
Abydos, Hellespont
Encyclopedia
For other uses, see Abydos (disambiguation)
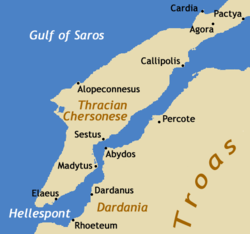 Abydos (Greek: Άβυδος), an ancient city of Mysia
Abydos (Greek: Άβυδος), an ancient city of Mysia
, in Asia Minor
, situated at Nara Burnu or Nagara Point on the best harbor on the Asiatic shore of the Hellespont. Across Abydos lies Sestus on the European side marking the shortest point in the Dardanelles
, scarcely a mile broad. The strategic site has been a prohibited zone in the twentieth century. Hero and Leander
's story took place near Abydos.
Abydos was first mentioned in the catalogue of Trojan allies (Iliad
ii.836). It probably was a Thracian
town, as Strabo
has it, but was afterwards colonized by Milesians
, with the consent of Gyges, king of Lydia
, around 700 BC. It was occupied by the Persians in 514 BC, and Darius burnt it in 512. Here Xerxes built two bridges of boats and crossed the strait in 480 BC
when he invaded Greece
.
Abydos thereafter became a member of the Delian League
, until it revolted from Athenian rule in 411 BC
. It allied itself to Sparta
, until 394 BC
; King Agesilaus
of Sparta crossed here while returning to Greece. Abydos then passed under Achaemenid rule, until 334 BC
. Alexander the Great threw a spear to Abydos while crossing the strait and claimed Asia as his own.
Abydos is celebrated for the vigorous resistance it made against Philip V of Macedon
in 200 BC
, and is famed in myth as the home of Leander
. It minted coins from the early fifth century BC to the mid-third century AD.
The town remained until late Byzantine times an important toll and customs station of the Hellespont, its importance thereafter being transferred to the Dardanelles
, after the building of the "Old Castles" by Sultan Mehmet II (c. 1456).

Mysia
Mysia was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor or Anatolia . It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the east, Phrygia on the southeast, Lydia on the south, Aeolis on the southwest, Troad on the west and by the Propontis on the north...
, in Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
, situated at Nara Burnu or Nagara Point on the best harbor on the Asiatic shore of the Hellespont. Across Abydos lies Sestus on the European side marking the shortest point in the Dardanelles
Dardanelles
The Dardanelles , formerly known as the Hellespont, is a narrow strait in northwestern Turkey connecting the Aegean Sea to the Sea of Marmara. It is one of the Turkish Straits, along with its counterpart the Bosphorus. It is located at approximately...
, scarcely a mile broad. The strategic site has been a prohibited zone in the twentieth century. Hero and Leander
Hero and Leander
Hero and Leander is a Byzantine myth, relating the story of Hērō and like "hero" in English), a priestess of Aphrodite who dwelt in a tower in Sestos on the European side of the Dardanelles, and Leander , a young man from Abydos on the opposite side of the strait. Leander fell in love with Hero...
's story took place near Abydos.
Abydos was first mentioned in the catalogue of Trojan allies (Iliad
Iliad
The Iliad is an epic poem in dactylic hexameters, traditionally attributed to Homer. Set during the Trojan War, the ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Greek states, it tells of the battles and events during the weeks of a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles...
ii.836). It probably was a Thracian
Thracians
The ancient Thracians were a group of Indo-European tribes inhabiting areas including Thrace in Southeastern Europe. They spoke the Thracian language – a scarcely attested branch of the Indo-European language family...
town, as Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
has it, but was afterwards colonized by Milesians
Miletus
Miletus was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia , near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Caria...
, with the consent of Gyges, king of Lydia
Gyges of Lydia
Gyges was the founder of the third or Mermnad dynasty of Lydian kings and reigned from 716 BC to 678 BC . He was succeeded by his son Ardys II.-Allegorical accounts of Gyges' rise to power:...
, around 700 BC. It was occupied by the Persians in 514 BC, and Darius burnt it in 512. Here Xerxes built two bridges of boats and crossed the strait in 480 BC
480 BC
Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus...
when he invaded Greece
Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire of Persia and city-states of the Hellenic world that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus...
.
Abydos thereafter became a member of the Delian League
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in circa 477 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, members numbering between 150 to 173, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Greco–Persian Wars...
, until it revolted from Athenian rule in 411 BC
411 BC
Year 411 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Mugillanus and Rutilus...
. It allied itself to Sparta
History of Sparta
The History of Sparta describes the destiny of the ancient Dorian Greek state known as Sparta from its beginning in the legendary period to its forced incorporation into the Achaean League under the late Roman Republic, its conquerors, in 146 BCE, a period of roughly 1000 years...
, until 394 BC
394 BC
Year 394 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Camillus, Poplicola, Medullinus, Albinus, Mamercinus and Scipio...
; King Agesilaus
Agesilaus
Agesilaus was a Greek historian who wrote a work on the early history of Italy, fragments of which are preserved in Plutarch's "Parallel Lives", and in Stobaeus' Florilegium....
of Sparta crossed here while returning to Greece. Abydos then passed under Achaemenid rule, until 334 BC
334 BC
Year 334 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caudinus and Calvinus...
. Alexander the Great threw a spear to Abydos while crossing the strait and claimed Asia as his own.
Abydos is celebrated for the vigorous resistance it made against Philip V of Macedon
Philip V of Macedon
Philip V was King of Macedon from 221 BC to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of Rome. Philip was attractive and charismatic as a young man...
in 200 BC
200 BC
Year 200 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Maximus and Cotta...
, and is famed in myth as the home of Leander
Hero and Leander
Hero and Leander is a Byzantine myth, relating the story of Hērō and like "hero" in English), a priestess of Aphrodite who dwelt in a tower in Sestos on the European side of the Dardanelles, and Leander , a young man from Abydos on the opposite side of the strait. Leander fell in love with Hero...
. It minted coins from the early fifth century BC to the mid-third century AD.
The town remained until late Byzantine times an important toll and customs station of the Hellespont, its importance thereafter being transferred to the Dardanelles
Dardanelles
The Dardanelles , formerly known as the Hellespont, is a narrow strait in northwestern Turkey connecting the Aegean Sea to the Sea of Marmara. It is one of the Turkish Straits, along with its counterpart the Bosphorus. It is located at approximately...
, after the building of the "Old Castles" by Sultan Mehmet II (c. 1456).
Additional sources
- Richard Stillwell, ed. Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites, 1976: "Abydos, (Naara Point) Turkey"

