
Market value-weighted index
Encyclopedia
A capitalization-weighted index is an index
whose components are weighted according to the total market value
of their outstanding shares. Also called a market-value-weighted index. The impact of a component's price change is proportional to the issue's overall market value, which is the share price times the number of shares outstanding.
For example, the AMEX Composite Index (XAX) has more than 800 component stocks. The weighting of each stock constantly shifts with changes in the stock's price and the number of shares outstanding. The index fluctuates in line with the price move of the stocks.
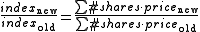
index such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average
, the price of each component stock is the only consideration when determining the value of the index. Thus, price movement of even a single security will heavily influence the value of the index even though the dollar shift is less significant in a relatively high-value name. In a market-share weighted index, price is weighted relative to the number of shares, rather than their total value. In a fundamentally weighted index, stocks are weighted by fundamental factors like sales or book value.
Traditionally, capitalization-weighted indices in the United States tended to have a full weighting, i.e., all outstanding shares were included; overseas, because partial government ownership of large companies was more common, so-called float-weighted indexing has been the norm for many non-U.S. indices. Recently, many of the U.S. indices, such as the S&P 500, have been changed to a float-adjusted weighting which makes their calculation more consistent with non-U.S. indices.
A free float adjustment factor is introduced in calculations for the index. This represents the proportion of shares that is free floated as a percentage of issued shares and then is rounded to the nearest multiple of 5% for calculation purposes. To find the free-float capitalization of a company, first find its market cap (number of outstanding shares x share price) then multiply its free-float factor. The free-float method, therefore, does not include restricted stocks, such as those held by company insiders.
Index (economics)
In economics and finance, an index is a statistical measure of changes in a representative group of individual data points. These data may be derived from any number of sources, including company performance, prices, productivity, and employment. Economic indices track economic health from...
whose components are weighted according to the total market value
Market value
Market value is the price at which an asset would trade in a competitive auction setting. Market value is often used interchangeably with open market value, fair value or fair market value, although these terms have distinct definitions in different standards, and may differ in some...
of their outstanding shares. Also called a market-value-weighted index. The impact of a component's price change is proportional to the issue's overall market value, which is the share price times the number of shares outstanding.
For example, the AMEX Composite Index (XAX) has more than 800 component stocks. The weighting of each stock constantly shifts with changes in the stock's price and the number of shares outstanding. The index fluctuates in line with the price move of the stocks.
Mathematical formula
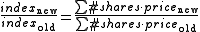
Other types of indices
An index may also be classified according to the method used to determine its price. In a price-weightedPrice-weighted
A price-weighted index is a stock market index where each constituent makes up a fraction of the index that is proportional to its price. For a stock market index this implies that stocks are included in proportions based on their quoted prices. A stock trading at $100 will thus be making up 10...
index such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average
Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average , also called the Industrial Average, the Dow Jones, the Dow 30, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index, and one of several indices created by Wall Street Journal editor and Dow Jones & Company co-founder Charles Dow...
, the price of each component stock is the only consideration when determining the value of the index. Thus, price movement of even a single security will heavily influence the value of the index even though the dollar shift is less significant in a relatively high-value name. In a market-share weighted index, price is weighted relative to the number of shares, rather than their total value. In a fundamentally weighted index, stocks are weighted by fundamental factors like sales or book value.
Traditionally, capitalization-weighted indices in the United States tended to have a full weighting, i.e., all outstanding shares were included; overseas, because partial government ownership of large companies was more common, so-called float-weighted indexing has been the norm for many non-U.S. indices. Recently, many of the U.S. indices, such as the S&P 500, have been changed to a float-adjusted weighting which makes their calculation more consistent with non-U.S. indices.
A free float adjustment factor is introduced in calculations for the index. This represents the proportion of shares that is free floated as a percentage of issued shares and then is rounded to the nearest multiple of 5% for calculation purposes. To find the free-float capitalization of a company, first find its market cap (number of outstanding shares x share price) then multiply its free-float factor. The free-float method, therefore, does not include restricted stocks, such as those held by company insiders.
Some capitalization-weighted indices
- NASDAQ CompositeNasdaq CompositeThe Nasdaq Composite is a stock market index of the common stocks and similar securities listed on the NASDAQ stock market, meaning that it has over 3,000 components. It is highly followed in the U.S. as an indicator of the performance of stocks of technology companies and growth companies. ...
- NASDAQ-100NASDAQ-100The NASDAQ-100 is a stock market index of 100 of the largest non-financial companies listed on the NASDAQ. It is a modified capitalization-weighted index. The companies' weights in the index are based on their market capitalizations, with certain rules capping the influence of the largest components...
- NYSE CompositeNYSE CompositeThe NYSE Composite is a stock market index covering all common stock listed on the New York Stock Exchange, including American Depositary Receipts, Real Estate Investment Trusts, tracking stocks, and foreign listings...
- FTSE-100
- Hang Seng IndexHang Seng IndexThe Hang Seng Index is a freefloat-adjusted market capitalization-weighted stock market index in Hong Kong. It is used to record and monitor daily changes of the largest companies of the Hong Kong stock market and is the main indicator of the overall market performance in Hong Kong...
in Hong Kong - Russell 2000Russell 2000The Russell 2000 Index is a small-cap stock market index of the bottom 2,000 stocks in the Russell 3000 Index.The Russell 2000 is by far the most common benchmarkfor mutual funds that identify themselves as "small-cap",...
- S&P 500S&P 500The S&P 500 is a free-float capitalization-weighted index published since 1957 of the prices of 500 large-cap common stocks actively traded in the United States. The stocks included in the S&P 500 are those of large publicly held companies that trade on either of the two largest American stock...
- Now float-weighted - SENSEX in India
- Standard & Poor'sStandard & Poor'sStandard & Poor's is a United States-based financial services company. It is a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks and bonds. It is well known for its stock-market indices, the US-based S&P 500, the Australian S&P/ASX 200, the Canadian...
100 Index (OEX) - now float weighted - IBEX 35IBEX 35The IBEX 35 is the benchmark stock market index of the Bolsa de Madrid, Spain's principal stock exchange. Initiated in 1992, the index is administered and calculated by Sociedad de Bolsas, a subsidiary of Bolsas y Mercados Españoles , the company which runs Spain's securities markets...
- index comprising the 35 most liquid Spanish stocks traded in the continuous market, and is Bolsa de MadridBolsa de MadridBolsa de Madrid is the largest and most international of Spain's four regional stock exchanges that trade shares and convertible bonds and fixed income securities, and both government and private-sector debt...
's benchmark. - Indice de Precios y CotizacionesIndice de Precios y CotizacionesThe Indice de Precios y Cotizaciones is an index of 35 stocks that trade on the Bolsa Mexicana de Valores.The companies of Carlos Slim represent 43% of this index.-Components:2003#Alfa#América Móvil#América Telecom#Apasco#Carso Telekom...
(IPC) - index of 35 of the Bolsa Mexicana de ValoresBolsa Mexicana de ValoresThe Mexican Stock Exchange is Mexico's only stock exchange. It is situated on Paseo de la Reforma, a prestigious avenue in central Mexico City...
(BMV) most highly marketable issuers with a minimum market value of $100 million; revised every six months. - Kuala Lumpur Composite IndexKuala Lumpur Composite IndexThe Kuala Lumpur Composite Index is a capitalization-weighted stock market index. Introduced in 1986, it is now known as the FTSE Bursa Malaysia KLCI...
(KLCI) - FTSE TechMark
- CAC 40CAC 40The CAC 40 is a benchmark French stock market index. The index represents a capitalization-weighted measure of the 40 most significant values among the 100 highest market caps on the Paris Bourse...
- VN-Index
- Taiwan Capitalization Weighted Stock IndexTaiwan Capitalization Weighted Stock IndexTaiwan Capitalization Weighted Stock Index is a stock market index for companies traded on the Taiwan Stock Exchange . TAIEX covers all of the listed stocks excluding preferred stocks, full-delivery stocks and newly listed stocks, which are listed for less than one calendar month...
See also
- Stock market indexStock market indexA stock market index is a method of measuring a section of the stock market. Many indices are cited by news or financial services firms and are used as benchmarks, to measure the performance of portfolios such as mutual funds....
- Index(economics)Index (economics)In economics and finance, an index is a statistical measure of changes in a representative group of individual data points. These data may be derived from any number of sources, including company performance, prices, productivity, and employment. Economic indices track economic health from...
- Index fundIndex fundAn index fund or index tracker is a collective investment scheme that aims to replicate the movements of an index of a specific financial market, or a set of rules of ownership that are held constant, regardless of market conditions.-Tracking:Tracking can be achieved by trying to hold all of the...
- Index investing
- List of stock market indices
- Fundamental weighting
- Capitalization weighted methodology via Wikinvest

