
Greco-Persian Wars
Encyclopedia
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire
of Persia and city-states of the Hellenic world
that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great
conquered Ionia
in 547 BC. Struggling to rule the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed tyrant
s to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike.
In 499 BC, the then tyrant of Miletus
, Aristagoras
, embarked on an expedition
to conquer the island of Naxos, with Persian support; however, the expedition was a debacle and, pre-empting his dismissal, Aristagoras incited all of Hellenic Asia Minor
into rebellion against the Persians. This was the beginning of the Ionian Revolt
, which would last until 493 BC, progressively drawing more regions of Asia Minor into the conflict. Aristagoras secured military support from Athens
and Eretria
, and in 498 BC these forces helped to capture and burn the Persian regional capital of Sardis
. The Persian king Darius the Great
vowed to have revenge on Athens and Eretria for this act. The revolt continued, with the two sides effectively stalemated throughout 497–495 BC. In 494 BC, the Persians regrouped, and attacked the epicentre of the revolt in Miletus. At the Battle of Lade
, the Ionians suffered a decisive defeat, and the rebellion collapsed, with the final members being stamped out the following year.
Seeking to secure his empire from further revolts and from the interference of the mainland Greeks, Darius embarked on a scheme to conquer Greece and to punish Athens and Eretria for burning Sardis. The first Persian invasion of Greece
began in 492 BC, with the Persian general Mardonius
conquering Thrace
and Macedon
before several mishaps forced an early end to the campaign. In 490 BC a second force was sent to Greece, this time across the Aegean Sea
, under the command of Datis
and Artaphernes
. This expedition subjugated the Cyclades
, before besieging, capturing and razing
Eretria. However, while on route to attack Athens, the Persian force was decisively defeated by the Athenians at the Battle of Marathon
, ending Persian efforts for the time being. Darius then began to plan to complete the conquest of Greece, but died in 486 BC and responsibility for the conquest passed to his son Xerxes I. In 480 BC, Xerxes personally led the second Persian invasion of Greece
with one of the largest ancient armies ever assembled. Victory over the 'Allied' Greek states (led by Sparta
and Athens) at the Battle of Thermopylae
allowed the Persians to overrun most of Greece. However, while seeking to destroy the combined Greek fleet, the Persians suffered a severe defeat at the Battle of Salamis
. The following year, the confederated Greeks went on the offensive, defeating the Persian army at the Battle of Plataea
, and ending the invasion of Greece.
The allied Greeks followed up their success by destroying the rest of the Persian fleet at the Battle of Mycale
, before expelling Persian garrisons from Sestos
(479 BC) and Byzantium
(478 BC). The actions of the general Pausanias
at the siege of Byzantium alienated many of the Greek states from the Spartans, and the anti-Persian alliance was therefore reconstituted around Athenian leadership, as the so-called Delian League
. The Delian League continued to campaign
against Persia for the next three decades, beginning with the expulsion of the remaining Persian garrisons from Europe. At the Battle of the Eurymedon
in 466 BC, the League won a double victory that finally secured freedom for the cities of Ionia. However, the League's involvement in an Egyptian revolt (from 460–454 BC) resulted in a disastrous defeat, and further campaigning was suspended. A fleet was sent to Cyprus
in 451 BC, but achieved little, and when it withdrew the Greco-Persian Wars drew to a quiet end. Some historical sources suggest the end of hostilities was marked by a peace treaty between Athens and Persia, the so-called Peace of Callias
.

 Almost all the primary sources for the Greco-Persian Wars are Greek; there are no surviving historical accounts from the Persian side. By some distance, the main source for the Greco-Persian Wars is the Greek historian Herodotus
Almost all the primary sources for the Greco-Persian Wars are Greek; there are no surviving historical accounts from the Persian side. By some distance, the main source for the Greco-Persian Wars is the Greek historian Herodotus
. Herodotus, who has been called the "Father of History", was born in 484 BC in Halicarnassus
, Asia Minor (then part of the Persian empire). He wrote his 'Enquiries' (Greek—Historia; English—(The) Histories
) around 440–430 BC, trying to trace the origins of the Greco-Persian Wars, which would still have been recent history. Herodotus's approach was novel and, at least in Western society, he invented 'history' as a discipline. As Holland has it: "For the first time, a chronicler set himself to trace the origins of a conflict not to a past so remote so as to be utterly fabulous, nor to the whims and wishes of some god, nor to a people's claim to manifest destiny, but rather explanations he could verify personally."
Some later ancient historians, starting with Thucydides
, criticised Herodotus. Nevertheless, Thucydides chose to begin his history where Herodotus left off (at the Siege of Sestos) and felt Herodotus's history was accurate enough not to need re-writing or correcting. Plutarch
criticised Herodotus in his essay "On The Malignity of Herodotus", describing Herodotus as "Philobarbaros" (barbarian-lover) for not being pro-Greek enough, which suggests that Herodotus might actually have done a reasonable job of being even-handed. A negative view of Herodotus was passed on to Renaissance Europe, though he remained well read. However, since the 19th century his reputation has been dramatically rehabilitated by archaeological finds that have repeatedly confirmed his version of events. The prevailing modern view is that Herodotus did a remarkable job in his Historia, but that some of his specific details (particularly troop numbers and dates) should be viewed with skepticism. Nevertheless, there are still some historians who believe Herodotus made up much of his story.
Unfortunately, the military history of Greece between the end of the second Persian invasion of Greece
and the Peloponnesian War
(479–431 BC) is not well supported by surviving ancient sources. This period, sometimes referred to as the pentekontaetia by ancient scholars, was a period of relative peace and prosperity within Greece. The richest source for the period, and also the most contemporaneous, is Thucydides' History of the Peloponnesian War
, which is generally considered by modern historians to be a reliable primary account. Thucydides only mentions this period in a digression on the growth of Athenian power in the run up to the Peloponnesian War, and the account is brief, probably selective and lacks any dates. Nevertheless, Thucydides's account can be, and is, used by historians to draw up a skeleton chronology for the period, on to which details from archaeological records and other writers can be superimposed.
More detail for the whole period is provided by Plutarch, in his biographies
of Themistocles
, Aristides
and especially Cimon. Plutarch was writing some 600 years after the events in question, and is therefore a secondary source, but he often names his sources, which allows some degree of verification of his statements. In his biographies, he draws directly from many ancient histories that have not survived, and thus often preserves details of the period that are omitted in Herodotus and Thucydides's accounts. The final major existing source for the period is the universal history (Bibliotheca historica
) of the 1st century BC Sicilian, Diodorus Siculus
. Much of Diodorus's writing about this period is drawn from the much earlier Greek historian Ephorus
, who also wrote a universal history. Diodorus is also a secondary source and often derided by modern historians for his style and inaccuracies, but he preserves many details of the ancient period found nowhere else.
Further scattered details can be found in Pausanias
's Description of Greece, while the Byzantine
Suda
dictionary of the 10th century AD preserves some anecdotes found nowhere else. Minor sources for the period include the works of Pompeius Trogus
(epitomized by Justinus), Cornelius Nepos
and Ctesias of Cnidus
(epitomized by Photius), which are not in their original textual form. These works are not considered reliable (especially Ctesias), and are not particularly useful for reconstructing the history of this period.
that followed the collapse of the Mycenaean civilization
, significant numbers of Greeks fled and had emigrated to Asia Minor and settled there. Modern historians generally accept this migration as historic (but separate from the later colonization of the Mediterranean by the Greeks). There are, however, those who believe the Ionian migration cannot be explained as simply as the classical Greeks claimed. These settlers were from three tribal groups: the Aeolians
, Dorians and Ionians
. The Ionians had settled about the coasts of Lydia
and Caria
, founding the twelve cities that made up Ionia
. These cities were Miletus
, Myus
and Priene
in Caria; Ephesus
, Colophon, Lebedos, Teos
, Clazomenae
, Phocaea
and Erythrae
in Lydia; and the islands of Samos
and Chios
. Although the Ionian cities were independent of one another, they recognized their shared heritage and supposedly had a common temple and meeting place, the Panionion. They thus formed a 'cultural league', to which they would admit no other cities, or even other tribal Ionians.
The cities of Ionia had remained independent until they were conquered by the Lydians
of western Asia Minor. The Lydian king Alyattes II
attacked Miletus, a conflict that ended with a treaty of alliance between Miletus and Lydia, that meant that Miletus would have internal autonomy but follow Lydia in foreign affairs. At this time, the Lydians were also in conflict with the Median
Empire, and the Milesians sent an army to aid the Lydians in this conflict. Eventually a peaceable settlement was established between the Medes and the Lydians, with the Halys River
set up as the border between the kingdoms. The famous Lydian king Croesus
succeeded his father Alyattes in around 560 BC and set about conquering the other Greek city states of Asia Minor.
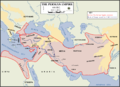
The Persian prince Cyrus
led a rebellion against the last Median king Astyages
in 553 BC. Cyrus was a grandson of Astyages and was supported by part of the Median aristocracy. By 550 BC, the rebellion was over, and Cyrus had emerged victorious, founding the Achaemenid Empire
in place of the Median kingdom in the process. Croesus saw the disruption in the Median Empire and Persia as an opportunity to extend his realm and asked the oracle of Delphi
whether he should attack them. The Oracle supposedly replied the famously ambiguous answer that "if Croesus was to cross the Halys he would destroy a great empire". Blind to the ambiguity of this prophecy, Croesus attacked the Persians, but was eventually defeated and Lydia fell to Cyrus.
 While fighting the Lydians, Cyrus had sent messages to the Ionians asking them to revolt against Lydian rule, which the Ionians had refused to do. After Cyrus finished the conquest of Lydia, the Ionian cities now offered to be his subjects under the same terms as they had been subjects of Croesus. Cyrus refused, citing the Ionians' unwillingness to help him previously. The Ionians thus prepared to defend themselves, and Cyrus sent the Median general Harpagus
While fighting the Lydians, Cyrus had sent messages to the Ionians asking them to revolt against Lydian rule, which the Ionians had refused to do. After Cyrus finished the conquest of Lydia, the Ionian cities now offered to be his subjects under the same terms as they had been subjects of Croesus. Cyrus refused, citing the Ionians' unwillingness to help him previously. The Ionians thus prepared to defend themselves, and Cyrus sent the Median general Harpagus
to conquer them. He first attacked Phocaea; the Phocaeans decided to abandon their city entirely and sail into exile in Sicily, rather than become Persian subjects (although many later returned). Some Teians also chose to emigrate when Harpagus attacked Teos, but the rest of the Ionians remained, and were each in turn conquered.
In the years following their conquest, the Persians found the Ionians difficult to rule. Elsewhere in the empire, Cyrus identified elite native groups such as the priesthood of Judea - to help him rule his new subjects. No such group existed in Greek cities at this time; while there was usually an aristocracy, this was inevitably divided into feuding factions. The Persians thus settled for sponsoring a tyrant in each Ionian city, even though this drew them into the Ionians' internal conflicts. Furthermore, certain tyrants might develop an independent streak and have to be replaced. The tyrants themselves faced a difficult task; they had to deflect the worst of their fellow citizens' hatred, while staying in the favour of the Persians. In the past, Greek states had often been ruled by tyrants, but that form of government was on the decline. Past tyrants had also tended and needed to be strong and able leaders, whereas the rulers appointed by the Persians were simply place-men. Backed by the Persian military might, these tyrants did not need the support of the population, and could thus rule absolutely. On the eve of the Greco-Persian wars, it is probable that the Ionian population had become discontent and was ready for rebellion. Ionia, unlike the many other areas of the empire, did not revolt in the civil war period between the reigns of Cyrus and Darius I of Persia
, and it is therefore possible to argue that the Greeks were not so dissatisfied with Persian rule as some historians propose.
', had no bows, carried larger wicker shields and were sometimes armed with longer spears. Their role was to protect the back ranks of the formation. The cavalry probably fought as lightly armed missile cavalry.
'), was based around the hoplite
phalanx
supported by missile troops. The 'hoplite
s' were foot soldiers usually drawn from the members of the middle-classes (in Athens called the zeugites), who could afford the equipment necessary to fight in this manner. The heavy armour usually included a breastplate or a linothorax
, greaves, a helmet, and a large round, concave shield (the aspis
or hoplon). Hoplites were armed with long spears (the dory
), which were significantly longer than Persian spears, and a sword (the xiphos). The heavy armour and longer spears made them superior in hand-to-hand combat and gave them significant protection against ranged attacks. Lightly armed skirmishers, the psiloi
also comprised a part of Greek armies growing in importance during the conflict; at the Battle of Plataea, for instance, they may have formed over half the Greek army. Use of cavalry in Greek armies is not reported in the battles of the Greco-Persian Wars.
, a warship powered by three banks of oars. The most common naval tactics during the period were ramming (triremes were equipped with a ram at the bows), or boarding by ship-borne marines. More experienced naval powers had by this time also begun to use a manoeuver known as diekplous. It is not clear what this was, but it probably involved sailing into gaps between enemy ships and then ramming them in the side.
The Persian naval forces were primarily provided by the Phoenicia
ns, Egyptians
, Cilicia
ns and Cypriots
. Other coastal regions of the Persian Empire would contribute ships throughout the course of the wars.
and associated revolts in Aeolis
, Doris
, Cyprus
, and Caria
were military rebellions by several regions of Asia Minor
against Persian rule, lasting from 499 to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with opposition to the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus
and Aristagoras. In 499 BC the then tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes
to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position in Miletus (both financially and in terms of prestige). The mission
was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.
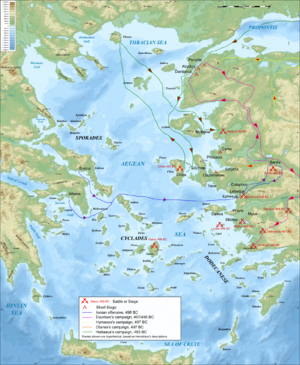 In 498 BC, supported by troops from Athens and Eretria, the Ionians marched on, captured, and burnt Sardis. However, on their return journey to Ionia, they were followed by Persian troops, and decisively beaten at the Battle of Ephesus. This campaign was the only offensive action taken by the Ionians, who subsequently went on the defensive. The Persians responded in 497 BC with a three-pronged attack aimed at recapturing the outlying areas of the rebellious territory, but the spread of the revolt to Caria meant the largest army, under Darius, moved there instead. While at first campaigning successfully in Caria, this army was wiped out in an ambush at the Battle of Pedasus. This resulted in a stalemate for the rest of 496 and 495 BC.
In 498 BC, supported by troops from Athens and Eretria, the Ionians marched on, captured, and burnt Sardis. However, on their return journey to Ionia, they were followed by Persian troops, and decisively beaten at the Battle of Ephesus. This campaign was the only offensive action taken by the Ionians, who subsequently went on the defensive. The Persians responded in 497 BC with a three-pronged attack aimed at recapturing the outlying areas of the rebellious territory, but the spread of the revolt to Caria meant the largest army, under Darius, moved there instead. While at first campaigning successfully in Caria, this army was wiped out in an ambush at the Battle of Pedasus. This resulted in a stalemate for the rest of 496 and 495 BC.
By 494 BC the Persian army and navy had regrouped, and they made straight for the epicentre of the rebellion at Miletus. The Ionian fleet sought to defend Miletus by sea, but was defeated decisively at the Battle of Lade
, after the Samians
had defected. Miletus was then besieged, captured, and its population was enslaved. This double defeat effectively ended the revolt, and the Carians surrendered to the Persians as a result. The Persians spent 493 BC reducing the cities along the west coast that still held out against them, before finally imposing a peace settlement on Ionia that was considered to be both just and fair.
The Ionian Revolt constituted the first major conflict between Greece and the Achaemenid Empire and represents the first phase of the Greco-Persian Wars. Asia Minor had been brought back into the Persian fold, but Darius had vowed to punish Athens and Eretria for their support for the revolt. Moreover, seeing that the political situation in Greece posed a continued threat to the stability of his Empire, he decided to embark on the conquest of all Greece.
consisted of two main campaigns.
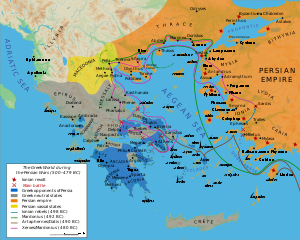 The first campaign, in 492 BC, was led by Darius's son-in-law Mardonius
The first campaign, in 492 BC, was led by Darius's son-in-law Mardonius
, who re-subjugated Thrace
, which had nominally been part of the Persian empire since 513 BC. Mardonius was also able to force Macedon
to become a client kingdom of Persia; it had previously been allied but independent. However, further progress in this campaign was prevented when Mardonius's fleet was wrecked in a storm off the coast of Mount Athos
. Mardonius himself was then injured in a raid on his camp by a Thracian tribe, and after this he returned with the rest of the expedition to Asia.
The following year, having given clear warning of his plans, Darius sent ambassadors to all the cities of Greece, demanding their submission. He received it from almost all of them, except Athens and Sparta
, both of whom instead executed the ambassadors. With Athens still defiant, and Sparta now also effectively at war with him, Darius ordered a further military campaign for the following year.
and Artaphernes
(son of the satrap Artaphernes
) were given command of an amphibious invasion force, and set sail from Cilicia
. The Persian force sailed from Cilicia first to the island of Rhodes
, where a Lindian Temple Chronicle records that Datis
besieged the city of Lindos
, but was unsuccessful. The fleet sailed next to Naxos, to punish the Naxians for their resistance to the failed expedition the Persians had mounted there a decade earlier. Many of the inhabitants fled to the mountains; those that the Persians caught were enslaved. The Persians then burnt the city and temples of the Naxians. The fleet then proceeded to island-hop across the rest of the Aegean on its way to Eretria, taking hostages and troops from each island.
The task force sailed on to Euboea
, and to the first major target, Eretria. The Eretrians made no attempt to stop the Persians from landing or advancing and thus allowed themselves to be besieged
. For six days, the Persians attacked the walls, with losses on both sides; however, on the seventh day two reputable Eretrians opened the gates and betrayed the city to the Persians. The city was razed, and temples and shrines were looted and burned. Furthermore, according to Darius's commands, the Persians enslaved all the remaining townspeople.
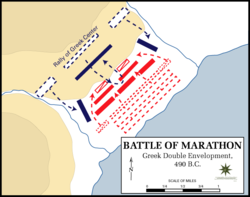 The Persian fleet next headed south down the coast of Attica
The Persian fleet next headed south down the coast of Attica
, landing at the bay of Marathon
, roughly 25 miles (40.2 km) from Athens Under the guidance of Miltiades
, the general with the greatest experience of fighting the Persians, the Athenian army marched to block the two exits from the plain of Marathon. Stalemate ensued for five days, before the Athenians (for reasons that are unclear) decided to attack the Persians. Despite the numerical advantage of the Persians, the hoplite
s proved devastatingly effective against the more lightly armed Persian infantry, routing the wings before turning in on the centre of the Persian line. The remnants of the Persian army fled to their ships and left the battle. Herodotus records that 6,400 Persian bodies were counted on the battlefield; the Athenians lost only 192 men.
As soon as the Persian survivors had put to sea, the Athenians marched as quickly as possible to Athens. They arrived in time to prevent Artaphernes from securing a landing in Athens. Seeing his opportunity lost, Artaphernes ended the year's campaign and returned to Asia.
The Battle of Marathon was a watershed in the Greco-Persian wars, showing the Greeks that the Persians could be beaten. It also highlighted the superiority of the more heavily armoured Greek hoplites, and showed their potential when used wisely. The Battle of Marathon is perhaps now more famous as the inspiration for the Marathon
race.
subjects revolted, indefinitely postponing any Greek expedition. Darius died while preparing to march on Egypt, and the throne of Persia passed to his son Xerxes I. Xerxes crushed the Egyptian revolt, and very quickly restarted the preparations for the invasion of Greece. Since this was to be a full scale invasion, it needed longterm planning, stockpiling and conscription. Xerxes decided the Hellespont would be bridged to allow his army to cross to Europe, and that a canal should be dug across the isthmus of Mount Athos
(a Persian fleet had been destroyed in 492 BC while rounding this coastline). These were both feats of exceptional ambition that would have been beyond any contemporary state. However, the campaign was delayed by one year because of another revolt in Egypt and Babylonia
.
The Persians had the sympathy of several Greek city-states, including Argos
, which had pledged to defect when the Persians reached their borders. The Aleuadae
family, who ruled Larissa
in Thessaly
, saw the invasion as an opportunity to extend their power. Thebes
, though not explicitly 'Medising', was suspected of being willing to aid the Persians once the invasion force arrived.
In 481 BC
, after roughly four years of preparation, Xerxes began to muster the troops to invade Europe. Herodotus gives the names of 46 nations from which troops were drafted. The Persian army was gathered in Asia Minor in the summer and autumn of 481 BC
. The armies from the Eastern satrapies were gathered in Kritala, Cappadocia
and were led by Xerxes to Sardis where they passed the winter. Early in spring, it moved to Abydos
where it was joined with the armies of the western satrapies. Then the army that Xerxes had mustered marched towards Europe, crossing the Hellespont on two pontoon bridge
s.
The numbers of troops that Xerxes mustered for the second invasion of Greece have been the subject of endless dispute. Most modern scholars reject as unrealistic the figures of 2.5 million given by Herodotus and other ancient sources because the victors likely miscalculated or exaggerated. The topic has been hotly debated, but the consensus revolves around the figure of 200,000.
The size of the Persian fleet is also disputed, although perhaps less so. Other ancient authors agree with Herodotus' number of 1,207. These numbers are by ancient standards consistent, and this could be interpreted that a number around 1,200 is correct. Among modern scholars, some have accepted this number, although suggesting the number must have been lower by the Battle of Salamis
. Other recent works on the Persian Wars reject this number, viewing 1,207 as more of a reference to the combined Greek fleet in the Iliad
. These works generally claim that the Persians could have launched no more than around 600 warships into the Aegean.
 The politician Themistocles
The politician Themistocles
, with a power base firmly established amongst the poor, filled the vacuum left by Miltiades's death, and in the following decade became the most influential politician in Athens. During this period, Themistocles continued to support expanding Athenian naval power. The Athenians were aware throughout this period that the Persian interest in Greece had not ended, and Themistocles's naval policies may be seen in the light of the potential threat from Persia. Aristides, Themistocles's great rival, and champion of the zeugites (the upper, 'hoplite-class') vigorously opposed such a policy.
In 483 BC, a massive new seam of silver was found in the Athenian mines at Laurium
. Themistocles proposed that the silver should be used to build a new fleet of triremes, ostensibly to assist in a long running war with Aegina
. Plutarch suggests that Themistocles deliberately avoided mentioning Persia, believing that it was too distant a threat for the Athenians to act on, but that countering Persia was the fleet's aim. Fine suggests that many Athenians must have admitted that such a fleet would be needed to resist the Persians, whose preparations for the coming campaign were known about. Themistocles's motion was passed easily, despite strong opposition from Aristides. Its passage was probably due to the desire of many of the poorer Athenians for paid employment as rowers in the fleet. It is unclear from the ancient sources whether 100 or 200 ships initially authorised; both Fine and Holland suggest that at first 100 ships were authorised and that a second vote increased this number to the levels seen during the second invasion. Aristides continued to oppose Themistocles's policy, and tension between the two camps built over the winter, so the ostracism of 482 BC became a direct contest between Themistocles and Aristides. In what Holland characterises as, in essence, the world's first referendum, Aristides was ostracised, and Themistocles's policies were endorsed. Indeed, becoming aware of the Persian preparations for the coming invasion, the Athenians voted to build more ships than Themistocles had asked for. In the run up to the Persian invasion, Themistocles had thus become the leading politician in Athens.
had been stripped of his kingship in 491 BC, and replaced with his cousin Leotychides. Sometime after 490 BC, the humiliated Demaratus had chosen to go into exile, and had made his way to Darius's court in Susa
. Demaratus would from then on act as an advisor to Darius, and later Xerxes, on Greek affairs, and accompanied Xerxes during the second Persian invasion. At the end of Herodotus's book 7, there is an anecdote relating that in the run-up to the second invasion, Demaratus sent an apparently blank wax tablet to Sparta. When the wax was removed, a message was found scratched on the wooden backing, warning the Spartans of Xerxes's plans. However, many historians believe that this chapter was inserted into the text by a later author, possibly to fill a gap
between the end of book 7 and the start of book 8. The veracity of this anecdote is therefore unclear.
in late autumn of 481 BC, and a confederate alliance of Greek city-states
was formed. This confederation had the power to send envoys asking for assistance and to dispatch troops from the member states to defensive points after joint consultation. Herodotus does not formulate an abstract name for the union but simply calls them "" (the Greeks) and "the Greeks who had sworn alliance" (Godley translation) or "the Greeks who had banded themselves together" (Rawlinson translation). From now on, they will be referred to as the 'Allies'. Sparta and Athens had a leading role in the congress but the interests of all the states played a part in determining defensive strategy. Little is known about the internal workings of the congress or the discussions during its meetings. Only 70 of the nearly 700 Greek city-states sent representatives. Nevertheless, this was remarkable for the disjointed Greek world, especially since many of the city-states present were still technically at war with one another.
where it was joined by the fleet. Xerxes reorganized the troops into tactical units replacing the national formations used earlier for the march.
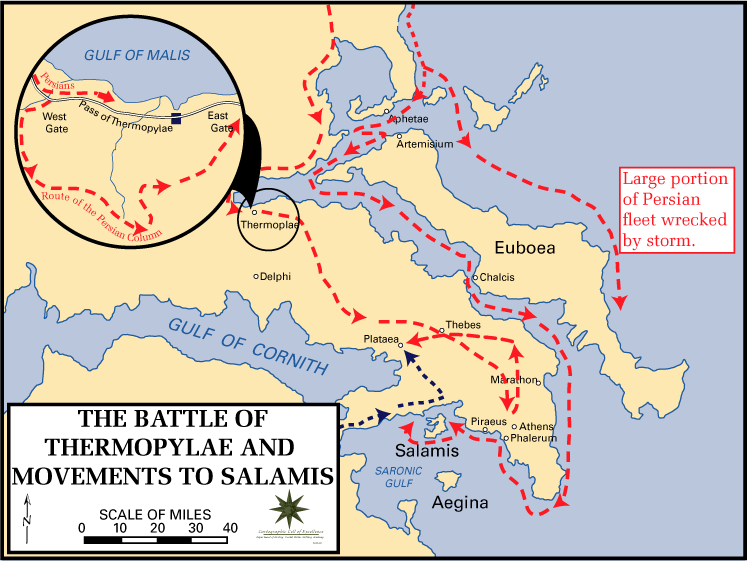 The Allied 'congress' met again in the spring of 480 BC and agreed to defend the narrow Vale of Tempe
The Allied 'congress' met again in the spring of 480 BC and agreed to defend the narrow Vale of Tempe
on the borders of Thessaly and block Xerxes's advance. However, once there, they were warned by Alexander I of Macedon
that the vale could be bypassed and that the army of Xerxes was overwhelmingly large, thus the Greeks retreated. Shortly afterwards, they received the news that Xerxes had crossed the Hellespont. At this point, a second strategy was suggested by Themistocles to the allies. The route to southern Greece (Boeotia
, Attica
and the Peloponnesus) would require the army of Xerxes to travel through the narrow pass of Thermopylae
. This could easily be blocked by the Greek hoplites, despite the overwhelming numbers of Persians. Furthermore, to prevent the Persians bypassing Thermopylae by sea, the Athenian and allied navies could block the straits of Artemisium
. This dual strategy was adopted by the congress. However, the Peloponnesian cities made fall-back plans to defend the Isthmus of Corinth
should it come to it, while the women and children of Athens were evacuated to the Peloponnesian city of Troezen
.
with his personal bodyguard (the Hippeis) of 300 men. The customary elite young men in the Hippeis were replaced by veterans who already had children. Leonidas was supported by contingents from the Allied Peloponnesian cities, and other forces that the Allies picked up on the way to Thermopylae. The Allies proceeded to occupy the pass, rebuilt the wall the Phocians had built at the narrowest point of the pass, and waited for Xerxes's arrival.
 When the Persians arrived at Thermopylae in mid-August, they initially waited for three days for the Allies to disperse. When Xerxes was eventually persuaded that the Allies intended to contest the pass, he sent his troops to attack. However, the Allied position was ideally suited to hoplite
When the Persians arrived at Thermopylae in mid-August, they initially waited for three days for the Allies to disperse. When Xerxes was eventually persuaded that the Allies intended to contest the pass, he sent his troops to attack. However, the Allied position was ideally suited to hoplite
warfare, the Persian contingents being forced to attack the Greek phalanx
head on. The Allies withstood two full days of Persian attacks, including those by the elite Persian Immortals
. However, towards the end of the second day, they were betrayed by a local resident named Ephialtes who revealed to Xerxes a mountain path that led behind the Allied lines. Made aware by scouts that they were being outflanked, Leonidas dismissed most of the Allied army, remaining to guard the rear with perhaps 2,000 men. On the final day of the battle, the remaining Allies sallied forth from the wall to meet the Persians in the wider part of the pass to slaughter as many Persians as they could, but eventually they were all killed or captured.
Simultaneous with the battle at Thermopylae, an Allied naval force of 271 triremes defended the Straits of Artemisium
against the Persians, thus protecting the flank of the forces at Thermopylae. Here the Allied fleet held off the Persians for three days; however, on the third evening the Allies received news of the fate of Leonidas and the Allied troops at Thermopylae. Since the Allied fleet was badly damaged, and since it no longer needed to defend the flank of Thermopylae, the Allies retreated from Artemisium to the island of Salamis
.
fell to Xerxes; and left Attica open to invasion. The remaining population of Athens was evacuated, with the aid of the Allied fleet, to Salamis. The Peloponnesian Allies began to prepare a defensive line across the Isthmus of Corinth
, building a wall, and demolishing the road from Megara
, abandoning Athens to the Persians. Athens thus fell to the Persians; the small number of Athenians who had barricaded themselves on the Acropolis
were eventually defeated, and Xerxes then ordered Athens to be razed.
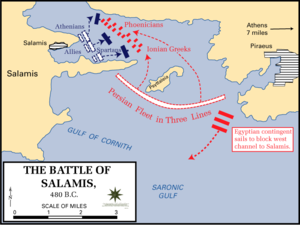 The Persians had now captured most of Greece, but Xerxes had perhaps not expected such defiance; his priority was now to complete the war as quickly as possible. If Xerxes could destroy the Allied navy, he would be in a strong position to force an Allied surrender; conversely by avoiding destruction, or as Themistocles hoped, by destroying the Persian fleet, the Allies could prevent conquest from being completed. The Allied fleet thus remained off the coast of Salamis into September, despite the imminent arrival of the Persians. Even after Athens fell, the Allied fleet remained off the coast of Salamis, trying to lure the Persian fleet to battle. Partly because of deception by Themistocles, the navies met in the cramped Straits of Salamis. There, the Persian numbers became a hindrance, as ships struggled to maneuver and became disorganised. Seizing the opportunity, the Allied fleet attacked, and scored a decisive victory, sinking or capturing at least 200 Persian ships, therefore ensuring the safety of the Peloponnessus.
The Persians had now captured most of Greece, but Xerxes had perhaps not expected such defiance; his priority was now to complete the war as quickly as possible. If Xerxes could destroy the Allied navy, he would be in a strong position to force an Allied surrender; conversely by avoiding destruction, or as Themistocles hoped, by destroying the Persian fleet, the Allies could prevent conquest from being completed. The Allied fleet thus remained off the coast of Salamis into September, despite the imminent arrival of the Persians. Even after Athens fell, the Allied fleet remained off the coast of Salamis, trying to lure the Persian fleet to battle. Partly because of deception by Themistocles, the navies met in the cramped Straits of Salamis. There, the Persian numbers became a hindrance, as ships struggled to maneuver and became disorganised. Seizing the opportunity, the Allied fleet attacked, and scored a decisive victory, sinking or capturing at least 200 Persian ships, therefore ensuring the safety of the Peloponnessus.
According to Herodotus, after the loss of the battle Xerxes attempted to build a causeway across the channel to attack the Athenian evacuees on Salamis, but this project was soon abandoned. With the Persians' naval superiority removed, Xerxes feared that the Allies might sail to the Hellespont and destroy the pontoon bridges. His general Mardonius volunteered to remain in Greece and complete the conquest with a hand-picked group of troops, while Xerxes retreated to Asia with the bulk of the army. Mardonius over-wintered in Boeotia and Thessaly; the Athenians were thus able to return to their burnt-out city for the winter.
remained in Thessaly, knowing an attack on the Isthmus was pointless, while the Allies refused to send an army outside the Peloponessus. Mardonius moved to break the stalemate, by offering peace to the Athenians, using Alexander I of Macedon
as an intermediate. The Athenians made sure that a Spartan delegation was on hand to hear the offer, but rejected it. Athens was thus evacuated again, and the Persians marched south and re-took possession of it. Mardonius now repeated his offer of peace to the Athenian refugees on Salamis. Athens, with Megara
and Plataea
, sent emissaries to Sparta demanding assistance, and threatening to accept the Persian terms if they were not aided. In response, the Spartans summonded a large army from the Peloponnese cities and marched to meet the Persians.
When Mardonius heard the Allied army was on the march, he retreated into Boeotia, near Plataea
, trying to draw the Allies into open terrain where he could use his cavalry. The Allied army, under the command of the regent Pausanias
, stayed on high ground above Plataea to protect themselves against such tactics. After several days of maneuver and stalemate, Pausanias ordered a night-time retreat towards the Allies' original positions. This maneuver went awry, leaving the Athenians, and Spartans and Tegeans isolated on separate hills, with the other contingents scattered further away near Plataea. Seeing that the Persians might never have a better opportunity to attack, Mardonius ordered his whole army forward. However, the Persian infantry proved no match for the heavily armoured Greek hoplites, and the Spartans broke through to Mardonius's bodyguard and killed him. After this the Persian force dissolved in rout; 40,000 troops managed to escape via the road to Thessaly, but the rest fled to the Persian camp where they were trapped and slaughtered by the Greeks, finalising the Greek victory.
Herodotus recounts that, on the afternoon of the Battle of Plataea
, a rumour of their victory at that battle reached the Allies' navy, at that time off the coast of Mount Mycale
in Ionia. Their morale boosted, the Allied marines fought and won a decisive victory at the Battle of Mycale
that same day, destroying the remnants of the Persian fleet, crippling Xerxes' sea power, and marking the ascendancy of the Greek fleet. Whilst many modern historians doubt that Mycale took place on the same day as Plataea, the battle may well only have occurred once the Allies received news of the events unfolding in Greece.
, still held by the Persians. The Persians and their allies made for Sestos
, the strongest town in the region. Amongst them was one Oeobazus of Cardia
, who had with him the cables and other equipment from the pontoon bridges. The Persian governor, Artayctes
had not prepared for a siege, not believing that the Allies would attack. The Athenians therefore were able to lay a siege around Sestos. The siege dragged on for several months, causing some discontent amongst the Athenian troops, but eventually, when the food ran out in the City, the Persians fled at night from the least guarded area of the city. The Athenians were thus able to take possession of the city the next day.
Most of the Athenian troops were sent straight away to pursue the Persians. The party of Oeobazus was captured by a Thracian tribe, and Oeobazus was sacrificed to the god Plistorus. The Athenians eventually caught Artayctes, killing some of the Persians with him but taking most of them, including Artayctes, captive. Artayctes was crucified at the request of the people of Elaeus
, a town which Artayctes had plundered while governor of the Chersonesos. The Athenians, having pacified the region, then sailed back to Athens, taking the cables from the pontoon bridges with them as trophies.
, which they besieged and eventually captured. Control of both Sestos and Byzantium gave the allies command of the straits between Europe and Asia (over which the Persians had crossed), and allowed them access to the merchant trade of the Black Sea.
The aftermath of the siege was to prove troublesome for Pausanias. Exactly what happened is unclear; Thucydides gives few details, although later writers added plenty of lurid insinuations. Through his arrogance and arbitrary actions (Thucydides says "violence"), Pausanias managed to alienate many of the Allied contingents, particularly those that had just been freed from Persian overlordship. The Ionians and others asked the Athenians to take leadership of the campaign, to which they agreed. The Spartans, hearing of his behaviour, recalled Pausanias and tried him on charges of collaborating with the enemy. Although he was acquitted, his reputation was tarnished and he was not restored to his command.
Pausanias returned to Byzantium as a private citizen in 477 BC, and took command of the city until he was expelled by the Athenians. He then crossed the Bosporus
and settled in Colonae in the Troad, until he was again accused of collaborating with the Persians and was recalled by the Spartans for a trial after which he starved himself to death. The timescale is unclear, but Pausanias may have remained in possession of Byzantium until 470 BC.
In the meantime, the Spartans had sent Dorkis to Byzantium with a small force, to take command of the Allied force. However, he found that the rest of the Allies were no longer prepared to accept Spartan leadership, and therefore returned home.
 After Byzantium, the Spartans were allegedly eager to end their involvement in the war. The Spartans were supposedly of the view that, with the liberation of mainland Greece and the Greek cities of Asia Minor, the war's purpose had already been reached. There was also perhaps a feeling that securing long-term security for the Asian Greeks would prove impossible. In the aftermath of Mycale, the Spartan king Leotychides had proposed transplanting all the Greeks from Asia Minor to Europe as the only method of permanently freeing them from Persian dominion. Xanthippus
After Byzantium, the Spartans were allegedly eager to end their involvement in the war. The Spartans were supposedly of the view that, with the liberation of mainland Greece and the Greek cities of Asia Minor, the war's purpose had already been reached. There was also perhaps a feeling that securing long-term security for the Asian Greeks would prove impossible. In the aftermath of Mycale, the Spartan king Leotychides had proposed transplanting all the Greeks from Asia Minor to Europe as the only method of permanently freeing them from Persian dominion. Xanthippus
, the Athenian commander at Mycale, had furiously rejected this; the Ionian cities were originally Athenian colonies, and the Athenians, if no-one else, would protect the Ionians. This marks the point at which the leadership of the Greek Alliance effectively passed to the Athenians. With the Spartan withdrawal after Byzantium, the leadership of the Athenians became explicit.
The loose alliance of city-states that had fought against Xerxes's invasion had been dominated by Sparta and the Peloponnesian league. With the withdrawal of these states, a congress was called on the holy island of Delos
to institute a new alliance to continue the fight against the Persians. This alliance, now including many of the Aegean islands, was formally constituted as the
'First Athenian Alliance', commonly known as the Delian League
. According to Thucydides, the official aim of the League was to "avenge the wrongs they suffered by ravaging the territory of the king". In reality, this goal was divided into three main efforts—to prepare for future invasion, to seek revenge against Persia, and to organize a means of dividing spoils of war. The members were given a choice of either supplying armed forces or paying a tax to the joint treasury; most states chose the tax.
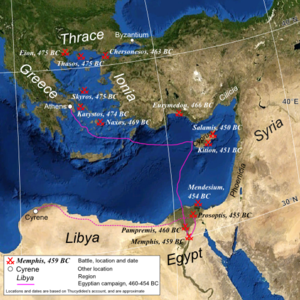 Throughout the 470s BC, the Delian League campaigned in Thrace and the Aegean to remove the remaining Persian garrisons from the region, primarily under the command of the Athenian politician Cimon. In the early part of the next decade, Cimon began campaigning in Asia Minor
Throughout the 470s BC, the Delian League campaigned in Thrace and the Aegean to remove the remaining Persian garrisons from the region, primarily under the command of the Athenian politician Cimon. In the early part of the next decade, Cimon began campaigning in Asia Minor
, seeking to strengthen the Greek position there. At the Battle of the Eurymedon
in Pamphylia
, the Athenians and allied fleet achieved a stunning double victory, destroying a Persian fleet and then landing the ships' marines to attack and rout the Persian army. After this battle, the Persians took an essentially passive role in the conflict, anxious not to risk battle if possible.
Towards the end of the 460s BC, the Athenians took the ambitious decision to support a revolt in the Egyptian
satrapy of the Persian empire. Although the Greek task force achieved initial successes, they were unable to capture the Persian garrison in Memphis
, despite a 3-year long siege. The Persians then counterattacked, and the Athenian force was itself besieged for 18 months, before being wiped out. This disaster, coupled with ongoing warfare
in Greece, dissuaded the Athenians from resuming conflict with Persia. In 451 BC however, a truce was agreed in Greece, and Cimon was then able to lead an expedition to Cyprus. However, while besieging Kition, Cimon died, and the Athenian force decided to withdraw, winning another double victory at the Battle of Salamis-in-Cyprus in order to extricate themselves. This campaign marked the end of hostilities between the Delian League and Persia, and therefore the end of the Greco-Persian Wars.
at this point, who in turn was presumably influenced by his teacher Isocrates
—from whom there is the earliest reference to the supposed peace, in 380 BC. Even during the 4th century BC, the idea of the treaty was controversial, and two authors from that period, Callisthenes
and Theopompus
, appear to reject its existence.
It is possible that the Athenians had attempted to negotiate with the Persians previously. Plutarch suggests that in the aftermath of the victory at the Eurymedon, Artaxerxes had agreed a peace treaty with the Greeks, even naming Callias as the Athenian ambassador involved. However, as Plutarch admits, Callisthenes denied that such a peace was made at this point (ca. 466 BC). Herodotus also mentions, in passing, an Athenian embassy headed by Callias
, which was sent to Susa
to negotiate with Artaxerxes. This embassy included some Argive
representatives and can probably be therefore dated to ca. 461 BC (after an alliance was agreed between Athens and Argos). This embassy may have been an attempt to reach some kind of peace agreement, and it has even been suggested that the failure of these hypothetical negotiations led to the Athenian decision to support the Egyptian revolt. The ancient sources therefore disagree as to whether there was an official peace or not, and, if there was, when it was agreed.
Opinion amongst modern historians is also split; for instance, Fine accepts the concept of the Peace of Callias, whereas Sealey effectively rejects it. Holland accepts that some kind of accommodation was made between Athens and Persia, but no actual treaty. Fine argues that Callisthenes's denial that a treaty was made after the Eurymedon does not preclude a peace being made at another point. Further, he suggests that Theopompus was actually referring to a treaty that had allegedly been negotiated with Persia in 423 BC. If these views are correct, it would remove one major obstacle to the acceptance of the treaty's existence. A further argument for the existence of the treaty is the sudden withdrawal of the Athenians from Cyprus in 449 BC, which Fine suggests makes most sense in the light of some kind of peace agreement. On the other hand, if there was indeed some kind of accommodation, Thucydides's failure to mention it is odd. In his digression on the pentekontaetia, his aim is to explain the growth of Athenian power, and such a treaty, and the fact that the Delian allies were not released from their obligations after it, would have marked a major step in the Athenian ascendancy. Conversely, it has been suggested that certain passages elsewhere in Thucydides's history are best interpreted as referring to a peace agreement. There is thus no clear consensus amongst modern historians as to the treaty's existence.
If the treaty did indeed exist, its terms were humiliating for Persia. The ancient sources that give details of the treaty are reasonably consistent in their description of the terms:
became the Athenian Empire reached its conclusion. The allies of Athens were not released from their obligations to provide either money or ships, despite the cessation of hostilities. In Greece, the First Peloponnesian War
between the power-blocs of Athens and Sparta, which had continued on/off since 460 BC, finally ended in 445 BC, with the agreement of a thirty-year truce. However, the growing enmity between Sparta and Athens would lead, just 14 years later, into the outbreak of the Second Peloponnesian War
. This disastrous conflict, which dragged on for 27 years, would eventually result in the utter destruction of Athenian power, the dismemberment of the Athenian empire, and the establishment of a Spartan hegemony
over Greece. However, not just Athens suffered—the conflict would significantly weaken the whole of Greece.
Repeatedly defeated in battle by the Greeks, and plagued by internal rebellions that hindered their ability to fight the Greeks, after 449 BC Artaxerxes I and his successors instead adopted a policy of divide-and-rule. Avoiding fighting the Greeks themselves, the Persians instead attempted to set Athens against Sparta, regularly bribing politicians to achieve their aims. In this way, they ensured that the Greeks remained distracted by internal conflicts, and were unable to turn their attentions to Persia. There was no open conflict between the Greeks and Persia until 396 BC, when the Spartan king Agesilaus
briefly invaded Asia Minor; as Plutarch points out, the Greeks were far too busy overseeing the destruction of their own power to fight against the "barbarians".
If the wars of the Delian League shifted the balance of power between Greece and Persia in favour of the Greeks, then the subsequent half-century of internecine conflict in Greece did much to restore the balance of power to Persia. The Persians entered the Peloponnesian War in 411 BC forming a mutual-defence pact with Sparta and combining their naval resources against Athens in exchange for sole Persian control of Ionia. In 404 BC when Cyrus the Younger
attempted to seize the Persian throne, he recruited 13,000 Greek mercenaries from all over the Greek world of which Sparta sent 700–800, believing they were following the terms of the treaty and unaware of the army's true purpose. After the failure of Cyrus, Persia tried to regain control of the Ionian city-states, which had rebelled during the conflict. The Ionians refused to capitulate and called upon Sparta for assistance, which she provided, in 396–395 BC. Athens, however, sided with the Persians, which led in turn to another large-scale conflict in Greece, the Corinthian War
. Towards the end of that conflict, in 387 BC, Sparta sought the aid of Persia to shore up her position. Under the so-called "King's Peace"
that brought the war to an end, Artaxerxes II demanded and received the return of the cities of Asia Minor from the Spartans, in return for which the Persians threatened to make war on any Greek state that did not make peace. This humiliating treaty, which undid all the Greek gains of the previous century, sacrificed the Greeks of Asia Minor so that the Spartans could maintain their hegemony over Greece. It is in the aftermath of this treaty that Greek orators began to refer to the Peace of Callias (whether fictional or not), as a counterpoint to the shame of the King's Peace, and a glorious example of the "good old days" when the Greeks of the Aegean had been freed from Persian rule by the Delian League. The final confrontation between the Greek world and Achaemenid Persia began just 53 years after that, with the army of Alexander the Great crossing into Asia, marking the beginning of what would result in the razing of Persepolis and the end of the Achaemenid Empire
.
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
of Persia and city-states of the Hellenic world
Classical Greece
Classical Greece was a 200 year period in Greek culture lasting from the 5th through 4th centuries BC. This classical period had a powerful influence on the Roman Empire and greatly influenced the foundation of Western civilizations. Much of modern Western politics, artistic thought, such as...
that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great
Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia , commonly known as Cyrus the Great, also known as Cyrus the Elder, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Under his rule, the empire embraced all the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanded vastly and eventually conquered most of Southwest Asia and much...
conquered Ionia
Ionia
Ionia is an ancient region of central coastal Anatolia in present-day Turkey, the region nearest İzmir, which was historically Smyrna. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements...
in 547 BC. Struggling to rule the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed tyrant
Tyrant
A tyrant was originally one who illegally seized and controlled a governmental power in a polis. Tyrants were a group of individuals who took over many Greek poleis during the uprising of the middle classes in the sixth and seventh centuries BC, ousting the aristocratic governments.Plato and...
s to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike.
In 499 BC, the then tyrant of Miletus
Miletus
Miletus was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia , near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Caria...
, Aristagoras
Aristagoras
Aristagoras was the leader of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC.- Background :Aristagoras served as deputy governor of Miletus, a polis on the western coast of Anatolia around 500 BC. He was the son of Molpagoras, and son-in-law of Histiaeus, whom the Persians had set up...
, embarked on an expedition
Siege of Naxos (499 BC)
The Siege of Naxos was a failed attempt by the Milesian tyrant Aristagoras, operating with support from, and in the name of the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, to conquer the island of Naxos...
to conquer the island of Naxos, with Persian support; however, the expedition was a debacle and, pre-empting his dismissal, Aristagoras incited all of Hellenic Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
into rebellion against the Persians. This was the beginning of the Ionian Revolt
Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC...
, which would last until 493 BC, progressively drawing more regions of Asia Minor into the conflict. Aristagoras secured military support from Athens
Classical Athens
The city of Athens during the classical period of Ancient Greece was a notable polis of Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Hippias...
and Eretria
Eretria
Erétria was a polis in Ancient Greece, located on the western coast of the island of Euboea, south of Chalcis, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow Euboean Gulf. Eretria was an important Greek polis in the 6th/5th century BC. However, it lost its importance already in antiquity...
, and in 498 BC these forces helped to capture and burn the Persian regional capital of Sardis
Sardis
Sardis or Sardes was an ancient city at the location of modern Sart in Turkey's Manisa Province...
. The Persian king Darius the Great
Darius I of Persia
Darius I , also known as Darius the Great, was the third king of kings of the Achaemenid Empire...
vowed to have revenge on Athens and Eretria for this act. The revolt continued, with the two sides effectively stalemated throughout 497–495 BC. In 494 BC, the Persians regrouped, and attacked the epicentre of the revolt in Miletus. At the Battle of Lade
Battle of Lade
The Battle of Lade was a naval battle which occurred during the Ionian Revolt, in 494 BC. It was fought between an alliance of the Ionian cities and the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, and resulted in a decisive victory for the Persians which all but ended the revolt.The Ionian Revolt was...
, the Ionians suffered a decisive defeat, and the rebellion collapsed, with the final members being stamped out the following year.
Seeking to secure his empire from further revolts and from the interference of the mainland Greeks, Darius embarked on a scheme to conquer Greece and to punish Athens and Eretria for burning Sardis. The first Persian invasion of Greece
First Persian invasion of Greece
The first Persian invasion of Greece, during the Persian Wars, began in 492 BCE, and ended with the decisive Athenian victory at the Battle of Marathon in 490 BCE. The invasion, consisting of two distinct campaigns, was ordered by the Persian king Darius I primarily in order to punish the...
began in 492 BC, with the Persian general Mardonius
Mardonius
Mardonius was a leading Persian military commander during the Persian Wars with Greece in the early 5th century BC.-Early years:Mardonius was the son of Gobryas, a Persian nobleman who had assisted the Achaemenid prince Darius when he claimed the throne...
conquering Thrace
Thrace
Thrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
and Macedon
Macedon
Macedonia or Macedon was an ancient kingdom, centered in the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, the region of Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south....
before several mishaps forced an early end to the campaign. In 490 BC a second force was sent to Greece, this time across the Aegean Sea
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea[p] is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus...
, under the command of Datis
Datis
For other uses of the word Dati, see Dati .Datis or Datus was a Median admiral who served the Persian Empire, under Darius the Great...
and Artaphernes
Artaphernes (son of Artaphernes)
Artaphernes, son of Artaphernes, was the nephew of Darius the Great, and a general of the Achaemenid Empire.He was appointed, together with Datis, to take command of the expedition sent by Darius to punish Athens and Eretria for their support for the Ionian Revolt. Artaphernes and Datis besieged...
. This expedition subjugated the Cyclades
Cyclades
The Cyclades is a Greek island group in the Aegean Sea, south-east of the mainland of Greece; and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the islands around the sacred island of Delos...
, before besieging, capturing and razing
Siege of Eretria
The Siege of Eretria took place in 490 BC, during the first Persian invasion of Greece. The city of Eretria, on Euboea, was besieged by a strong Persian force under the command of Datis and Artaphernes....
Eretria. However, while on route to attack Athens, the Persian force was decisively defeated by the Athenians at the Battle of Marathon
Battle of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC, during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. It was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugate...
, ending Persian efforts for the time being. Darius then began to plan to complete the conquest of Greece, but died in 486 BC and responsibility for the conquest passed to his son Xerxes I. In 480 BC, Xerxes personally led the second Persian invasion of Greece
Second Persian invasion of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece at the Battle of Marathon which ended Darius I's attempts...
with one of the largest ancient armies ever assembled. Victory over the 'Allied' Greek states (led by Sparta
Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
and Athens) at the Battle of Thermopylae
Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, led by King Leonidas of Sparta, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I over the course of three days, during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place simultaneously with the naval battle at Artemisium, in August...
allowed the Persians to overrun most of Greece. However, while seeking to destroy the combined Greek fleet, the Persians suffered a severe defeat at the Battle of Salamis
Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis was fought between an Alliance of Greek city-states and the Persian Empire in September 480 BCE, in the straits between the mainland and Salamis, an island in the Saronic Gulf near Athens...
. The following year, the confederated Greeks went on the offensive, defeating the Persian army at the Battle of Plataea
Battle of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states, including Sparta, Athens, Corinth and Megara, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes...
, and ending the invasion of Greece.
The allied Greeks followed up their success by destroying the rest of the Persian fleet at the Battle of Mycale
Battle of Mycale
The Battle of Mycale was one of the two major battles that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It took place on or about August 27, 479 BC on the slopes of Mount Mycale, on the coast of Ionia, opposite the island of Samos...
, before expelling Persian garrisons from Sestos
Sestos
200px|200px|thumb|The Ancient Map of Gallipoli PeninsulaSestos was an ancient Greek town of the Thracian Chersonese, the modern Gallipoli peninsula in European Turkey. Situated on the Hellespont opposite Abydos, it was the home of Hero in the legend of Hero and Leander, where according to legend...
(479 BC) and Byzantium
Byzantium
Byzantium was an ancient Greek city, founded by Greek colonists from Megara in 667 BC and named after their king Byzas . The name Byzantium is a Latinization of the original name Byzantion...
(478 BC). The actions of the general Pausanias
Pausanias (general)
Pausanias was a Spartan general of the 5th century BC. He was the son of Cleombrotus and nephew of Leonidas I, serving as regent after the latter's death, since Leonidas' son Pleistarchus was still under-age. Pausanias was also the father of Pleistoanax, who later became king, and Cleomenes...
at the siege of Byzantium alienated many of the Greek states from the Spartans, and the anti-Persian alliance was therefore reconstituted around Athenian leadership, as the so-called Delian League
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in circa 477 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, members numbering between 150 to 173, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Greco–Persian Wars...
. The Delian League continued to campaign
Wars of the Delian League
The Wars of the Delian League were a series of campaigns fought between the Delian League of Athens and her allies , and the Achaemenid Empire of Persia...
against Persia for the next three decades, beginning with the expulsion of the remaining Persian garrisons from Europe. At the Battle of the Eurymedon
Battle of the Eurymedon
The Battle of the Eurymedon was a double battle, taking place both on water and land, between the Delian League of Athens and her Allies, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. It took place in either 469 or 466 BC, in the vicinity of the mouth of the Eurymedon River in Pamphylia, Asia Minor...
in 466 BC, the League won a double victory that finally secured freedom for the cities of Ionia. However, the League's involvement in an Egyptian revolt (from 460–454 BC) resulted in a disastrous defeat, and further campaigning was suspended. A fleet was sent to Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
in 451 BC, but achieved little, and when it withdrew the Greco-Persian Wars drew to a quiet end. Some historical sources suggest the end of hostilities was marked by a peace treaty between Athens and Persia, the so-called Peace of Callias
Peace of Callias
The Peace of Callias is a purported treaty established around 449 BC between the Delian League and Persia, ending the Persian Wars. The peace was agreed as the first compromise treaty between Achaemenid Persia and a Greek city....
.
Sources


Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
. Herodotus, who has been called the "Father of History", was born in 484 BC in Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus was an ancient Greek city at the site of modern Bodrum in Turkey. It was located in southwest Caria on a picturesque, advantageous site on the Ceramic Gulf. The city was famous for the tomb of Mausolus, the origin of the word mausoleum, built between 353 BC and 350 BC, and...
, Asia Minor (then part of the Persian empire). He wrote his 'Enquiries' (Greek—Historia; English—(The) Histories
Histories (Herodotus)
The Histories of Herodotus is considered one of the seminal works of history in Western literature. Written from the 450s to the 420s BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, The Histories serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that...
) around 440–430 BC, trying to trace the origins of the Greco-Persian Wars, which would still have been recent history. Herodotus's approach was novel and, at least in Western society, he invented 'history' as a discipline. As Holland has it: "For the first time, a chronicler set himself to trace the origins of a conflict not to a past so remote so as to be utterly fabulous, nor to the whims and wishes of some god, nor to a people's claim to manifest destiny, but rather explanations he could verify personally."
Some later ancient historians, starting with Thucydides
Thucydides
Thucydides was a Greek historian and author from Alimos. His History of the Peloponnesian War recounts the 5th century BC war between Sparta and Athens to the year 411 BC...
, criticised Herodotus. Nevertheless, Thucydides chose to begin his history where Herodotus left off (at the Siege of Sestos) and felt Herodotus's history was accurate enough not to need re-writing or correcting. Plutarch
Plutarch
Plutarch then named, on his becoming a Roman citizen, Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus , c. 46 – 120 AD, was a Greek historian, biographer, essayist, and Middle Platonist known primarily for his Parallel Lives and Moralia...
criticised Herodotus in his essay "On The Malignity of Herodotus", describing Herodotus as "Philobarbaros" (barbarian-lover) for not being pro-Greek enough, which suggests that Herodotus might actually have done a reasonable job of being even-handed. A negative view of Herodotus was passed on to Renaissance Europe, though he remained well read. However, since the 19th century his reputation has been dramatically rehabilitated by archaeological finds that have repeatedly confirmed his version of events. The prevailing modern view is that Herodotus did a remarkable job in his Historia, but that some of his specific details (particularly troop numbers and dates) should be viewed with skepticism. Nevertheless, there are still some historians who believe Herodotus made up much of his story.
Unfortunately, the military history of Greece between the end of the second Persian invasion of Greece
Second Persian invasion of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece at the Battle of Marathon which ended Darius I's attempts...
and the Peloponnesian War
Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War, 431 to 404 BC, was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases...
(479–431 BC) is not well supported by surviving ancient sources. This period, sometimes referred to as the pentekontaetia by ancient scholars, was a period of relative peace and prosperity within Greece. The richest source for the period, and also the most contemporaneous, is Thucydides' History of the Peloponnesian War
History of the Peloponnesian War
The History of the Peloponnesian War is an account of the Peloponnesian War in Ancient Greece, fought between the Peloponnesian League and the Delian League . It was written by Thucydides, an Athenian general who served in the war. It is widely considered a classic and regarded as one of the...
, which is generally considered by modern historians to be a reliable primary account. Thucydides only mentions this period in a digression on the growth of Athenian power in the run up to the Peloponnesian War, and the account is brief, probably selective and lacks any dates. Nevertheless, Thucydides's account can be, and is, used by historians to draw up a skeleton chronology for the period, on to which details from archaeological records and other writers can be superimposed.
More detail for the whole period is provided by Plutarch, in his biographies
Parallel Lives
Plutarch's Lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans, commonly called Parallel Lives or Plutarch's Lives, is a series of biographies of famous men, arranged in tandem to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings, written in the late 1st century...
of Themistocles
Themistocles
Themistocles ; c. 524–459 BC, was an Athenian politician and a general. He was one of a new breed of politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy, along with his great rival Aristides...
, Aristides
Aristides
Aristides , 530 BC – 468 BC was an Athenian statesman, nicknamed "the Just".- Biography :Aristides was the son of Lysimachus, and a member of a family of moderate fortune. Of his early life, it is only told that he became a follower of the statesman Cleisthenes and sided with the aristocratic party...
and especially Cimon. Plutarch was writing some 600 years after the events in question, and is therefore a secondary source, but he often names his sources, which allows some degree of verification of his statements. In his biographies, he draws directly from many ancient histories that have not survived, and thus often preserves details of the period that are omitted in Herodotus and Thucydides's accounts. The final major existing source for the period is the universal history (Bibliotheca historica
Bibliotheca historica
Bibliotheca historica , is a work of universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, and describe the history and culture of Egypt , of Mesopotamia, India, Scythia, and Arabia , of North...
) of the 1st century BC Sicilian, Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus was a Greek historian who flourished between 60 and 30 BC. According to Diodorus' own work, he was born at Agyrium in Sicily . With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about Diodorus' life and doings beyond what is to be found in his own work, Bibliotheca...
. Much of Diodorus's writing about this period is drawn from the much earlier Greek historian Ephorus
Ephorus
Ephorus or Ephoros , of Cyme in Aeolia, in Asia Minor, was an ancient Greek historian. Information on his biography is limited; he was the father of Demophilus, who followed in his footsteps as a historian, and to Plutarch's claim that Ephorus declined Alexander the Great's offer to join him on his...
, who also wrote a universal history. Diodorus is also a secondary source and often derided by modern historians for his style and inaccuracies, but he preserves many details of the ancient period found nowhere else.
Further scattered details can be found in Pausanias
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias was a Greek traveler and geographer of the 2nd century AD, who lived in the times of Hadrian, Antoninus Pius and Marcus Aurelius. He is famous for his Description of Greece , a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from firsthand observations, and is a crucial link between classical...
's Description of Greece, while the Byzantine
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
Suda
Suda
The Suda or Souda is a massive 10th century Byzantine encyclopedia of the ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Suidas. It is an encyclopedic lexicon, written in Greek, with 30,000 entries, many drawing from ancient sources that have since been lost, and often...
dictionary of the 10th century AD preserves some anecdotes found nowhere else. Minor sources for the period include the works of Pompeius Trogus
Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus
Gnaeus Pompēius Trōgus, known as Pompeius Trogus, Pompey Trogue, or Trogue Pompey, was a 1st century BC Roman historian of the Celtic tribe of the Vocontii in Gallia Narbonensis, flourished during the age of Augustus, nearly contemporary with Livy.His grandfather served in the war against Sertorius...
(epitomized by Justinus), Cornelius Nepos
Cornelius Nepos
Cornelius Nepos was a Roman biographer. He was born at Hostilia, a village in Cisalpine Gaul not far from Verona. His Gallic origin is attested by Ausonius, and Pliny the Elder calls him Padi accola...
and Ctesias of Cnidus
Ctesias
Ctesias of Cnidus was a Greek physician and historian from Cnidus in Caria. Ctesias, who lived in the 5th century BC, was physician to Artaxerxes Mnemon, whom he accompanied in 401 BC on his expedition against his brother Cyrus the Younger....
(epitomized by Photius), which are not in their original textual form. These works are not considered reliable (especially Ctesias), and are not particularly useful for reconstructing the history of this period.
Origins of the conflict
The Greeks of the classical period believed that, in the dark ageGreek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Age or Ages also known as Geometric or Homeric Age are terms which have regularly been used to refer to the period of Greek history from the presumed Dorian invasion and end of the Mycenaean Palatial civilization around 1200 BC, to the first signs of the Greek city-states in the 9th...
that followed the collapse of the Mycenaean civilization
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece was a cultural period of Bronze Age Greece taking its name from the archaeological site of Mycenae in northeastern Argolis, in the Peloponnese of southern Greece. Athens, Pylos, Thebes, and Tiryns are also important Mycenaean sites...
, significant numbers of Greeks fled and had emigrated to Asia Minor and settled there. Modern historians generally accept this migration as historic (but separate from the later colonization of the Mediterranean by the Greeks). There are, however, those who believe the Ionian migration cannot be explained as simply as the classical Greeks claimed. These settlers were from three tribal groups: the Aeolians
Aeolians
The Aeolians were one of the four major ancient Greek tribes comprising Ancient Greeks. Their name derives from Aeolus, the mythical ancestor of the Aeolic branch and son of Hellen, the mythical patriarch of the Greek nation...
, Dorians and Ionians
Ionians
The Ionians were one of the four major tribes into which the Classical Greeks considered the population of Hellenes to have been divided...
. The Ionians had settled about the coasts of Lydia
Lydia
Lydia was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern Turkish provinces of Manisa and inland İzmir. Its population spoke an Anatolian language known as Lydian....
and Caria
Caria
Caria was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there...
, founding the twelve cities that made up Ionia
Ionia
Ionia is an ancient region of central coastal Anatolia in present-day Turkey, the region nearest İzmir, which was historically Smyrna. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements...
. These cities were Miletus
Miletus
Miletus was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia , near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Caria...
, Myus
Myus
Myus, Caria was an ancient city-state and was one of twelve major settlements formed in the Ionian Confederation, called the Ionian League. The city was said to have been founded by Cyaretus , a son of Codrus. Myus was a small peninsula, it is now however surrounded by land...
and Priene
Priene
Priene was an ancient Greek city of Ionia at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about north of the then course of the Maeander River, from today's Aydin, from today's Söke and from ancient Miletus...
in Caria; Ephesus
Ephesus
Ephesus was an ancient Greek city, and later a major Roman city, on the west coast of Asia Minor, near present-day Selçuk, Izmir Province, Turkey. It was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League during the Classical Greek era...
, Colophon, Lebedos, Teos
Teos
Teos or Teo was a maritime city of Ionia, on a peninsula between Chytrium and Myonnesus, colonized by Orchomenian Minyans, Ionians, and Boeotians. The city is situated on a low hilly narrow strip of land connecting two larger areas of land . Teos ranked among twelve cities comprising the Ionian...
, Clazomenae
Clazomenae
Klazomenai was an ancient Greek city of Ionia and a member of the Ionian Dodecapolis , it was one of the first cities to issue silver coinage.-Location:Klazomenai is located in modern Urla on the western coast of...
, Phocaea
Phocaea
Phocaea, or Phokaia, was an ancient Ionian Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia. Greek colonists from Phocaea founded the colony of Massalia in 600 BC, Emporion in 575 BC and Elea in 540 BC.-Geography:Phocaea was the northernmost...
and Erythrae
Erythrae
Erythrae or Erythrai later Litri, was one of the twelve Ionian cities of Asia Minor, situated 22 km north-east of the port of Cyssus , on a small peninsula stretching into the Bay of Erythrae, at an equal distance from the mountains Mimas and Corycus, and directly opposite the island of Chios...
in Lydia; and the islands of Samos
Samoš
Samoš is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Kovačica municipality, in the South Banat District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 1,247 people .-See also:...
and Chios
Chios
Chios is the fifth largest of the Greek islands, situated in the Aegean Sea, seven kilometres off the Asia Minor coast. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. The island is noted for its strong merchant shipping community, its unique mastic gum and its medieval villages...
. Although the Ionian cities were independent of one another, they recognized their shared heritage and supposedly had a common temple and meeting place, the Panionion. They thus formed a 'cultural league', to which they would admit no other cities, or even other tribal Ionians.
The cities of Ionia had remained independent until they were conquered by the Lydians
Lydians
The Lydians were the inhabitants of Lydia, a region in western Anatolia, who spoke the distinctive Lydian language, an Indo-European language of the Anatolian group....
of western Asia Minor. The Lydian king Alyattes II
Alyattes II
Alyattes, king of Lydia , considered to be the founder of the Lydian empire, was the son of Sadyattes, of the house of the Mermnadae....
attacked Miletus, a conflict that ended with a treaty of alliance between Miletus and Lydia, that meant that Miletus would have internal autonomy but follow Lydia in foreign affairs. At this time, the Lydians were also in conflict with the Median
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
Empire, and the Milesians sent an army to aid the Lydians in this conflict. Eventually a peaceable settlement was established between the Medes and the Lydians, with the Halys River
Halys River
The Kızılırmak , also known as the Halys River , is the longest river in Turkey. It is a source of hydroelectric power and is not used for navigation.- Geography :...
set up as the border between the kingdoms. The famous Lydian king Croesus
Croesus
Croesus was the king of Lydia from 560 to 547 BC until his defeat by the Persians. The fall of Croesus made a profound impact on the Hellenes, providing a fixed point in their calendar. "By the fifth century at least," J.A.S...
succeeded his father Alyattes in around 560 BC and set about conquering the other Greek city states of Asia Minor.
The Persian prince Cyrus
Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia , commonly known as Cyrus the Great, also known as Cyrus the Elder, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Under his rule, the empire embraced all the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanded vastly and eventually conquered most of Southwest Asia and much...
led a rebellion against the last Median king Astyages
Astyages
Astyages Astyages Astyages (spelled by Herodotus as Ἀστυάγης - Astyages; by Ctesias as Astyigas; by Diodorus as Aspadas; Akkadian: Ištumegu, was the last king of the Median Empire, r...
in 553 BC. Cyrus was a grandson of Astyages and was supported by part of the Median aristocracy. By 550 BC, the rebellion was over, and Cyrus had emerged victorious, founding the Achaemenid Empire
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
in place of the Median kingdom in the process. Croesus saw the disruption in the Median Empire and Persia as an opportunity to extend his realm and asked the oracle of Delphi
Delphi
Delphi is both an archaeological site and a modern town in Greece on the south-western spur of Mount Parnassus in the valley of Phocis.In Greek mythology, Delphi was the site of the Delphic oracle, the most important oracle in the classical Greek world, and a major site for the worship of the god...
whether he should attack them. The Oracle supposedly replied the famously ambiguous answer that "if Croesus was to cross the Halys he would destroy a great empire". Blind to the ambiguity of this prophecy, Croesus attacked the Persians, but was eventually defeated and Lydia fell to Cyrus.

Harpagus
Harpagus, also known as Harpagos or Hypargus , was a Median general from the 6th century BCE, credited by Herodotus as having put Cyrus the Great on the throne through his defection during the battle of Pasargadae.-Biography:According to Herodotus' Histories, Harpagus was a member of the Median...
to conquer them. He first attacked Phocaea; the Phocaeans decided to abandon their city entirely and sail into exile in Sicily, rather than become Persian subjects (although many later returned). Some Teians also chose to emigrate when Harpagus attacked Teos, but the rest of the Ionians remained, and were each in turn conquered.
In the years following their conquest, the Persians found the Ionians difficult to rule. Elsewhere in the empire, Cyrus identified elite native groups such as the priesthood of Judea - to help him rule his new subjects. No such group existed in Greek cities at this time; while there was usually an aristocracy, this was inevitably divided into feuding factions. The Persians thus settled for sponsoring a tyrant in each Ionian city, even though this drew them into the Ionians' internal conflicts. Furthermore, certain tyrants might develop an independent streak and have to be replaced. The tyrants themselves faced a difficult task; they had to deflect the worst of their fellow citizens' hatred, while staying in the favour of the Persians. In the past, Greek states had often been ruled by tyrants, but that form of government was on the decline. Past tyrants had also tended and needed to be strong and able leaders, whereas the rulers appointed by the Persians were simply place-men. Backed by the Persian military might, these tyrants did not need the support of the population, and could thus rule absolutely. On the eve of the Greco-Persian wars, it is probable that the Ionian population had become discontent and was ready for rebellion. Ionia, unlike the many other areas of the empire, did not revolt in the civil war period between the reigns of Cyrus and Darius I of Persia
Darius I of Persia
Darius I , also known as Darius the Great, was the third king of kings of the Achaemenid Empire...
, and it is therefore possible to argue that the Greeks were not so dissatisfied with Persian rule as some historians propose.
Warfare in the ancient Mediterranean
In the Greco-Persian wars both sides made use of spear-armed infantry and light missile troops, Greek armies placed the emphasis on heavier infantry, while Persian armies favoured lighter troop types.Persia
The Persian military consisted of a diverse group of men drawn from across the empire. However, according to Herodotus, there was at least a general conformity in armour and style of fighting. The troops were usually armed with a bow, a 'short spear' and a sword or axe, carried a wicker shield. They wore a leather jerkin, although individuals of high stature wore high quality metal armor. The Persians most likely used their bows to wear down the enemy, then closed in to deliver the final blow with spears and swords. The first rank of Persian infantry formations, the so-called 'sparabaraSparabara
The Sparabara, meaning "shield bearers" in Persian, were the heavy front line infantry of the Achaemenid Persian Empire. They were usually the first to engage in hand to hand combat with the enemy...
', had no bows, carried larger wicker shields and were sometimes armed with longer spears. Their role was to protect the back ranks of the formation. The cavalry probably fought as lightly armed missile cavalry.
Greece
The style of warfare between the Greek city-states, which dates back until at least 650 BC (as dated by the 'Chigi vaseChigi vase
The Chigi vase is a Protocorinthian olpe, or pitcher, that is the name vase of the Chigi Painter. It was found in an Etruscan tomb at Monte Aguzzo, near Cesena, on Prince Mario Chigi’s estate in 1881. The vase has been variously assigned to the middle and late protocorinthian periods and given a...
'), was based around the hoplite
Hoplite
A hoplite was a citizen-soldier of the Ancient Greek city-states. Hoplites were primarily armed as spearmen and fought in a phalanx formation. The word "hoplite" derives from "hoplon" , the type of the shield used by the soldiers, although, as a word, "hopla" could also denote weapons held or even...
phalanx
Phalanx formation
The phalanx is a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar weapons...
supported by missile troops. The 'hoplite
Hoplite
A hoplite was a citizen-soldier of the Ancient Greek city-states. Hoplites were primarily armed as spearmen and fought in a phalanx formation. The word "hoplite" derives from "hoplon" , the type of the shield used by the soldiers, although, as a word, "hopla" could also denote weapons held or even...
s' were foot soldiers usually drawn from the members of the middle-classes (in Athens called the zeugites), who could afford the equipment necessary to fight in this manner. The heavy armour usually included a breastplate or a linothorax
Linothorax
The linothorax was a type of upper body armor used by the Ancient Greeks, as well as other civilizations, from the Mycenaean Period through the Hellenistic Period. The earliest attested account of a linothorax used for battle is recorded in Book 2 of Homer's Iliad . It is worn by Ajax the lesser...
, greaves, a helmet, and a large round, concave shield (the aspis
Aspis
"Aspis" is the generic term for the word shield. The aspis, which is carried by Greek infantry of various periods, is often referred to as a hoplon .According to Diodorus Siculus:-Construction:...
or hoplon). Hoplites were armed with long spears (the dory
Dory (spear)
The dory or doru - ie not pronounced like the fish - is a spear that was the chief armament of hoplites in Ancient Greece. The word "dory" is first attested in Homer with the meanings of "wood" and "spear". Homeric heroes hold two dorys...
), which were significantly longer than Persian spears, and a sword (the xiphos). The heavy armour and longer spears made them superior in hand-to-hand combat and gave them significant protection against ranged attacks. Lightly armed skirmishers, the psiloi
Psiloi
In Ancient Greek warfare, psiloi were extremely light infantry who acted as skirmishers and missile troops....
also comprised a part of Greek armies growing in importance during the conflict; at the Battle of Plataea, for instance, they may have formed over half the Greek army. Use of cavalry in Greek armies is not reported in the battles of the Greco-Persian Wars.
Naval warfare
At the beginning of the conflict, all naval forces in the eastern Mediterranean had switched to the triremeTrireme
A trireme was a type of galley, a Hellenistic-era warship that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greeks and Romans.The trireme derives its name from its three rows of oars on each side, manned with one man per oar...
, a warship powered by three banks of oars. The most common naval tactics during the period were ramming (triremes were equipped with a ram at the bows), or boarding by ship-borne marines. More experienced naval powers had by this time also begun to use a manoeuver known as diekplous. It is not clear what this was, but it probably involved sailing into gaps between enemy ships and then ramming them in the side.
The Persian naval forces were primarily provided by the Phoenicia
Phoenicia
Phoenicia , was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the Fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550...
ns, Egyptians
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
, Cilicia
Cilicia
In antiquity, Cilicia was the south coastal region of Asia Minor, south of the central Anatolian plateau. It existed as a political entity from Hittite times into the Byzantine empire...
ns and Cypriots
Ancient history of Cyprus
The ancient history of Cyprus, also known as Classical Antiquity, dates from the 8th century BC to the Middle Ages. The earliest written records relating to Cyprus date to the Middle Bronze Age , see Alasiya.-Assyrian Period:...
. Other coastal regions of the Persian Empire would contribute ships throughout the course of the wars.
Ionian Revolt (499–493 BC)
The Ionian RevoltIonian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC...
and associated revolts in Aeolis
Aeolis
Aeolis or Aeolia was an area that comprised the west and northwestern region of Asia Minor, mostly along the coast, and also several offshore islands , where the Aeolian Greek city-states were located...
, Doris
Doris (Asia Minor)
Doris was a small region of ancient Asia Minor inhabited by Dorians; the territory is now in modern-day Turkey. Pliny says, Caria mediae Doridi circumfunditur ad mare utroque latere ambiens, by which he means that Doris is surrounded by Caria on all sides, except where it is bordered by the sea....
, Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
, and Caria
Caria
Caria was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there...
were military rebellions by several regions of Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
against Persian rule, lasting from 499 to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with opposition to the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus
Histiaeus
Histiaeus , the son of Lysagoras, was the tyrant of Miletus in the late 6th century BC.Histiaeus owed his status as tyrant of Miletus to Darius I, king of Persia, who had subjugated Miletus and the other Ionian states in Asia Minor....
and Aristagoras. In 499 BC the then tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes
Artaphernes
Artaphernes , was the brother of the king of Persia, Darius I of Persia, and satrap of Sardis.In 497 BC, Artaphernes received an embassy from Athens, probably sent by Cleisthenes, and subsequently advised the Athenians that they should receive back the tyrant Hippias.Subsequently he took an...
to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position in Miletus (both financially and in terms of prestige). The mission
Siege of Naxos (499 BC)
The Siege of Naxos was a failed attempt by the Milesian tyrant Aristagoras, operating with support from, and in the name of the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, to conquer the island of Naxos...
was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.

By 494 BC the Persian army and navy had regrouped, and they made straight for the epicentre of the rebellion at Miletus. The Ionian fleet sought to defend Miletus by sea, but was defeated decisively at the Battle of Lade
Battle of Lade
The Battle of Lade was a naval battle which occurred during the Ionian Revolt, in 494 BC. It was fought between an alliance of the Ionian cities and the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, and resulted in a decisive victory for the Persians which all but ended the revolt.The Ionian Revolt was...
, after the Samians
Samoš
Samoš is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Kovačica municipality, in the South Banat District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 1,247 people .-See also:...
had defected. Miletus was then besieged, captured, and its population was enslaved. This double defeat effectively ended the revolt, and the Carians surrendered to the Persians as a result. The Persians spent 493 BC reducing the cities along the west coast that still held out against them, before finally imposing a peace settlement on Ionia that was considered to be both just and fair.
The Ionian Revolt constituted the first major conflict between Greece and the Achaemenid Empire and represents the first phase of the Greco-Persian Wars. Asia Minor had been brought back into the Persian fold, but Darius had vowed to punish Athens and Eretria for their support for the revolt. Moreover, seeing that the political situation in Greece posed a continued threat to the stability of his Empire, he decided to embark on the conquest of all Greece.
First invasion of Greece (492–490 BC)
After conquering Ionia, the Persians began to plan their next moves: extinguishing the threat to their empire from Greece and punishing Athens and Eretria. The resultant first Persian invasion of GreeceFirst Persian invasion of Greece
The first Persian invasion of Greece, during the Persian Wars, began in 492 BCE, and ended with the decisive Athenian victory at the Battle of Marathon in 490 BCE. The invasion, consisting of two distinct campaigns, was ordered by the Persian king Darius I primarily in order to punish the...
consisted of two main campaigns.
492 BC: Mardonius's campaign

Mardonius
Mardonius was a leading Persian military commander during the Persian Wars with Greece in the early 5th century BC.-Early years:Mardonius was the son of Gobryas, a Persian nobleman who had assisted the Achaemenid prince Darius when he claimed the throne...
, who re-subjugated Thrace
Thrace
Thrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
, which had nominally been part of the Persian empire since 513 BC. Mardonius was also able to force Macedon
Macedon
Macedonia or Macedon was an ancient kingdom, centered in the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, the region of Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south....
to become a client kingdom of Persia; it had previously been allied but independent. However, further progress in this campaign was prevented when Mardonius's fleet was wrecked in a storm off the coast of Mount Athos
Mount Athos
Mount Athos is a mountain and peninsula in Macedonia, Greece. A World Heritage Site, it is home to 20 Eastern Orthodox monasteries and forms a self-governed monastic state within the sovereignty of the Hellenic Republic. Spiritually, Mount Athos comes under the direct jurisdiction of the...
. Mardonius himself was then injured in a raid on his camp by a Thracian tribe, and after this he returned with the rest of the expedition to Asia.
The following year, having given clear warning of his plans, Darius sent ambassadors to all the cities of Greece, demanding their submission. He received it from almost all of them, except Athens and Sparta
Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
, both of whom instead executed the ambassadors. With Athens still defiant, and Sparta now also effectively at war with him, Darius ordered a further military campaign for the following year.
490 BC: Datis and Artaphernes' campaign
In 490 BC, DatisDatis
For other uses of the word Dati, see Dati .Datis or Datus was a Median admiral who served the Persian Empire, under Darius the Great...
and Artaphernes
Artaphernes (son of Artaphernes)
Artaphernes, son of Artaphernes, was the nephew of Darius the Great, and a general of the Achaemenid Empire.He was appointed, together with Datis, to take command of the expedition sent by Darius to punish Athens and Eretria for their support for the Ionian Revolt. Artaphernes and Datis besieged...
(son of the satrap Artaphernes
Artaphernes
Artaphernes , was the brother of the king of Persia, Darius I of Persia, and satrap of Sardis.In 497 BC, Artaphernes received an embassy from Athens, probably sent by Cleisthenes, and subsequently advised the Athenians that they should receive back the tyrant Hippias.Subsequently he took an...
) were given command of an amphibious invasion force, and set sail from Cilicia
Cilicia
In antiquity, Cilicia was the south coastal region of Asia Minor, south of the central Anatolian plateau. It existed as a political entity from Hittite times into the Byzantine empire...
. The Persian force sailed from Cilicia first to the island of Rhodes
Rhodes
Rhodes is an island in Greece, located in the eastern Aegean Sea. It is the largest of the Dodecanese islands in terms of both land area and population, with a population of 117,007, and also the island group's historical capital. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within...
, where a Lindian Temple Chronicle records that Datis
Datis
For other uses of the word Dati, see Dati .Datis or Datus was a Median admiral who served the Persian Empire, under Darius the Great...
besieged the city of Lindos
Lindos
Lindos is an archaeological site, a town and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which it is a municipal unit. It lies on the east coast of the island...
, but was unsuccessful. The fleet sailed next to Naxos, to punish the Naxians for their resistance to the failed expedition the Persians had mounted there a decade earlier. Many of the inhabitants fled to the mountains; those that the Persians caught were enslaved. The Persians then burnt the city and temples of the Naxians. The fleet then proceeded to island-hop across the rest of the Aegean on its way to Eretria, taking hostages and troops from each island.
The task force sailed on to Euboea
Euboea
Euboea is the second largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. The narrow Euripus Strait separates it from Boeotia in mainland Greece. In general outline it is a long and narrow, seahorse-shaped island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to...
, and to the first major target, Eretria. The Eretrians made no attempt to stop the Persians from landing or advancing and thus allowed themselves to be besieged
Siege of Eretria
The Siege of Eretria took place in 490 BC, during the first Persian invasion of Greece. The city of Eretria, on Euboea, was besieged by a strong Persian force under the command of Datis and Artaphernes....
. For six days, the Persians attacked the walls, with losses on both sides; however, on the seventh day two reputable Eretrians opened the gates and betrayed the city to the Persians. The city was razed, and temples and shrines were looted and burned. Furthermore, according to Darius's commands, the Persians enslaved all the remaining townspeople.
Battle of Marathon

Attica
Attica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
, landing at the bay of Marathon
Marathon, Greece
Marathon is a town in Greece, the site of the battle of Marathon in 490 BC, in which the heavily outnumbered Athenian army defeated the Persians. The tumulus or burial mound for the 192 Athenian dead that was erected near the battlefield remains a feature of the coastal plain...
, roughly 25 miles (40.2 km) from Athens Under the guidance of Miltiades
Miltiades the Younger
Miltiades the Younger or Miltiades IV was the son of one Cimon, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer. Miltiades considered himself a member of the Aeacidae, and is known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon; as well as his rather tragic downfall afterwards. His son Cimon was a major Athenian...
, the general with the greatest experience of fighting the Persians, the Athenian army marched to block the two exits from the plain of Marathon. Stalemate ensued for five days, before the Athenians (for reasons that are unclear) decided to attack the Persians. Despite the numerical advantage of the Persians, the hoplite
Hoplite
A hoplite was a citizen-soldier of the Ancient Greek city-states. Hoplites were primarily armed as spearmen and fought in a phalanx formation. The word "hoplite" derives from "hoplon" , the type of the shield used by the soldiers, although, as a word, "hopla" could also denote weapons held or even...
s proved devastatingly effective against the more lightly armed Persian infantry, routing the wings before turning in on the centre of the Persian line. The remnants of the Persian army fled to their ships and left the battle. Herodotus records that 6,400 Persian bodies were counted on the battlefield; the Athenians lost only 192 men.
As soon as the Persian survivors had put to sea, the Athenians marched as quickly as possible to Athens. They arrived in time to prevent Artaphernes from securing a landing in Athens. Seeing his opportunity lost, Artaphernes ended the year's campaign and returned to Asia.
The Battle of Marathon was a watershed in the Greco-Persian wars, showing the Greeks that the Persians could be beaten. It also highlighted the superiority of the more heavily armoured Greek hoplites, and showed their potential when used wisely. The Battle of Marathon is perhaps now more famous as the inspiration for the Marathon
Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance running event with an official distance of 42.195 kilometres , that is usually run as a road race...
race.
Achaemenid Empire
After the failure of the first invasion, Darius began raising a huge new army with which he meant to subjugate Greece completely; however, in 486 BC, his EgyptianAncient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
subjects revolted, indefinitely postponing any Greek expedition. Darius died while preparing to march on Egypt, and the throne of Persia passed to his son Xerxes I. Xerxes crushed the Egyptian revolt, and very quickly restarted the preparations for the invasion of Greece. Since this was to be a full scale invasion, it needed longterm planning, stockpiling and conscription. Xerxes decided the Hellespont would be bridged to allow his army to cross to Europe, and that a canal should be dug across the isthmus of Mount Athos
Mount Athos
Mount Athos is a mountain and peninsula in Macedonia, Greece. A World Heritage Site, it is home to 20 Eastern Orthodox monasteries and forms a self-governed monastic state within the sovereignty of the Hellenic Republic. Spiritually, Mount Athos comes under the direct jurisdiction of the...
(a Persian fleet had been destroyed in 492 BC while rounding this coastline). These were both feats of exceptional ambition that would have been beyond any contemporary state. However, the campaign was delayed by one year because of another revolt in Egypt and Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
.
The Persians had the sympathy of several Greek city-states, including Argos
Argos
Argos is a city and a former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. It is 11 kilometres from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour...
, which had pledged to defect when the Persians reached their borders. The Aleuadae
Aleuadae
The Aleuadae were an ancient Thessalian family of Larissa who claimed descent from the mythical Aleuas. The Aleuadae were the noblest and most powerful among all the families of Thessaly, whence Herodotus calls its members "rulers" or "kings" .-Aleuas:The first Aleuas, who bore the epithet of...
family, who ruled Larissa
Larissa
Larissa is the capital and biggest city of the Thessaly region of Greece and capital of the Larissa regional unit. It is a principal agricultural centre and a national transportation hub, linked by road and rail with the port of Volos, the city of Thessaloniki and Athens...
in Thessaly
Thessaly
Thessaly is a traditional geographical region and an administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia, and appears thus in Homer's Odyssey....
, saw the invasion as an opportunity to extend their power. Thebes
Thebes, Greece
Thebes is a city in Greece, situated to the north of the Cithaeron range, which divides Boeotia from Attica, and on the southern edge of the Boeotian plain. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others...
, though not explicitly 'Medising', was suspected of being willing to aid the Persians once the invasion force arrived.
In 481 BC
481 BC
Year 481 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Fusus...
, after roughly four years of preparation, Xerxes began to muster the troops to invade Europe. Herodotus gives the names of 46 nations from which troops were drafted. The Persian army was gathered in Asia Minor in the summer and autumn of 481 BC
481 BC
Year 481 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Fusus...
. The armies from the Eastern satrapies were gathered in Kritala, Cappadocia
Cappadocia
Cappadocia is a historical region in Central Anatolia, largely in Nevşehir Province.In the time of Herodotus, the Cappadocians were reported as occupying the whole region from Mount Taurus to the vicinity of the Euxine...
and were led by Xerxes to Sardis where they passed the winter. Early in spring, it moved to Abydos
Abydos, Hellespont
For other uses, see Abydos Abydos , an ancient city of Mysia, in Asia Minor, situated at Nara Burnu or Nagara Point on the best harbor on the Asiatic shore of the Hellespont. Across Abydos lies Sestus on the European side marking the shortest point in the Dardanelles, scarcely a mile broad...
where it was joined with the armies of the western satrapies. Then the army that Xerxes had mustered marched towards Europe, crossing the Hellespont on two pontoon bridge
Pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge or floating bridge is a bridge that floats on water and in which barge- or boat-like pontoons support the bridge deck and its dynamic loads. While pontoon bridges are usually temporary structures, some are used for long periods of time...
s.
Size of the Persian forces
- For further information see Size of the Persian Forces
The numbers of troops that Xerxes mustered for the second invasion of Greece have been the subject of endless dispute. Most modern scholars reject as unrealistic the figures of 2.5 million given by Herodotus and other ancient sources because the victors likely miscalculated or exaggerated. The topic has been hotly debated, but the consensus revolves around the figure of 200,000.
The size of the Persian fleet is also disputed, although perhaps less so. Other ancient authors agree with Herodotus' number of 1,207. These numbers are by ancient standards consistent, and this could be interpreted that a number around 1,200 is correct. Among modern scholars, some have accepted this number, although suggesting the number must have been lower by the Battle of Salamis
Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis was fought between an Alliance of Greek city-states and the Persian Empire in September 480 BCE, in the straits between the mainland and Salamis, an island in the Saronic Gulf near Athens...
. Other recent works on the Persian Wars reject this number, viewing 1,207 as more of a reference to the combined Greek fleet in the Iliad
Iliad
The Iliad is an epic poem in dactylic hexameters, traditionally attributed to Homer. Set during the Trojan War, the ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Greek states, it tells of the battles and events during the weeks of a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles...
. These works generally claim that the Persians could have launched no more than around 600 warships into the Aegean.
Athens
A year after Marathon, Miltiades, the hero of Marathon, was injured in a minor battle. Taking advantage of his incapacitation, the powerful Alcmaeonid family arranged for him to be prosecuted. Miltiades was given a massive fine for the crime of 'deceiving the Athenian people', but died weeks later from his wound.
Themistocles
Themistocles ; c. 524–459 BC, was an Athenian politician and a general. He was one of a new breed of politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy, along with his great rival Aristides...
, with a power base firmly established amongst the poor, filled the vacuum left by Miltiades's death, and in the following decade became the most influential politician in Athens. During this period, Themistocles continued to support expanding Athenian naval power. The Athenians were aware throughout this period that the Persian interest in Greece had not ended, and Themistocles's naval policies may be seen in the light of the potential threat from Persia. Aristides, Themistocles's great rival, and champion of the zeugites (the upper, 'hoplite-class') vigorously opposed such a policy.
In 483 BC, a massive new seam of silver was found in the Athenian mines at Laurium
Laurium
Laurium or Lavrio is a town in southeastern part of Attica, Greece. It is the seat of the municipality of Lavreotiki...
. Themistocles proposed that the silver should be used to build a new fleet of triremes, ostensibly to assist in a long running war with Aegina
Aegina
Aegina is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece in the Saronic Gulf, from Athens. Tradition derives the name from Aegina, the mother of Aeacus, who was born in and ruled the island. During ancient times, Aegina was a rival to Athens, the great sea power of the era.-Municipality:The municipality...
. Plutarch suggests that Themistocles deliberately avoided mentioning Persia, believing that it was too distant a threat for the Athenians to act on, but that countering Persia was the fleet's aim. Fine suggests that many Athenians must have admitted that such a fleet would be needed to resist the Persians, whose preparations for the coming campaign were known about. Themistocles's motion was passed easily, despite strong opposition from Aristides. Its passage was probably due to the desire of many of the poorer Athenians for paid employment as rowers in the fleet. It is unclear from the ancient sources whether 100 or 200 ships initially authorised; both Fine and Holland suggest that at first 100 ships were authorised and that a second vote increased this number to the levels seen during the second invasion. Aristides continued to oppose Themistocles's policy, and tension between the two camps built over the winter, so the ostracism of 482 BC became a direct contest between Themistocles and Aristides. In what Holland characterises as, in essence, the world's first referendum, Aristides was ostracised, and Themistocles's policies were endorsed. Indeed, becoming aware of the Persian preparations for the coming invasion, the Athenians voted to build more ships than Themistocles had asked for. In the run up to the Persian invasion, Themistocles had thus become the leading politician in Athens.
Sparta
The Spartan king DemaratusDemaratus
Demaratus was a king of Sparta from 515 until 491 BC, of the Eurypontid line, successor to his father Ariston. As king, he is known chiefly for his opposition to the other, co-ruling Spartan king, Cleomenes I.-Biography:...
had been stripped of his kingship in 491 BC, and replaced with his cousin Leotychides. Sometime after 490 BC, the humiliated Demaratus had chosen to go into exile, and had made his way to Darius's court in Susa
Susa
Susa was an ancient city of the Elamite, Persian and Parthian empires of Iran. It is located in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris River, between the Karkheh and Dez Rivers....
. Demaratus would from then on act as an advisor to Darius, and later Xerxes, on Greek affairs, and accompanied Xerxes during the second Persian invasion. At the end of Herodotus's book 7, there is an anecdote relating that in the run-up to the second invasion, Demaratus sent an apparently blank wax tablet to Sparta. When the wax was removed, a message was found scratched on the wooden backing, warning the Spartans of Xerxes's plans. However, many historians believe that this chapter was inserted into the text by a later author, possibly to fill a gap
Lacuna (manuscripts)
A lacunaPlural lacunae. From Latin lacūna , diminutive form of lacus . is a gap in a manuscript, inscription, text, painting, or a musical work...
between the end of book 7 and the start of book 8. The veracity of this anecdote is therefore unclear.
Hellenic alliance
In 481 BC, Xerxes sent ambassadors around Greece asking for earth and water, but deliberately bypassed Athens and Sparta. Support thus began to coalesce around these two states. A congress of states met at CorinthCorinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
in late autumn of 481 BC, and a confederate alliance of Greek city-states
History of Greece
The history of Greece encompasses the history of the territory of the modern state of Greece, as well as that of the Greek people and the areas they ruled historically. The scope of Greek habitation and rule has varied much through the ages, and, as a result, the history of Greece is similarly...
was formed. This confederation had the power to send envoys asking for assistance and to dispatch troops from the member states to defensive points after joint consultation. Herodotus does not formulate an abstract name for the union but simply calls them "" (the Greeks) and "the Greeks who had sworn alliance" (Godley translation) or "the Greeks who had banded themselves together" (Rawlinson translation). From now on, they will be referred to as the 'Allies'. Sparta and Athens had a leading role in the congress but the interests of all the states played a part in determining defensive strategy. Little is known about the internal workings of the congress or the discussions during its meetings. Only 70 of the nearly 700 Greek city-states sent representatives. Nevertheless, this was remarkable for the disjointed Greek world, especially since many of the city-states present were still technically at war with one another.
Second invasion of Greece (480–479 BC)
Early 480 BC: Thrace, Macedonia and Thessaly
Having crossed into Europe in April 480 BC, the Persian army began its march to Greece, taking 3 months to travel unopposed from the Hellespont to Therme. It paused at DoriskosDoriskos
Doriskos was an ancient Greek city located in Thrace, located in the region between the river Nestos to the river Hebros. It was a fortified stronghold located in the homonymous plain and beach extending west of the Hebros delta and east of the peraia of Samothrace, actually located in the river...
where it was joined by the fleet. Xerxes reorganized the troops into tactical units replacing the national formations used earlier for the march.

Vale of Tempe
The Vale of Tempe is a gorge in northern Thessaly, Greece, located between Olympus to the north and Ossa to the south. The valley is 10 kilometers long and as narrow as 25 meters in places, with cliffs nearly 500 meters high, and through it flows the Pineios River on its way to the Aegean Sea...
on the borders of Thessaly and block Xerxes's advance. However, once there, they were warned by Alexander I of Macedon
Alexander I of Macedon
- Biography :Alexander was the son of Amyntas I and Queen Eurydice.According to Herodotus, he was unfriendly to Persia, and had the envoys of Darius I killed when they arrived at the court of his father during the Ionian Revolt...
that the vale could be bypassed and that the army of Xerxes was overwhelmingly large, thus the Greeks retreated. Shortly afterwards, they received the news that Xerxes had crossed the Hellespont. At this point, a second strategy was suggested by Themistocles to the allies. The route to southern Greece (Boeotia
Boeotia
Boeotia, also spelled Beotia and Bœotia , is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. It was also a region of ancient Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, the second largest city being Thebes.-Geography:...
, Attica
Attica
Attica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
and the Peloponnesus) would require the army of Xerxes to travel through the narrow pass of Thermopylae
Thermopylae
Thermopylae is a location in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur springs. "Hot gates" is also "the place of hot springs and cavernous entrances to Hades"....
. This could easily be blocked by the Greek hoplites, despite the overwhelming numbers of Persians. Furthermore, to prevent the Persians bypassing Thermopylae by sea, the Athenian and allied navies could block the straits of Artemisium
Artemisium
Artemisium is a cape north of Euboea, Greece. The legendary hollow cast bronze statue of a debatable Zeus or Poseidon was found off this cape in a sunken ship.-See also:* Temple of Artemis...
. This dual strategy was adopted by the congress. However, the Peloponnesian cities made fall-back plans to defend the Isthmus of Corinth
Isthmus of Corinth
The Isthmus of Corinth is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The word "isthmus" comes from the Ancient Greek word for "neck" and refers to the narrowness of the land. The Isthmus was known in the ancient...
should it come to it, while the women and children of Athens were evacuated to the Peloponnesian city of Troezen
Troezen
Troezen is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Troizinia, of which it is a municipal unit....
.
August 480 BC: Battles of Thermopylae and Artemisium
Xerxes's estimated time of arrival at Thermopylae coincided with both the Olympic Games and the festival of Carneia. For the Spartans, warfare during these periods was considered sacrilegious. Despite the uncomfortable timing, the Spartans considered the threat so grave that they dispatched their king Leonidas ILeonidas I
Leonidas I was a hero-king of Sparta, the 17th of the Agiad line, one of the sons of King Anaxandridas II of Sparta, who was believed in mythology to be a descendant of Heracles, possessing much of the latter's strength and bravery...
with his personal bodyguard (the Hippeis) of 300 men. The customary elite young men in the Hippeis were replaced by veterans who already had children. Leonidas was supported by contingents from the Allied Peloponnesian cities, and other forces that the Allies picked up on the way to Thermopylae. The Allies proceeded to occupy the pass, rebuilt the wall the Phocians had built at the narrowest point of the pass, and waited for Xerxes's arrival.

Hoplite
A hoplite was a citizen-soldier of the Ancient Greek city-states. Hoplites were primarily armed as spearmen and fought in a phalanx formation. The word "hoplite" derives from "hoplon" , the type of the shield used by the soldiers, although, as a word, "hopla" could also denote weapons held or even...
warfare, the Persian contingents being forced to attack the Greek phalanx
Phalanx formation
The phalanx is a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar weapons...
head on. The Allies withstood two full days of Persian attacks, including those by the elite Persian Immortals
Persian Immortals
The "Immortals" was the name given by Herodotus to an elite force of soldiers who fought for the Achaemenid Empire. This force performed the dual roles of both Imperial Guard and standing army during the Persian Empire's expansion and during the Greco-Persian Wars...
. However, towards the end of the second day, they were betrayed by a local resident named Ephialtes who revealed to Xerxes a mountain path that led behind the Allied lines. Made aware by scouts that they were being outflanked, Leonidas dismissed most of the Allied army, remaining to guard the rear with perhaps 2,000 men. On the final day of the battle, the remaining Allies sallied forth from the wall to meet the Persians in the wider part of the pass to slaughter as many Persians as they could, but eventually they were all killed or captured.
Simultaneous with the battle at Thermopylae, an Allied naval force of 271 triremes defended the Straits of Artemisium
Artemisium
Artemisium is a cape north of Euboea, Greece. The legendary hollow cast bronze statue of a debatable Zeus or Poseidon was found off this cape in a sunken ship.-See also:* Temple of Artemis...
against the Persians, thus protecting the flank of the forces at Thermopylae. Here the Allied fleet held off the Persians for three days; however, on the third evening the Allies received news of the fate of Leonidas and the Allied troops at Thermopylae. Since the Allied fleet was badly damaged, and since it no longer needed to defend the flank of Thermopylae, the Allies retreated from Artemisium to the island of Salamis
Salamis Island
Salamis , is the largest Greek island in the Saronic Gulf, about 1 nautical mile off-coast from Piraeus and about 16 km west of Athens. The chief city, Salamina , lies in the west-facing core of the crescent on Salamis Bay, which opens into the Saronic Gulf...
.
September 480 BC: Battle of Salamis
Victory at Thermopylae meant that all BoeotiaBoeotia
Boeotia, also spelled Beotia and Bœotia , is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. It was also a region of ancient Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, the second largest city being Thebes.-Geography:...
fell to Xerxes; and left Attica open to invasion. The remaining population of Athens was evacuated, with the aid of the Allied fleet, to Salamis. The Peloponnesian Allies began to prepare a defensive line across the Isthmus of Corinth
Isthmus of Corinth
The Isthmus of Corinth is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The word "isthmus" comes from the Ancient Greek word for "neck" and refers to the narrowness of the land. The Isthmus was known in the ancient...
, building a wall, and demolishing the road from Megara
Megara
Megara is an ancient city in Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being taken by Athens. Megara was one of the four districts of Attica, embodied in the four mythic sons of King...
, abandoning Athens to the Persians. Athens thus fell to the Persians; the small number of Athenians who had barricaded themselves on the Acropolis
Acropolis
Acropolis means "high city" in Greek, literally city on the extremity and is usually translated into English as Citadel . For purposes of defense, early people naturally chose elevated ground to build a new settlement, frequently a hill with precipitous sides...
were eventually defeated, and Xerxes then ordered Athens to be razed.

According to Herodotus, after the loss of the battle Xerxes attempted to build a causeway across the channel to attack the Athenian evacuees on Salamis, but this project was soon abandoned. With the Persians' naval superiority removed, Xerxes feared that the Allies might sail to the Hellespont and destroy the pontoon bridges. His general Mardonius volunteered to remain in Greece and complete the conquest with a hand-picked group of troops, while Xerxes retreated to Asia with the bulk of the army. Mardonius over-wintered in Boeotia and Thessaly; the Athenians were thus able to return to their burnt-out city for the winter.
June 479 BC: Battles of Plataea and Mycale
Over the winter, there was some tension between the Allies. In particular, the Athenians, who were not protected by the Isthmus, but whose fleet was the key to the security of the Peloponnesus, felt hard done by, and refused to join the Allied navy in Spring. MardoniusMardonius
Mardonius was a leading Persian military commander during the Persian Wars with Greece in the early 5th century BC.-Early years:Mardonius was the son of Gobryas, a Persian nobleman who had assisted the Achaemenid prince Darius when he claimed the throne...
remained in Thessaly, knowing an attack on the Isthmus was pointless, while the Allies refused to send an army outside the Peloponessus. Mardonius moved to break the stalemate, by offering peace to the Athenians, using Alexander I of Macedon
Alexander I of Macedon
- Biography :Alexander was the son of Amyntas I and Queen Eurydice.According to Herodotus, he was unfriendly to Persia, and had the envoys of Darius I killed when they arrived at the court of his father during the Ionian Revolt...
as an intermediate. The Athenians made sure that a Spartan delegation was on hand to hear the offer, but rejected it. Athens was thus evacuated again, and the Persians marched south and re-took possession of it. Mardonius now repeated his offer of peace to the Athenian refugees on Salamis. Athens, with Megara
Megara
Megara is an ancient city in Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being taken by Athens. Megara was one of the four districts of Attica, embodied in the four mythic sons of King...
and Plataea
Plataea
Plataea or Plataeae was an ancient city, located in Greece in southeastern Boeotia, south of Thebes. It was the location of the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC, in which an alliance of Greek city-states defeated the Persians....
, sent emissaries to Sparta demanding assistance, and threatening to accept the Persian terms if they were not aided. In response, the Spartans summonded a large army from the Peloponnese cities and marched to meet the Persians.
When Mardonius heard the Allied army was on the march, he retreated into Boeotia, near Plataea
Plataea
Plataea or Plataeae was an ancient city, located in Greece in southeastern Boeotia, south of Thebes. It was the location of the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC, in which an alliance of Greek city-states defeated the Persians....
, trying to draw the Allies into open terrain where he could use his cavalry. The Allied army, under the command of the regent Pausanias
Pausanias (general)
Pausanias was a Spartan general of the 5th century BC. He was the son of Cleombrotus and nephew of Leonidas I, serving as regent after the latter's death, since Leonidas' son Pleistarchus was still under-age. Pausanias was also the father of Pleistoanax, who later became king, and Cleomenes...
, stayed on high ground above Plataea to protect themselves against such tactics. After several days of maneuver and stalemate, Pausanias ordered a night-time retreat towards the Allies' original positions. This maneuver went awry, leaving the Athenians, and Spartans and Tegeans isolated on separate hills, with the other contingents scattered further away near Plataea. Seeing that the Persians might never have a better opportunity to attack, Mardonius ordered his whole army forward. However, the Persian infantry proved no match for the heavily armoured Greek hoplites, and the Spartans broke through to Mardonius's bodyguard and killed him. After this the Persian force dissolved in rout; 40,000 troops managed to escape via the road to Thessaly, but the rest fled to the Persian camp where they were trapped and slaughtered by the Greeks, finalising the Greek victory.
Herodotus recounts that, on the afternoon of the Battle of Plataea
Battle of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states, including Sparta, Athens, Corinth and Megara, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes...
, a rumour of their victory at that battle reached the Allies' navy, at that time off the coast of Mount Mycale
Mycale
Mycale, also Mykale and Mycali , called Samsun Daği and Dilek Daği in modern Turkey, is a mountain on the west coast of central Anatolia in Turkey, north of the mouth of the Maeander and divided from the Greek island of Samos by the 1300 metre wide Samos Strait...
in Ionia. Their morale boosted, the Allied marines fought and won a decisive victory at the Battle of Mycale
Battle of Mycale
The Battle of Mycale was one of the two major battles that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It took place on or about August 27, 479 BC on the slopes of Mount Mycale, on the coast of Ionia, opposite the island of Samos...
that same day, destroying the remnants of the Persian fleet, crippling Xerxes' sea power, and marking the ascendancy of the Greek fleet. Whilst many modern historians doubt that Mycale took place on the same day as Plataea, the battle may well only have occurred once the Allies received news of the events unfolding in Greece.
Mycale and Ionia
Mycale was, in many ways, the beginning of a new phase in the conflict, in which the Greeks would go on the offensive against the Persians. The immediate result of the victory at Mycale a second revolt amongst the Greek cities of Asia Minor. The Samians and Milesians had actively fought against the Persians at Mycale, thus openly declaring their rebellion, and the other cities followed in their example.Sestos
Shortly after Mycale, the Allied fleet sailed to the Hellespont to break down the pontoon bridges, but found that this had already been done. The Peloponnesians sailed home, but the Athenians remained to attack the ChersonesosThracian Chersonese
The Thracian Chersonese was the ancient name of the Gallipoli peninsula, in the part of historic Thrace that is now part of modern Turkey.The peninsula runs in a south-westerly direction into the Aegean Sea, between the Hellespont and the bay of Melas . Near Agora it was protected by a wall...
, still held by the Persians. The Persians and their allies made for Sestos
Sestos
200px|200px|thumb|The Ancient Map of Gallipoli PeninsulaSestos was an ancient Greek town of the Thracian Chersonese, the modern Gallipoli peninsula in European Turkey. Situated on the Hellespont opposite Abydos, it was the home of Hero in the legend of Hero and Leander, where according to legend...
, the strongest town in the region. Amongst them was one Oeobazus of Cardia
Cardia (Thrace)
Cardia , anciently the chief town of the Thracian Chersonese , was situated at the head of the gulf of Melas...
, who had with him the cables and other equipment from the pontoon bridges. The Persian governor, Artayctes
Artayctes
Artaÿctes is a historical figure described in Herodotus' The Histories. According to Herodotus, Artayctes was a Persian General, who was in command of the Mossonoikan and Makronian forces in the army of Xerxes during the second Persian invasion of Greece...
had not prepared for a siege, not believing that the Allies would attack. The Athenians therefore were able to lay a siege around Sestos. The siege dragged on for several months, causing some discontent amongst the Athenian troops, but eventually, when the food ran out in the City, the Persians fled at night from the least guarded area of the city. The Athenians were thus able to take possession of the city the next day.
Most of the Athenian troops were sent straight away to pursue the Persians. The party of Oeobazus was captured by a Thracian tribe, and Oeobazus was sacrificed to the god Plistorus. The Athenians eventually caught Artayctes, killing some of the Persians with him but taking most of them, including Artayctes, captive. Artayctes was crucified at the request of the people of Elaeus
Elaeus
Elaeus is a Greek city in Thracian Chersonese, a colony of Ionian Teos, hometown of the mythological hero Protesilaus....
, a town which Artayctes had plundered while governor of the Chersonesos. The Athenians, having pacified the region, then sailed back to Athens, taking the cables from the pontoon bridges with them as trophies.
Cyprus
In 478 BC, still operating under the terms of the Hellenic alliance, the Allies sent out a fleet composed of 20 Peloponnesian and 30 Athenian ships supported by an unspecified number of allies, under the overall command of Pausanias. According to Thucydides, this fleet sailed to Cyprus and "subdued most of the island". Exactly what Thucydides means by this is unclear. Sealey suggests that this was essentially a raid to gather as much booty as possible from the Persian garrisons on Cyprus. There is no indication that the Allies attempted to take possession of the island, and, shortly after, they sailed to Byzantium. Certainly, the fact that the Delian League repeatedly campaigned in Cyprus suggests either that the island was not garrisoned by the Allies in 478 BC, or that the garrisons were quickly expelled.Byzantium
The Greek fleet then sailed to ByzantiumByzantium
Byzantium was an ancient Greek city, founded by Greek colonists from Megara in 667 BC and named after their king Byzas . The name Byzantium is a Latinization of the original name Byzantion...
, which they besieged and eventually captured. Control of both Sestos and Byzantium gave the allies command of the straits between Europe and Asia (over which the Persians had crossed), and allowed them access to the merchant trade of the Black Sea.
The aftermath of the siege was to prove troublesome for Pausanias. Exactly what happened is unclear; Thucydides gives few details, although later writers added plenty of lurid insinuations. Through his arrogance and arbitrary actions (Thucydides says "violence"), Pausanias managed to alienate many of the Allied contingents, particularly those that had just been freed from Persian overlordship. The Ionians and others asked the Athenians to take leadership of the campaign, to which they agreed. The Spartans, hearing of his behaviour, recalled Pausanias and tried him on charges of collaborating with the enemy. Although he was acquitted, his reputation was tarnished and he was not restored to his command.
Pausanias returned to Byzantium as a private citizen in 477 BC, and took command of the city until he was expelled by the Athenians. He then crossed the Bosporus
Bosporus
The Bosphorus or Bosporus , also known as the Istanbul Strait , is a strait that forms part of the boundary between Europe and Asia. It is one of the Turkish Straits, along with the Dardanelles...
and settled in Colonae in the Troad, until he was again accused of collaborating with the Persians and was recalled by the Spartans for a trial after which he starved himself to death. The timescale is unclear, but Pausanias may have remained in possession of Byzantium until 470 BC.
In the meantime, the Spartans had sent Dorkis to Byzantium with a small force, to take command of the Allied force. However, he found that the rest of the Allies were no longer prepared to accept Spartan leadership, and therefore returned home.
Delian League

Xanthippus
Xanthippus was a Greek mercenary general hired by the Carthaginians to aid in their war against the Romans during the First Punic War...
, the Athenian commander at Mycale, had furiously rejected this; the Ionian cities were originally Athenian colonies, and the Athenians, if no-one else, would protect the Ionians. This marks the point at which the leadership of the Greek Alliance effectively passed to the Athenians. With the Spartan withdrawal after Byzantium, the leadership of the Athenians became explicit.
The loose alliance of city-states that had fought against Xerxes's invasion had been dominated by Sparta and the Peloponnesian league. With the withdrawal of these states, a congress was called on the holy island of Delos
Delos
The island of Delos , isolated in the centre of the roughly circular ring of islands called the Cyclades, near Mykonos, is one of the most important mythological, historical and archaeological sites in Greece...
to institute a new alliance to continue the fight against the Persians. This alliance, now including many of the Aegean islands, was formally constituted as the
'First Athenian Alliance', commonly known as the Delian League
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in circa 477 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, members numbering between 150 to 173, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Greco–Persian Wars...
. According to Thucydides, the official aim of the League was to "avenge the wrongs they suffered by ravaging the territory of the king". In reality, this goal was divided into three main efforts—to prepare for future invasion, to seek revenge against Persia, and to organize a means of dividing spoils of war. The members were given a choice of either supplying armed forces or paying a tax to the joint treasury; most states chose the tax.
Campaigns against Persia

Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
, seeking to strengthen the Greek position there. At the Battle of the Eurymedon
Battle of the Eurymedon
The Battle of the Eurymedon was a double battle, taking place both on water and land, between the Delian League of Athens and her Allies, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. It took place in either 469 or 466 BC, in the vicinity of the mouth of the Eurymedon River in Pamphylia, Asia Minor...
in Pamphylia
Pamphylia
In ancient geography, Pamphylia was the region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus . It was bounded on the north by Pisidia and was therefore a country of small extent, having a coast-line of only about 75 miles with a breadth of...
, the Athenians and allied fleet achieved a stunning double victory, destroying a Persian fleet and then landing the ships' marines to attack and rout the Persian army. After this battle, the Persians took an essentially passive role in the conflict, anxious not to risk battle if possible.
Towards the end of the 460s BC, the Athenians took the ambitious decision to support a revolt in the Egyptian
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
satrapy of the Persian empire. Although the Greek task force achieved initial successes, they were unable to capture the Persian garrison in Memphis
Memphis, Egypt
Memphis was the ancient capital of Aneb-Hetch, the first nome of Lower Egypt. Its ruins are located near the town of Helwan, south of Cairo.According to legend related by Manetho, the city was founded by the pharaoh Menes around 3000 BC. Capital of Egypt during the Old Kingdom, it remained an...
, despite a 3-year long siege. The Persians then counterattacked, and the Athenian force was itself besieged for 18 months, before being wiped out. This disaster, coupled with ongoing warfare
First Peloponnesian War
The First Peloponnesian War was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War...
in Greece, dissuaded the Athenians from resuming conflict with Persia. In 451 BC however, a truce was agreed in Greece, and Cimon was then able to lead an expedition to Cyprus. However, while besieging Kition, Cimon died, and the Athenian force decided to withdraw, winning another double victory at the Battle of Salamis-in-Cyprus in order to extricate themselves. This campaign marked the end of hostilities between the Delian League and Persia, and therefore the end of the Greco-Persian Wars.
Peace with Persia
After the Battle of Salamis-in-Cyprus, Thucydides makes no further mention of conflict with the Persians, simply saying that the Greeks returned home. Diodorus, on the other hand, claims that in the aftermath of Salamis, a full-blown peace treaty (the "Peace of Callias") was agreed with the Persians. Diodorus was probably following the history of EphorusEphorus
Ephorus or Ephoros , of Cyme in Aeolia, in Asia Minor, was an ancient Greek historian. Information on his biography is limited; he was the father of Demophilus, who followed in his footsteps as a historian, and to Plutarch's claim that Ephorus declined Alexander the Great's offer to join him on his...
at this point, who in turn was presumably influenced by his teacher Isocrates
Isocrates
Isocrates , an ancient Greek rhetorician, was one of the ten Attic orators. In his time, he was probably the most influential rhetorician in Greece and made many contributions to rhetoric and education through his teaching and written works....
—from whom there is the earliest reference to the supposed peace, in 380 BC. Even during the 4th century BC, the idea of the treaty was controversial, and two authors from that period, Callisthenes
Callisthenes
Callisthenes of Olynthus was a Greek historian. He was the son of Hero and Proxenus of Atarneus, which made him the great nephew of Aristotle by his sister Arimneste. They first met when Aristotle tutored Alexander the Great...
and Theopompus
Theopompus
Theopompus was a Greek historian and rhetorician- Biography :Theopompus was born on Chios. In early youth he seems to have spent some time at Athens, along with his father, who had been exiled on account of his Laconian sympathies...
, appear to reject its existence.
It is possible that the Athenians had attempted to negotiate with the Persians previously. Plutarch suggests that in the aftermath of the victory at the Eurymedon, Artaxerxes had agreed a peace treaty with the Greeks, even naming Callias as the Athenian ambassador involved. However, as Plutarch admits, Callisthenes denied that such a peace was made at this point (ca. 466 BC). Herodotus also mentions, in passing, an Athenian embassy headed by Callias
Callias
Callias was the head of a wealthy Athenian family, and fought at the Battle of Marathon in priestly attire. His son, Hipponicus, was also a military commander...
, which was sent to Susa
Susa
Susa was an ancient city of the Elamite, Persian and Parthian empires of Iran. It is located in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris River, between the Karkheh and Dez Rivers....
to negotiate with Artaxerxes. This embassy included some Argive
Argos
Argos is a city and a former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. It is 11 kilometres from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour...
representatives and can probably be therefore dated to ca. 461 BC (after an alliance was agreed between Athens and Argos). This embassy may have been an attempt to reach some kind of peace agreement, and it has even been suggested that the failure of these hypothetical negotiations led to the Athenian decision to support the Egyptian revolt. The ancient sources therefore disagree as to whether there was an official peace or not, and, if there was, when it was agreed.
Opinion amongst modern historians is also split; for instance, Fine accepts the concept of the Peace of Callias, whereas Sealey effectively rejects it. Holland accepts that some kind of accommodation was made between Athens and Persia, but no actual treaty. Fine argues that Callisthenes's denial that a treaty was made after the Eurymedon does not preclude a peace being made at another point. Further, he suggests that Theopompus was actually referring to a treaty that had allegedly been negotiated with Persia in 423 BC. If these views are correct, it would remove one major obstacle to the acceptance of the treaty's existence. A further argument for the existence of the treaty is the sudden withdrawal of the Athenians from Cyprus in 449 BC, which Fine suggests makes most sense in the light of some kind of peace agreement. On the other hand, if there was indeed some kind of accommodation, Thucydides's failure to mention it is odd. In his digression on the pentekontaetia, his aim is to explain the growth of Athenian power, and such a treaty, and the fact that the Delian allies were not released from their obligations after it, would have marked a major step in the Athenian ascendancy. Conversely, it has been suggested that certain passages elsewhere in Thucydides's history are best interpreted as referring to a peace agreement. There is thus no clear consensus amongst modern historians as to the treaty's existence.
If the treaty did indeed exist, its terms were humiliating for Persia. The ancient sources that give details of the treaty are reasonably consistent in their description of the terms:
- All Greek cities of Asia were to 'live by their own laws' or 'be autonomous' (depending on translation).
- Persian satraps (and presumably their armies) were not to travel west of the Halys RiverHalys RiverThe Kızılırmak , also known as the Halys River , is the longest river in Turkey. It is a source of hydroelectric power and is not used for navigation.- Geography :...
(IsocratesIsocratesIsocrates , an ancient Greek rhetorician, was one of the ten Attic orators. In his time, he was probably the most influential rhetorician in Greece and made many contributions to rhetoric and education through his teaching and written works....
) or closer than a day's journey on horseback to the Aegean Sea (CallisthenesCallisthenesCallisthenes of Olynthus was a Greek historian. He was the son of Hero and Proxenus of Atarneus, which made him the great nephew of Aristotle by his sister Arimneste. They first met when Aristotle tutored Alexander the Great...
) or closer than three days' journey on foot to the Aegean Sea (EphorusEphorusEphorus or Ephoros , of Cyme in Aeolia, in Asia Minor, was an ancient Greek historian. Information on his biography is limited; he was the father of Demophilus, who followed in his footsteps as a historian, and to Plutarch's claim that Ephorus declined Alexander the Great's offer to join him on his...
and Diodorus). - No Persian warship was to sail west of PhaselisPhaselisPhaselis is an ancient Lycian city in the province of Antalya in Turkey. It is located between the Bey Mountains and the forests of Olympos National Park, 16 km west of the touristic town of Kemer and on the 57th kilometre of the Antalya–Kumluca highway...
(on the southern coast of Asia Minor), nor west of the Cyanaean rocks (probably at the eastern end of the BosporusBosporusThe Bosphorus or Bosporus , also known as the Istanbul Strait , is a strait that forms part of the boundary between Europe and Asia. It is one of the Turkish Straits, along with the Dardanelles...
, on the north coast). - If the terms were observed by the king and his generals, then the Athenians were not to send troops to lands ruled by Persia.
Aftermath and later conflicts
Towards the end of the conflict with Persia, the process by which the Delian LeagueDelian League
The Delian League, founded in circa 477 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, members numbering between 150 to 173, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Greco–Persian Wars...
became the Athenian Empire reached its conclusion. The allies of Athens were not released from their obligations to provide either money or ships, despite the cessation of hostilities. In Greece, the First Peloponnesian War
First Peloponnesian War
The First Peloponnesian War was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War...
between the power-blocs of Athens and Sparta, which had continued on/off since 460 BC, finally ended in 445 BC, with the agreement of a thirty-year truce. However, the growing enmity between Sparta and Athens would lead, just 14 years later, into the outbreak of the Second Peloponnesian War
Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War, 431 to 404 BC, was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases...
. This disastrous conflict, which dragged on for 27 years, would eventually result in the utter destruction of Athenian power, the dismemberment of the Athenian empire, and the establishment of a Spartan hegemony
Spartan hegemony
The city-state of Sparta was the greatest military land power of classical Greek antiquity. During the classical period, Sparta owned, dominated or influenced the entire Peloponnese. Additionally, the defeat of the Athenians and the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War in 431-404 BCE resulted in...
over Greece. However, not just Athens suffered—the conflict would significantly weaken the whole of Greece.
Repeatedly defeated in battle by the Greeks, and plagued by internal rebellions that hindered their ability to fight the Greeks, after 449 BC Artaxerxes I and his successors instead adopted a policy of divide-and-rule. Avoiding fighting the Greeks themselves, the Persians instead attempted to set Athens against Sparta, regularly bribing politicians to achieve their aims. In this way, they ensured that the Greeks remained distracted by internal conflicts, and were unable to turn their attentions to Persia. There was no open conflict between the Greeks and Persia until 396 BC, when the Spartan king Agesilaus
Agesilaus
Agesilaus was a Greek historian who wrote a work on the early history of Italy, fragments of which are preserved in Plutarch's "Parallel Lives", and in Stobaeus' Florilegium....
briefly invaded Asia Minor; as Plutarch points out, the Greeks were far too busy overseeing the destruction of their own power to fight against the "barbarians".
If the wars of the Delian League shifted the balance of power between Greece and Persia in favour of the Greeks, then the subsequent half-century of internecine conflict in Greece did much to restore the balance of power to Persia. The Persians entered the Peloponnesian War in 411 BC forming a mutual-defence pact with Sparta and combining their naval resources against Athens in exchange for sole Persian control of Ionia. In 404 BC when Cyrus the Younger
Cyrus the Younger
Cyrus the Younger, son of Darius II of Persia and Parysatis, was a Persian prince and general. The time of his birth is unknown, but he died in 401 B.C. The history of Cyrus and of the retreat of the Greeks is told by Xenophon in his Anabasis. Another account, probably from Sophaenetus of...
attempted to seize the Persian throne, he recruited 13,000 Greek mercenaries from all over the Greek world of which Sparta sent 700–800, believing they were following the terms of the treaty and unaware of the army's true purpose. After the failure of Cyrus, Persia tried to regain control of the Ionian city-states, which had rebelled during the conflict. The Ionians refused to capitulate and called upon Sparta for assistance, which she provided, in 396–395 BC. Athens, however, sided with the Persians, which led in turn to another large-scale conflict in Greece, the Corinthian War
Corinthian War
The Corinthian War was an ancient Greek conflict lasting from 395 BC until 387 BC, pitting Sparta against a coalition of four allied states; Thebes, Athens, Corinth, and Argos; which were initially backed by Persia. The immediate cause of the war was a local conflict in northwest Greece in which...
. Towards the end of that conflict, in 387 BC, Sparta sought the aid of Persia to shore up her position. Under the so-called "King's Peace"
Peace of Antalcidas
The Peace of Antalcidas , also known as the King's Peace, was a peace treaty guaranteed by the Persian King Artaxerxes II that ended the Corinthian War in ancient Greece. The treaty's alternate name comes from Antalcidas, the Spartan diplomat who traveled to Susa to negotiate the terms of the...
that brought the war to an end, Artaxerxes II demanded and received the return of the cities of Asia Minor from the Spartans, in return for which the Persians threatened to make war on any Greek state that did not make peace. This humiliating treaty, which undid all the Greek gains of the previous century, sacrificed the Greeks of Asia Minor so that the Spartans could maintain their hegemony over Greece. It is in the aftermath of this treaty that Greek orators began to refer to the Peace of Callias (whether fictional or not), as a counterpoint to the shame of the King's Peace, and a glorious example of the "good old days" when the Greeks of the Aegean had been freed from Persian rule by the Delian League. The final confrontation between the Greek world and Achaemenid Persia began just 53 years after that, with the army of Alexander the Great crossing into Asia, marking the beginning of what would result in the razing of Persepolis and the end of the Achaemenid Empire
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
.
Ancient sources
- HerodotusHerodotusHerodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
, The HistoriesHistories (Herodotus)The Histories of Herodotus is considered one of the seminal works of history in Western literature. Written from the 450s to the 420s BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, The Histories serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that...
(Godley translation, 1920)- Commentary:
- ThucydidesThucydidesThucydides was a Greek historian and author from Alimos. His History of the Peloponnesian War recounts the 5th century BC war between Sparta and Athens to the year 411 BC...
, History of the Peloponnesian WarHistory of the Peloponnesian WarThe History of the Peloponnesian War is an account of the Peloponnesian War in Ancient Greece, fought between the Peloponnesian League and the Delian League . It was written by Thucydides, an Athenian general who served in the war. It is widely considered a classic and regarded as one of the... - XenophonXenophonXenophon , son of Gryllus, of the deme Erchia of Athens, also known as Xenophon of Athens, was a Greek historian, soldier, mercenary, philosopher and a contemporary and admirer of Socrates...
, AnabasisAnabasis (Xenophon)Anabasis is the most famous work, in seven books, of the Greek professional soldier and writer Xenophon. The journey it narrates is his best known accomplishment and "one of the great adventures in human history," as Will Durant expressed the common assessment.- The account :Xenophon accompanied...
, Hellenica - PlutarchPlutarchPlutarch then named, on his becoming a Roman citizen, Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus , c. 46 – 120 AD, was a Greek historian, biographer, essayist, and Middle Platonist known primarily for his Parallel Lives and Moralia...
, Parallel LivesParallel LivesPlutarch's Lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans, commonly called Parallel Lives or Plutarch's Lives, is a series of biographies of famous men, arranged in tandem to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings, written in the late 1st century...
; Themistocles, Aristides, Pericles, Cimon - Diodorus SiculusDiodorus SiculusDiodorus Siculus was a Greek historian who flourished between 60 and 30 BC. According to Diodorus' own work, he was born at Agyrium in Sicily . With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about Diodorus' life and doings beyond what is to be found in his own work, Bibliotheca...
, Bibliotheca historicaBibliotheca historicaBibliotheca historica , is a work of universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, and describe the history and culture of Egypt , of Mesopotamia, India, Scythia, and Arabia , of North... - Cornelius NeposCornelius NeposCornelius Nepos was a Roman biographer. He was born at Hostilia, a village in Cisalpine Gaul not far from Verona. His Gallic origin is attested by Ausonius, and Pliny the Elder calls him Padi accola...
, Lives of the Eminent Commanders; Miltiades, Themistocles
Modern sources
- de Souza, Philip (2003). The Greek and Persian Wars, 499-386 BC. Osprey Publishing, (ISBN 1-84176-358-6)

