
Administrative divisions of the Philippines
Encyclopedia
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
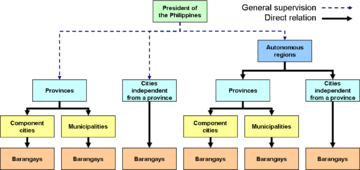
is divided into, from the highest division to the lowest:
- Autonomous regionRegions of the PhilippinesIn the Philippines, regions are administrative divisions that serve primarily to organize the provinces of the country for administrative convenience. Currently, the archipelagic republic of the Philippines is divided into 17 regions...
s- Regular administrative regions do not have political power.
- ProvincesProvinces of the PhilippinesThe Provinces of the Philippines are the primary political and administrative divisions of the Philippines. There are 80 provinces at present, further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are autonomous from any provincial...
and independent citiesCities of the PhilippinesA city is a tier of local government in the Philippines. All Philippine cities are chartered cities, whose existence as corporate and administrative entities is governed by their own specific charters in addition to the Local Government Code of 1991, which specifies the administrative structure... - MunicipalitiesMunicipalities of the PhilippinesA municipality is a local government unit in the Philippines. Municipalities are also called towns . They are distinct from cities, which are a different category of local government unit...
and component cities - BarangayBarangayA barangay is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines and is the native Filipino term for a village, district or ward...
s
Each division at each level from the provinces down to the barangays is a local government unit (LGU). For administrative purposes, the provinces
Provinces of the Philippines
The Provinces of the Philippines are the primary political and administrative divisions of the Philippines. There are 80 provinces at present, further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are autonomous from any provincial...
and cities
Cities of the Philippines
A city is a tier of local government in the Philippines. All Philippine cities are chartered cities, whose existence as corporate and administrative entities is governed by their own specific charters in addition to the Local Government Code of 1991, which specifies the administrative structure...
are grouped into regions
Regions of the Philippines
In the Philippines, regions are administrative divisions that serve primarily to organize the provinces of the country for administrative convenience. Currently, the archipelagic republic of the Philippines is divided into 17 regions...
. The President
President of the Philippines
The President of the Philippines is the head of state and head of government of the Philippines. The president leads the executive branch of the Philippine government and is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces of the Philippines...
has the prerogative to create, abolish and determine the composition of regions, which is done so most often in consultation with the local government units affected; with the exception of autonomous regions, where the residents of the local government units have to ratify in a plebiscite their inclusion in such a setup.
Other political divisions exist for the other branches of government:
- Legislative districts for the House of RepresentativesHouse of Representatives of the PhilippinesThe House of Representatives of the Philippines is the lower chamber of the...
- Judicial regions for the Regional Trial Courts.
Provinces
All regions except one (Metro Manila) are subdivided into provinces. Each province is headed by a governor. Its legislative body is the Sangguniang PanlalawiganSangguniang Panlalawigan
The Sangguniang Panlalawigan is the legislature of all provinces in the Philippines. It passes ordinances and resolutions for the effective administration of the province...
composed of the different members from Sanggunian districts, which in most cases are contiguous to the congressional districts.
Cities and municipalities
Regions, aside from having provinces may also have independent cities. Independent cities, classified either as highly urbanized or independent component cities, are cities which are not under the jurisdiction of a province. These cities are not administered by their mother provinces, do not share their tax revenues with the province, and in most cases their residents are not eligible to elect or be elected to provincial offices.Cities that are politically a part of a province are called component cities. The voters in these cities are allowed to vote and run for positions in the provincial government.
Municipalities are always components of a province, except Pateros, Metro Manila
Pateros, Metro Manila
The Municipality of Pateros is a First-class municipality in Metro Manila, Philippines. This small town is famous for its duck-raising industry and especially for producing balut, a Filipino delicacy that is boiled duck egg...
, which is independent.
Cities and municipalities are headed by a mayor. The legislative arm of these units are the Sangguniang Panlungsod
Sangguniang Panlungsod
The Sangguniang Panlungsod is the local legislative branch of city governments in the Philippines. The term is coined from the Tagalog words "sanggunian" and "lungsod" which means "city council". It passes ordinances and resolutions for the administration of the city. Its powers are defined by the...
for cities and Sangguniang Bayan
Sangguniang Bayan
The Sangguniang Bayan is the legislature of municipal governments in the Philippines. It passes ordinances and resolutions for the effective administration of the municipality...
for municipalities, which are composed of councilors elected at-large or in some cases, by Sanggunian district.
Barangays
Cities (both component and independent ones) and municipalities are further divided into barangays. The barangay is the smallest political unit. In some populous cities, barangays are grouped into zones and/or into districts for administrative purposes. In rural areas, sitioSitio
A sitio in the Philippines is a territorial enclave that forms part of a barangay, the location of which may be distant from the center of the barangay itself....
s or purok
Purok
Purok is a political subdivision of the barangay in the Philippines, especially in rural areas. Both barangay and SK councilors are in charge of leading their own respective puroks....
s are the preferred ways of subdividing barangays for administrative purposes. Each barangay is headed by a barangay captain.
Gated communities may either be a part of a barangay or a barangay itself. An example of a barangay coextensive with a gated community is Forbes Park, Makati City
Forbes Park, Makati City
Forbes Park, also known simply as Forbes, is a private subdivision and gated community in Makati City, Metro Manila, Philippines. Established in the 1940s, Forbes Park was named after William Cameron Forbes, an American Governor-General of the Philippines...
.
Other divisions
Regions
Regions are administrative groupings of provinces. All but one region do not have political power, but merely serve as administrative groupings of provinces. The Autonomous Region in Muslim MindanaoAutonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao
The Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao is the region, located in the Mindanao island group of the Philippines, that is composed of predominantly Muslim provinces, namely: Basilan , Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, Sulu and Tawi-Tawi. It is the only region that has its own government...
has political power, and is headed by a regional governor. If the Cordillera Administrative Region
Cordillera Administrative Region
The Cordillera Administrative Region is a region in the Philippines composed of the provinces of Abra, Apayao, Benguet, Ifugao, Kalinga and Mountain Province, as well as Baguio City, the regional center. The Cordillera Administrative Region encompasses most of the areas within the Cordillera...
becomes autonomous, it too, would have political power.
All but one region is divided into provinces. Metro Manila
Metro Manila
Metropolitan Manila , the National Capital Region , or simply Metro Manila, is the metropolitan region encompassing the City of Manila and its surrounding areas in the Philippines...
(the National Capital Region), due to its urban environment, is not divided into provinces, but instead is divided directly into cities and municipalities. The cities and municipalities of Metro Manila are grouped together into non-functional districts for administrative purposes.
The Supreme Court
Supreme Court of the Philippines
The Supreme Court of the Philippines is the Philippines' highest judicial court, as well as the court of last resort. The court consists of 14 Associate Justices and 1 Chief Justice...
has, in the past, ruled that a region must be composed of more than one province.
Legislative districts
In addition, the Philippines is also divided into legislative districts. The legislative districts may either be a single province, a group of cities and/or municipalities, a single city, or, in cases where a city has a large population, a group of barangays.The purpose of legislative districts is for the election of representatives to the House of Representatives
House of Representatives of the Philippines
The House of Representatives of the Philippines is the lower chamber of the...
, and in most instances, also representatives to the Sangguniang Panlalawigan
Sangguniang Panlalawigan
The Sangguniang Panlalawigan is the legislature of all provinces in the Philippines. It passes ordinances and resolutions for the effective administration of the province...
(provincial council) or Sangguniang Panlungsod
Sangguniang Panlungsod
The Sangguniang Panlungsod is the local legislative branch of city governments in the Philippines. The term is coined from the Tagalog words "sanggunian" and "lungsod" which means "city council". It passes ordinances and resolutions for the administration of the city. Its powers are defined by the...
(city council). Legislative districts exercise no administrative functions.
If a province or a city is composed of only one legislative district, it said to be the lone district (for example, the "Lone district of Muntinlupa City").
Judicial regions
The Philippines is divided into thirteen judicial regions, for the purpose of organizing the judicial hierarchy. The judicial regions still reflect the original regional configuration as introduced by former President MarcosFerdinand Marcos
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos, Sr. was a Filipino leader and an authoritarian President of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He was a lawyer, member of the Philippine House of Representatives and a member of the Philippine Senate...
.
Statistics
Here is table showing number of current provinces, municipalities, and cities of Philippines.| Type | Head of Administration | Filipino Title | Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Province Provinces of the Philippines The Provinces of the Philippines are the primary political and administrative divisions of the Philippines. There are 80 provinces at present, further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are autonomous from any provincial... |
Governor | Gobernador | 79 |
| Municipality Municipalities of the Philippines A municipality is a local government unit in the Philippines. Municipalities are also called towns . They are distinct from cities, which are a different category of local government unit... |
Mayor | Alkalde | 1514 |
| City Cities of the Philippines A city is a tier of local government in the Philippines. All Philippine cities are chartered cities, whose existence as corporate and administrative entities is governed by their own specific charters in addition to the Local Government Code of 1991, which specifies the administrative structure... |
Mayor | Alkalde | 136 |
See also
- Local government in the PhilippinesLocal government in the PhilippinesLocal government in the Philippines is divided into four levels:#Autonomous regions#Provinces and cities independent from a province#Component cities and municipalities#Barangays...
- Roman Catholic ChurchRoman Catholic ChurchThe Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
- List of the Roman Catholic dioceses of the Philippines

