stocks made by Standard & Poor's. It includes all stocks in the S&P 500, S&P 400, and S&P 600.-Annual returns:-External links:* * *...
and S&P Global 1200
S&P Global 1200
The S&P Global 1200 Index is a free-float weighted stock market index of global equities from Standard & Poor's. The index covers 31 countries and approximately 70 percent of global stock market capitalization...
stock market indices.
History
Standard & Poor'sStandard & Poor's
Standard & Poor's is a United States-based financial services company. It is a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks and bonds. It is well known for its stock-market indices, the US-based S&P 500, the Australian S&P/ASX 200, the Canadian...
introduced its first stock index in 1923. Before 1957, its primary daily stock market index was the "S&P 90", a value-weighted index based on 90 stocks. Standard & Poor's also published a weekly index of 423 companies. The S&P 500 index in its present form began on March 4, 1957. Thanks to the computer technology emerging at the time, this index could be calculated and disseminated in real time. The S&P 500 is widely employed as a measure of the general level of stock prices, as it includes both growth stock
Growth stock
In finance, a growth stock is a stockof a company that generates substantial and sustainable positive cash flow and whose revenues and earnings are expected to increase at a faster rate than the average company within the same industry...
s and the generally less volatile value stocks.
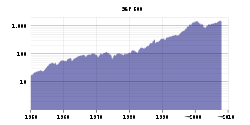
The index reached an all-time intraday high (which was not exceeded for over seven years) of 1,552.87 in trading on March 24, 2000, during the dot-com bubble
Dot-com bubble
The dot-com bubble was a speculative bubble covering roughly 1995–2000 during which stock markets in industrialized nations saw their equity value rise rapidly from growth in the more...
, and then lost approximately 50% of its value in a two-year bear market, spiking below 800 points in July 2002 and reaching a low of 768.63 intraday on October 10, 2002 during the stock market downturn of 2002
Stock market downturn of 2002
The stock market downturn of 2002 is the sharp drop in stock prices during 2002 in stock exchanges across the United States, Canada, Asia, and Europe...
. The S&P 500 remained below its year 2000 all-time high somewhat longer than the popular Dow Jones Industrial Average
Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average , also called the Industrial Average, the Dow Jones, the Dow 30, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index, and one of several indices created by Wall Street Journal editor and Dow Jones & Company co-founder Charles Dow...
and the more comprehensive Wilshire 5000
Wilshire 5000
The Wilshire 5000 Total Market Index, or more simply the Wilshire 5000, is a market-capitalization-weighted index of the market value of all stocks actively traded in the United States. Currently, the index contains over 4,100 components...
. However, on May 30, 2007, the S&P 500 closed at 1,530.23 to set its first all-time closing high in more than seven years. The highest point reached was 1,565.15 on October 9, 2007.
In mid-2007, difficulties stemming from subprime mortgage lending began spreading to the wider financial sector, resulting in the second bear market of the 21st century. The resulting crisis became acute in September 2008, ushering in a period of unusual volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
, encompassing record 100-point moves in both directions and reaching the highest levels since 1929. On November 20, 2008, the index closed at 752.44, its lowest close since early 1997. A modest recovery the following day still left the index down 45.5% for the year. This year-to-date loss was the greatest since 1931, when the broad market declined more than 50%; the total losses that ushered in the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
exceeded 80% over a three-year period. The market continued to decline between late 2008 and early 2009 surrounding the events involving the financial crisis of 2008, reaching a nearly 13-year closing low at 676.53 on March 9. Subsequently, the index has recovered sharply to close at 1,206.07 on December 1, 2010, up over 78% from the low but still down by more than 23% from the 2007 high; this respite has been alternately characterized as heralding a return to economic growth, or a significant counter-trend bear market rally. On April 29, 2011, the S&P 500 closed at 1,363.61, its highest close since June 5, 2008.
Selection
The components of the S&P 500 are selected by committee. This is similar to the Dow 30Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average , also called the Industrial Average, the Dow Jones, the Dow 30, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index, and one of several indices created by Wall Street Journal editor and Dow Jones & Company co-founder Charles Dow...
, but different from others such as the Russell 1000
Russell 1000
The Russell 1000 Index is a stock market index that represents the highest-ranking 1,000 stocks in the Russell 3000 Index, which represents about 90% of the total market capitalization of that index. The Russell 1000 Index has a weighted average market capitalization of $81 billion; the median...
, which are strictly rules-based.
The index does include a handful (13 as of November 22, 2011) of non-U.S. companies. This group includes both formerly U.S. companies that have reincorporated outside the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, as well as firms that have never been incorporated in the United States.
The committee selects the companies in the S&P 500 so they are representative of the industries in the United States economy. In addition, companies that do not have common stock that trades publicly (such as limited partnership
Limited partnership
A limited partnership is a form of partnership similar to a general partnership, except that in addition to one or more general partners , there are one or more limited partners . It is a partnership in which only one partner is required to be a general partner.The GPs are, in all major respects,...
s and companies that are privately or mutually held) and stocks that do not have sufficient liquidity are not in the index. By contrast, the Fortune 500
Fortune 500
The Fortune 500 is an annual list compiled and published by Fortune magazine that ranks the top 500 U.S. closely held and public corporations as ranked by their gross revenue after adjustments made by Fortune to exclude the impact of excise taxes companies collect. The list includes publicly and...
attempts to list the 500 largest public companies in the United States by gross revenue, regardless of whether their stocks trade or their liquidity, without adjustment for industry representation, and excluding companies incorporated outside the United States.
Versions
The "S&P 500" generally quoted is a price returnPrice return
The price return is the rate of return on an investment portfolio, where the return measure takes into account only the capital appreciation of the portfolio, while the income generated by the assets in the portfolio, in the form of interest and dividends, is ignored...
index; there are also "total return" and "net total return" versions of the index. These versions differ in how dividend
Dividend
Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholder members. It is the portion of corporate profits paid out to stockholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, that money can be put to two uses: it can either be re-invested in the business , or it can be distributed to...
s are accounted for. The price return version does not account for dividends; it only captures the changes in the prices of the index components. The total return
Total return index
A total return index is an index that measures the performance of a group of components by assuming that all cash distributions are reinvested, in addition to tracking the components' price movements. While it is common to refer to equity based indices, there are also total return indices for bonds...
version reflects the effects of dividend reinvestment. Finally, the net total return version reflects the effects of dividend reinvestment after the deduction of withholding tax
Withholding tax
Withholding tax, also called retention tax, is a government requirement for the payer of an item of income to withhold or deduct tax from the payment, and pay that tax to the government. In most jurisdictions, withholding tax applies to employment income. Many jurisdictions also require...
.
Weighting
The index has traditionally been market-value weightedMarket value-weighted index
A capitalization-weighted index is an index whose components are weighted according to the total market value of their outstanding shares. Also called a market-value-weighted index...
; that is, movements in the prices of stocks with higher market capitalization
Market capitalization
Market capitalization is a measurement of the value of the ownership interest that shareholders hold in a business enterprise. It is equal to the share price times the number of shares outstanding of a publicly traded company...
s (the share price times the number of shares outstanding) have a greater effect on the index than companies with smaller market caps.
The index is now float weighted. That is, Standard & Poor's now calculates the market caps relevant to the index using only the number of shares (called "float") available for public trading. This transition was made in two steps, the first on March 18, 2005 and the second on September 16, 2005.
Index maintenance
In order to keep the S&P 500 Index comparable across time, the index needs to take into account corporate actions such as stock splitStock split
A stock split or stock divide increases the number of shares in a public company. The price is adjusted such that the before and after market capitalization of the company remains the same and dilution does not occur. Options and warrants are included....
s, share issuance, dividends and restructuring events (such as merger or spinoffs). Additionally, in order to keep the Index reflective of American stocks, the constituent stocks need to be changed from time to time.
To prevent the value of the Index from changing merely as a result of corporate financial actions, all such actions affecting the market value of the Index require a Divisor adjustment. Also, when a company is dropped and replaced by another with a different market capitalization, the divisor needs to be adjusted in such a way that the value of the S&P 500 Index remains constant. All Divisor adjustments are made after the close of trading and after the calculation of the closing value of the S&P 500 Index.
| Type of Action | Divisor Adjustment |
| Stock Split (e.g. 2x1) | No |
| Share Issuance | Yes |
| Share Repurchase | Yes |
| Special Cash Dividend | Yes |
| Company Change | Yes |
| Rights offering | Yes |
| Spinoffs | Yes |
| Mergers | Yes |
Investing
Many index fundIndex fund
An index fund or index tracker is a collective investment scheme that aims to replicate the movements of an index of a specific financial market, or a set of rules of ownership that are held constant, regardless of market conditions.-Tracking:Tracking can be achieved by trying to hold all of the...
s and exchange-traded fund
Exchange-traded fund
An exchange-traded fund is an investment fund traded on stock exchanges, much like stocks. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, commodities, or bonds, and trades close to its net asset value over the course of the trading day. Most ETFs track an index, such as the S&P 500 or MSCI EAFE...
s attempt to replicate (before fees and expenses) the performance of the S&P 500 by holding the same stocks as the index, in the same proportions. Many other mutual funds are benchmarked to the S&P 500. Consequently, a company whose stock is added to the list of S&P 500 stocks may see its stock price rise, as the managers of index fund
Index fund
An index fund or index tracker is a collective investment scheme that aims to replicate the movements of an index of a specific financial market, or a set of rules of ownership that are held constant, regardless of market conditions.-Tracking:Tracking can be achieved by trying to hold all of the...
s normally choose to purchase that company's stock in order to continue tracking the S&P 500 index.
Several mutual fund
Mutual fund
A mutual fund is a professionally managed type of collective investment scheme that pools money from many investors to buy stocks, bonds, short-term money market instruments, and/or other securities.- Overview :...
managers also provide index fund
Index fund
An index fund or index tracker is a collective investment scheme that aims to replicate the movements of an index of a specific financial market, or a set of rules of ownership that are held constant, regardless of market conditions.-Tracking:Tracking can be achieved by trying to hold all of the...
s that track the S&P 500, the first of which was The Vanguard Group
The Vanguard Group
The Vanguard Group is an American investment management company based in Malvern, Pennsylvania, that manages approximately $1.6 trillion in assets. It offers mutual funds and other financial products and services to individual and institutional investors in the United States and abroad. Founder...
's Vanguard 500 in 1976. Many retirement plans offer such funds. For example, the Thrift Savings Plan
Thrift Savings Plan
The Thrift Savings Plan is a defined contribution plan for United States civil service employees and retirees as well as for members of the uniformed services....
's C Fund tracks the total return S&P 500 index.
In addition to investing in a mutual fund indexed to the S&P 500, investors may also purchase shares of an exchange-traded fund
Exchange-traded fund
An exchange-traded fund is an investment fund traded on stock exchanges, much like stocks. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, commodities, or bonds, and trades close to its net asset value over the course of the trading day. Most ETFs track an index, such as the S&P 500 or MSCI EAFE...
(ETF) which represents ownership in a portfolio of the equity securities that comprise the Standard & Poor's 500 Index. One of these ETF's is called the Standard & Poor's Depositary Receipts
Standard & Poor's Depositary Receipts
The Standard & Poor's Depositary Receipts were launched by Boston asset manager SSgA State Street Global Advisors on January 29, 1993 as the first exchange-traded fund in the United States ; and are part of the SPDRs ETF chain.Designed and developed by American Stock Exchange executives Nathan Most...
; , originating from a chain of ETFs called the SPDR
SPDR
SPDR can mean:* Standard & Poor's Depositary Receipts, an exchange-traded fund.* "System Peril Distributed Reflex" is the name given to one of the AIs in the alternate reality game The Haunted Apiary ....
s, pronounced "spiders", and is issued by SSgA State Street Global Advisors
State Street Global Advisors
State Street Global Advisors is the investment management division of State Street Corporation and the world’s second largest asset manager, with $1.9 trillion in assets under management as of June 2010....
. Typical volume for the SPY SPDR averages between 300-400 million shares per day; the highest of any US stock traded on any exchange.
On October 10, 2008, trading volume for the SPY SPDR surpassed 871 million shares; with a closing price of $88.50, the monetary value of traded shares which changed hands exceeded an astounding 77 billion dollars for the day. BlackRock
BlackRock
BlackRock, Inc. is an American multinational investment management corporation and the world's largest asset manager. BlackRock is headquartered in Manhattan, New York City, New York, United States and is the leading provider of investment, advisory, and risk management solutions...
offers
the iShares
IShares
iShares are a family of exchange-traded funds managed by BlackRock. The first iShares were known as WEBS but were since rebranded.Each iShares fund tracks a bond or stock market index...
S&P 500 , which is similar to the SPDRs, but is structured differently. Both the SPDRs and the iShares have a management expense ratio
Expense Ratio
The Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses is the line of the fee table in the prospectus that represents the total of all of a mutual fund's annual fund operating expenses, expressed as a percentage of the fund's average net assets...
of under 0.1% a year; making them an efficient proxy for the underlying index, while achieving a performance close to the S&P 500 (minus fees and expenses).
Through RydexShares, fund manager Rydex also offers an ETF, the S&P Equal Weight , which provides equal exposure to all the companies in the S&P 500. In addition, Rydex offers other related S&P 500 index ETFs such as the 2x , which attempts to match the daily performance of the S&P 500 by 200% and the Inverse 2x , which attempts to match the inverse daily performance by 200%. More heavily traded ProShares issued by ProFunds offer Inverse Performance for a bearish strategy on the index, Inverse 2x Performance , and 2x Performance . For additional leverage, ProFunds also offers 3x Performance , which attempts to match the daily performance of the S&P 500 by 300% as well as Inverse 3x Performance , which attempts to match the inverse daily performance of the S&P 500 by 300%.
In the derivatives
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
market, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange
Chicago Mercantile Exchange
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange is an American financial and commodity derivative exchange based in Chicago. The CME was founded in 1898 as the Chicago Butter and Egg Board. Originally, the exchange was a non-profit organization...
(CME) offers futures contract
Futures contract
In finance, a futures contract is a standardized contract between two parties to exchange a specified asset of standardized quantity and quality for a price agreed today with delivery occurring at a specified future date, the delivery date. The contracts are traded on a futures exchange...
s that track the index and trade on the exchange floor in an open outcry auction, or on CME's Globex platform, and are the exchange's most popular product. Additionally, the Chicago Board Options Exchange
Chicago Board Options Exchange
The Chicago Board Options Exchange , located at 400 South LaSalle Street in Chicago, is the largest U.S. options exchange with annual trading volume that hovered around one billion contracts at the end of 2007...
(CBOE) offers options
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
on the S&P 500 as well as S&P 500 ETFs, inverse ETFs and leveraged ETFs.
Records (a)
| Milestone | Closing Level | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 100.38 | June 4, 1968 |
| 200 | 201.41 | November 21, 1985 |
| 300 | 301.16 | March 23, 1987 |
| 400 | 404.84 | December 26, 1991 |
| 500 | 500.97 | March 24, 1995 |
| 600 | 600.07 | November 17, 1995 |
| 700 | 701.46 | October 4, 1996 |
| 800 | 802.77 | February 12, 1997 |
| 900 | 904.03 | July 2, 1997 |
| 1,000 | 1,001.27 | February 2, 1998 |
| 1,100 | 1,105.65 | March 24, 1998 |
| 1,200 | 1,202.84 | December 21, 1998 |
| 1,300 | 1,307.26 | March 15, 1999 |
| 1,400 | 1,403.28 | July 9, 1999 |
| 1,500 | 1,500.64 | March 22, 2000 |
| Highest close | 1,565.15 | October 9, 2007 |
| Highest intraday level | 1,576.09 | October 11, 2007 |
Total annual returns (b)
| Year | Annual Return |
$1.00 Investment Gives |
5 Year Annualized Return (g/i)=(1+ar)^5 |
10 Year Annualized Return (g/i)=(1+ar)^10 |
15 Year Annualized Return (g/i)=(1+ar)^15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1988 | 16.61% | $1.17 | - | - | - |
| 1989 | 31.69% | $1.54 | - | - | - |
| 1990 | −3.10% | $1.49 | - | - | - |
| 1991 | 30.47% | $1.94 | - | - | - |
| 1992 | 7.62% | $2.09 | 15.89% | - | - |
| 1993 | 10.08% | $2.30 | 14.55% | - | - |
| 1994 | 1.32% | $2.33 | 8.70% | - | - |
| 1995 | 37.58% | $3.21 | 16.59% | - | - |
| 1996 | 22.96% | $3.94 | 15.22% | - | - |
| 1997 | 33.36% | $5.26 | 20.27% | 18.05% | - |
| 1998 | 28.58% | $6.76 | 24.06% | 19.21% | - |
| 1999 | 21.04% | $8.18 | 28.56% | 18.21% | - |
| 2000 | −9.10% | $7.44 | 18.33% | 17.46% | - |
| 2001 | −11.89% | $6.55 | 10.70% | 12.94% | - |
| 2002 | −22.10% | $5.10 | −0.59% | 9.34% | 11.47% |
| 2003 | 28.69% | $6.57 | −0.57% | 11.07% | 12.19% |
| 2004 | 10.88% | $7.28 | −2.30% | 12.07% | 10.91% |
| 2005 | 4.91% | $7.64 | 0.54% | 9.07% | 11.51% |
| 2006 | 15.79% | $8.85 | 6.19% | 8.42% | 10.65% |
| 2007 | 5.49% | $9.33 | 12.83% | 5.91% | 10.48% |
| 2008 | −37.00% | $5.88 | −2.19% | −1.38% | 6.46% |
| 2009 | 26.46% | $7.26 | −0.06% | −1.19% | 7.87% |
| 2010 | 15.06% | $8.35 | 1.80% | 1.16% | 6.58% |
| High | 37.58% | 28.56% | 19.21% | 12.12% | |
| Low | −37.00% | −2.30% | −1.38% | 6.46% | |
| CAGR Compound annual growth rate Compound annual growth rate is a business and investing specific term for the smoothed annualized gain of an investment over a given time period... |
8.80% | ||||
| Median | 10.88% | 10.92% |
- (a) These are the closing milestones of the price return S&P 500 in 100-point increments, along with the all-time highs.
- (b) Total returnTotal returnThe total return on a portfolio of investments takes into account not only the capital appreciation on the portfolio, but also the income received on the portfolio. The income typically consists of interest, dividends, and securities lending fees...
s including reinvested dividends, in percent. In other words, these are the changes in the total return version of the index.
See also
- S&P CompletionS&P CompletionThe S&P Completion Index is a sub-index of the S&P Total Market Index , including all stocks eligible for the S&P TMI and excluding all current constituents of the S&P 500. Covering approximately 4,000 constituents, the S&P Completion Index offers broad market exposure to mid-, small-, and...
- Standard & Poor'sStandard & Poor'sStandard & Poor's is a United States-based financial services company. It is a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks and bonds. It is well known for its stock-market indices, the US-based S&P 500, the Australian S&P/ASX 200, the Canadian...
- List of S&P 500 companies
- Fortune 500Fortune 500The Fortune 500 is an annual list compiled and published by Fortune magazine that ranks the top 500 U.S. closely held and public corporations as ranked by their gross revenue after adjustments made by Fortune to exclude the impact of excise taxes companies collect. The list includes publicly and...
- FTSE 100
- S&P 400S&P 400The S&P 400 MidCap Index, more commonly known as the S&P 400, is a stock market index from Standard & Poor's.It covers roughly the mid-cap range of US stocks.-Investing:The following ETFs attempt to track this index and sub-indexes:*Index Fund: &...
- S&P 600S&P 600The S&P 600 SmallCap Index, more commonly known as the S&P 600, is a stock market index from Standard & Poor's. It covers roughly the small-cap range of US stocks, using a capitalization-weighted index...
- S&P 1500S&P 1500The S&P 1500, or S&P 1500 Composite Index, is a stock market index of US stocks made by Standard & Poor's. It includes all stocks in the S&P 500, S&P 400, and S&P 600.-Annual returns:-External links:* * *...
- S&P 100S&P 100The S&P 100 Index is a stock market index of United States stocks maintained by Standard & Poor's.Index options on the S&P 100 are traded with the ticker symbol "OEX". Because of the popularity of these options, investors often refer to the index by its ticker symbol.The S&P 100, a subset of the...
- E-mini S&PE-mini S&PE-Mini S&P, often abbreviated to "E-mini" and designated by the commodity ticker symbol ES, is a stock market index futures contract traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange's Globex electronic trading platform...
- Index fundIndex fundAn index fund or index tracker is a collective investment scheme that aims to replicate the movements of an index of a specific financial market, or a set of rules of ownership that are held constant, regardless of market conditions.-Tracking:Tracking can be achieved by trying to hold all of the...
- Exchange-traded fundExchange-traded fundAn exchange-traded fund is an investment fund traded on stock exchanges, much like stocks. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, commodities, or bonds, and trades close to its net asset value over the course of the trading day. Most ETFs track an index, such as the S&P 500 or MSCI EAFE...

