
Ketone bodies
Encyclopedia
By-product
A by-product is a secondary product derived from a manufacturing process or chemical reaction. It is not the primary product or service being produced.A by-product can be useful and marketable or it can be considered waste....
s when fatty acids are broken down for energy in the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
and kidney
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
. They are used as a source of energy in the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
and brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
. In the brain, they are a vital source of energy during fasting
Fasting
Fasting is primarily the act of willingly abstaining from some or all food, drink, or both, for a period of time. An absolute fast is normally defined as abstinence from all food and liquid for a defined period, usually a single day , or several days. Other fasts may be only partially restrictive,...
. Although termed "bodies", they are dissolved substances, not particles.
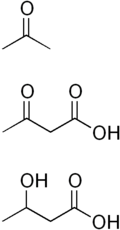
The three endogenous ketone bodies are acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
, acetoacetic acid
Acetoacetic acid
Acetoacetic acid is the organic compound with the formula CH3CCH2CO2H. It is the simplest beta-keto acid group and like other members of this class is unstable.- Synthesis and properties :...
, and beta-hydroxybutyric acid, although beta-hydroxybutyric acid is not technically a ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
but a carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
. Other ketone bodies such as beta-ketopentanoate and beta-hydroxypentanoate may be created as a result of the metabolism of synthetic triglycerides such as triheptanoin
Triheptanoin
Triheptanoin is triglyceride that is composed of three seven-carbon fatty acids. These odd-carbon fatty acids are able to provide anaplerotic substrates for the TCA cycle. Triheptanoin is used clinically in humans to treat inherited metabolic diseases, such as pyruvate carboxylase deficiency and...
.
Uses in the heart and brain
Ketone bodies can be used for energy. Ketone bodies are transported from the liverLiver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
to other tissues, where acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate
Beta-hydroxybutyrate
beta-Hydroxybutyric acid is a ketone body. It is a chiral compound having two enantiomers, D-3-hydroxybutyric acid and L-3-hydroxybutyric acid. Like the other ketone bodies , levels of beta-hydroxybutyrate are raised in ketosis...
can be reconverted to acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl-CoA is an important molecule in metabolism, used in many biochemical reactions. Its main function is to convey the carbon atoms within the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. In chemical structure, acetyl-CoA is the thioester...
to produce energy, via the citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
.
The heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
gets little energy from ketone bodies except under special circumstances; it uses mainly fatty acids.
The brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
gets a portion of its energy from ketone bodies when glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
is less available (e.g., during fasting
Fasting
Fasting is primarily the act of willingly abstaining from some or all food, drink, or both, for a period of time. An absolute fast is normally defined as abstinence from all food and liquid for a defined period, usually a single day , or several days. Other fasts may be only partially restrictive,...
, strenuous exercise, low carbohydrate, ketogenic diet
Ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate diet that in medicine is used primarily to treat difficult-to-control epilepsy in children. The diet mimics aspects of starvation by forcing the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates...
and in neonates). In the event of low blood glucose
Blood sugar
The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose level is the amount of glucose present in the blood of a human or animal. Normally in mammals, the body maintains the blood glucose level at a reference range between about 3.6 and 5.8 mM , or 64.8 and 104.4 mg/dL...
, most other tissues have additional energy sources besides ketone bodies (such as fatty acids), but the brain does not. After the diet has been changed to lower blood glucose for 3 days, the brain gets 25% of its energy from ketone bodies. After about 4 days, this goes up to 70% (during the initial stages the brain does not burn ketones, since they are an important substrate for lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
synthesis in the brain).
Production

Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl-CoA is an important molecule in metabolism, used in many biochemical reactions. Its main function is to convey the carbon atoms within the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. In chemical structure, acetyl-CoA is the thioester...
(see ketogenesis
Ketogenesis
Ketogenesis is the process by which ketone bodies are produced as a result of fatty acid breakdown.-Production:Ketone bodies are produced mainly in the mitochondria of liver cells. Its synthesis occurs in response to low glucose levels in the blood, and after exhaustion of cellular carbohydrate...
) mainly in the mitochondrial matrix of hepatocyte
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 70-80% of the liver's cytoplasmic mass.These cells are involved in:* Protein synthesis* Protein storage* Transformation of carbohydrates...
s when carbohydrate
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
s are so scarce that energy must be obtained from breaking down fatty acid
Fatty acid metabolism
Fatty acids are an important source of energy and adenosine triphosphate for many cellular organisms. Excess fatty acids, glucose, and other nutrients can be stored efficiently as fat. Triglycerides yield more than twice as much energy for the same mass as do carbohydrates or proteins. All cell...
s. Because of the high level of acetyl CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl-CoA is an important molecule in metabolism, used in many biochemical reactions. Its main function is to convey the carbon atoms within the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. In chemical structure, acetyl-CoA is the thioester...
present in the cell, the pyruvate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a complex of three enzymes that transform pyruvate into acetyl-CoA by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. Acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration, and this complex links the glycolysis metabolic pathway to the...
complex is inhibited, whereas pyruvate carboxylase
Pyruvate carboxylase
Pyruvate carboxylase is an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate .It is an important anaplerotic reaction that creates oxaloacetate from pyruvate...
becomes activated. Thus, the oxaloacetate produced will enter gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids....
rather than the citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
, as the latter is also inhibited by the elevated level of NADH resulting from ß-oxidation of fatty acids. The excess acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl-CoA is an important molecule in metabolism, used in many biochemical reactions. Its main function is to convey the carbon atoms within the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. In chemical structure, acetyl-CoA is the thioester...
is therefore rerouted to ketogenesis
Ketogenesis
Ketogenesis is the process by which ketone bodies are produced as a result of fatty acid breakdown.-Production:Ketone bodies are produced mainly in the mitochondria of liver cells. Its synthesis occurs in response to low glucose levels in the blood, and after exhaustion of cellular carbohydrate...
. Such a state in humans is referred to as the fasted state.
Acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
is produced by spontaneous decarboxylation
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that releases carbon dioxide . Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carbonation, the addition of CO2 to...
of acetoacetate, yielding levels of acetone much lower than those of other ketone bodies. Acetone cannot be converted back to acetyl-CoA, so it is excreted in the urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
, or (as a consequence of its high vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
) exhaled. Acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
is responsible for the characteristic "fruity" odor of the breath of persons in ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state associated with high concentrations of ketone bodies, formed by the breakdown of fatty acids and the deamination of amino acids. The two common ketones produced in humans are acetoacetic acid and β-hydroxybutyrate....
.
Ketosis and ketoacidosis
Any production of these compounds is called ketogenesisKetogenesis
Ketogenesis is the process by which ketone bodies are produced as a result of fatty acid breakdown.-Production:Ketone bodies are produced mainly in the mitochondria of liver cells. Its synthesis occurs in response to low glucose levels in the blood, and after exhaustion of cellular carbohydrate...
, and this is necessary in small amounts.
However, when excess ketone bodies accumulate, this abnormal state is called ketosis
Ketosis
Ketosis is a state of elevated levels of ketone bodies in the body. It is almost always generalized throughout the body, with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when the liver glycogen stores are depleted...
. Ketosis can be quantified by sampling the patient's exhaled air, and testing for acetone by gas chromatography. Many diabetics self test for the presence of ketones using blood or urine testing kits.
When even larger amounts of ketone bodies accumulate such that the blood's pH is lowered to dangerously acidic levels, this state is called ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state associated with high concentrations of ketone bodies, formed by the breakdown of fatty acids and the deamination of amino acids. The two common ketones produced in humans are acetoacetic acid and β-hydroxybutyrate....
.
Impact upon pH
Both acetoacetic acid and beta-hydroxybutyric acid are acidAcid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
ic, and, if levels of these ketone bodies are too high, the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
of the blood drops, resulting in ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state associated with high concentrations of ketone bodies, formed by the breakdown of fatty acids and the deamination of amino acids. The two common ketones produced in humans are acetoacetic acid and β-hydroxybutyrate....
.
This happens most often in untreated Type I diabetes, and somewhat less often in Type II (see diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a potentially life-threatening complication in patients with diabetes mellitus. It happens predominantly in those with type 1 diabetes, but it can occur in those with type 2 diabetes under certain circumstances...
).
External links
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis- Fat metabolism at unisanet.unisa.edu.au
- NHS Direct Online Health Encyclopaedia, Ketosis
- BioCarta Pathways Formation of Ketone Bodies

