
Acetoacetyl-CoA
Encyclopedia
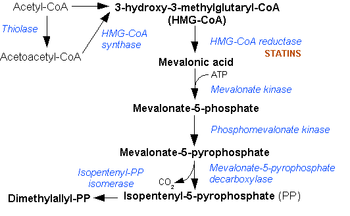
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA
in the Mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol synthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies
synthesis pathway of the liver
. In the ketone bodies
digestion pathway (in the tissue), it is no longer associated with having HMG-CoA
as a product or as a reactant.
It is created from acetyl-CoA
by thiolase
, and it is acted upon by HMG-CoA synthase
to form HMG-CoA
. (During the metabolism of leucine
, this last reaction is reversed.)
HMG-CoA
HMG-CoA is an intermediate in the Mevalonate pathway. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase.HMG-CoA reductase converts it into mevalonic acid....
in the Mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol synthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies
Ketone bodies
Ketone bodies are three water-soluble compounds that are produced as by-products when fatty acids are broken down for energy in the liver and kidney. They are used as a source of energy in the heart and brain. In the brain, they are a vital source of energy during fasting...
synthesis pathway of the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
. In the ketone bodies
Ketone bodies
Ketone bodies are three water-soluble compounds that are produced as by-products when fatty acids are broken down for energy in the liver and kidney. They are used as a source of energy in the heart and brain. In the brain, they are a vital source of energy during fasting...
digestion pathway (in the tissue), it is no longer associated with having HMG-CoA
HMG-CoA
HMG-CoA is an intermediate in the Mevalonate pathway. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase.HMG-CoA reductase converts it into mevalonic acid....
as a product or as a reactant.
It is created from acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl-CoA is an important molecule in metabolism, used in many biochemical reactions. Its main function is to convey the carbon atoms within the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. In chemical structure, acetyl-CoA is the thioester...
by thiolase
Thiolase
Thiolases also known as acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferases are enzymes which converts two units of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl CoA in the mevalonate pathway....
, and it is acted upon by HMG-CoA synthase
HMG-CoA synthase
In molecular biology, HMG-CoA synthase is an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction in which Acetyl-CoA condenses with acetoacetyl-CoA to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA . It is the second reaction in the mevalonate-dependent isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. HMG-CoA is an intermediate in both...
to form HMG-CoA
HMG-CoA
HMG-CoA is an intermediate in the Mevalonate pathway. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase.HMG-CoA reductase converts it into mevalonic acid....
. (During the metabolism of leucine
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
, this last reaction is reversed.)

See also
- Beta-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase

