Admittance parameters
Encyclopedia
Admittance parameters or Y-parameters (the elements of an admittance matrix or Y-matrix) are properties used in electrical engineering
, electronic engineering
, and communication systems
engineering describe the electrical behavior of linear
electrical network
s. They are also used to describe the small-signal (linearized
) response of non-linear networks. They are members of a family of similar parameters used in electronic engineering, other examples being: S-parameters, Z-parameters, H-parameters, T-parameters or ABCD-parameters.
with a number of ports. A port in this context is a pair of electrical terminals
carrying equal and opposite currents into and out-of the network, and having a particular voltage
between them. The Y-matrix gives no information about the behaviour of the network when the currents at any port are not balanced in this way (should this be possible), nor does it give any information about the voltage between terminals not belonging to the same port. Typically, it is intended that each external connection to the network is between the terminals of just one port, so that these limitations are appropriate.
For a generic multi-port network definition, it is assumed that each of the ports is allocated an integer n ranging from 1 to N, where N is the total number of ports. For port n, the associated Y-parameter definition is in terms of input voltages and output currents,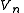 and
and 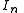 respectively.
respectively.
For all ports the output currents may be defined in terms of the Y-parameter matrix and the input voltages by the following matrix equation:
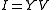
where Y is an N × N matrix the elements of which can be indexed using conventional matrix
notation. In general the elements of the Y-parameter matrix are complex number
s and functions of frequency. For a one-port network, the Y-matrix reduces to a single element, being the ordinary admittance
measured between the two terminals.
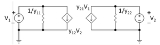
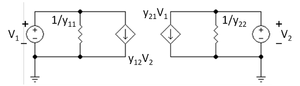 The Y-parameter matrix for the two-port network
The Y-parameter matrix for the two-port network
is probably the most common. In this case the relationship between the input voltages, output currents and the Y-parameter matrix is given by:
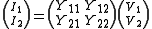 .
.
where
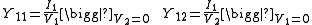
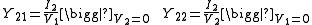
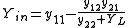
where YL is the admittance of the load connected to port two.
Similarly, the output admittance is given by:
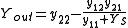
where YS is the admittance of the source connected to port one.
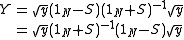
and
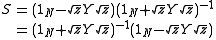
where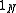 is the identity matrix
is the identity matrix
,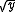 is a diagonal matrix
is a diagonal matrix
having the square root of the characteristic admittance (the reciprocal of the characteristic impedance
) at each port as its non-zero elements,
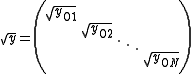
and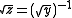 is the corresponding diagonal matrix of square roots of characteristic impedance
is the corresponding diagonal matrix of square roots of characteristic impedance
s. In these expressions the matrices represented by the bracketed factors commute
and so, as shown above, may be written in either order.Any square matrix commutes with itself and with the identity matrix, and if two matrices A and B commute, then so do A and B-1 (since AB-1 = B-1BAB-1 = B-1ABB-1 = B-1A)
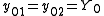 at each port, the above expressions reduce to
at each port, the above expressions reduce to
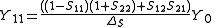
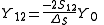
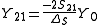
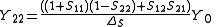
Where
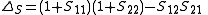
The above expressions will generally use complex numbers for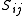 and
and 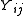 . Note that the value of
. Note that the value of 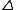 can become 0 for specific values of
can become 0 for specific values of 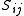 so the division by
so the division by 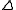 in the calculations of
in the calculations of 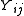 may lead to a division by 0.
may lead to a division by 0.
The two-port S-parameters may also be obtained from the equivalent two-port Y-parameters by means of the following expressions.
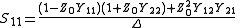
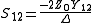
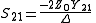
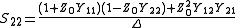
where
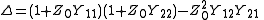
and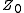 is the characteristic impedance
is the characteristic impedance
at each port (assumed the same for the two ports).
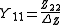
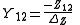
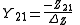
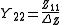
Where
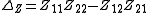
In this case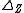 is the determinant
is the determinant
of the Z-parameter matrix.
Vice versa the Y-parameters can be used to determine the Z-parameters, essentially using the
same expressions since
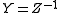
And
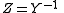
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, electronic engineering
Electronic engineering
Electronics engineering, also referred to as electronic engineering, is an engineering discipline where non-linear and active electrical components such as electron tubes, and semiconductor devices, especially transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, are utilized to design electronic...
, and communication systems
Communications system
In telecommunication, a communications system is a collection of individual communications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and data terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole...
engineering describe the electrical behavior of linear
Linear
In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
electrical network
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
s. They are also used to describe the small-signal (linearized
Linearization
In mathematics and its applications, linearization refers to finding the linear approximation to a function at a given point. In the study of dynamical systems, linearization is a method for assessing the local stability of an equilibrium point of a system of nonlinear differential equations or...
) response of non-linear networks. They are members of a family of similar parameters used in electronic engineering, other examples being: S-parameters, Z-parameters, H-parameters, T-parameters or ABCD-parameters.
The Y-parameter matrix
A Y-parameter matrix describes the behaviour of any linear electrical network that can be regarded as a black boxBlack box
A black box is a device, object, or system whose inner workings are unknown; only the input, transfer, and output are known characteristics.The term black box can also refer to:-In science and technology:*Black box theory, a philosophical theory...
with a number of ports. A port in this context is a pair of electrical terminals
Terminal (electronics)
A terminal is the point at which a conductor from an electrical component, device or network comes to an end and provides a point of connection to external circuits. A terminal may simply be the end of a wire or it may be fitted with a connector or fastener...
carrying equal and opposite currents into and out-of the network, and having a particular voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
between them. The Y-matrix gives no information about the behaviour of the network when the currents at any port are not balanced in this way (should this be possible), nor does it give any information about the voltage between terminals not belonging to the same port. Typically, it is intended that each external connection to the network is between the terminals of just one port, so that these limitations are appropriate.
For a generic multi-port network definition, it is assumed that each of the ports is allocated an integer n ranging from 1 to N, where N is the total number of ports. For port n, the associated Y-parameter definition is in terms of input voltages and output currents,
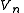 and
and 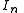 respectively.
respectively.For all ports the output currents may be defined in terms of the Y-parameter matrix and the input voltages by the following matrix equation:
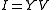
where Y is an N × N matrix the elements of which can be indexed using conventional matrix
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
notation. In general the elements of the Y-parameter matrix are complex number
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
s and functions of frequency. For a one-port network, the Y-matrix reduces to a single element, being the ordinary admittance
Admittance
In electrical engineering, the admittance is a measure of how easily a circuit or device will allow a current to flow. It is defined as the inverse of the impedance . The SI unit of admittance is the siemens...
measured between the two terminals.
Two-port networks

Two-port network
A two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
is probably the most common. In this case the relationship between the input voltages, output currents and the Y-parameter matrix is given by:
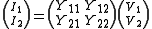 .
.where
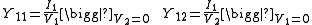
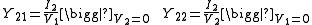
Admittance relations
The input admittance of a two-port network is given by: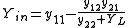
where YL is the admittance of the load connected to port two.
Similarly, the output admittance is given by:
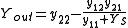
where YS is the admittance of the source connected to port one.
Relation to S-parameters
The Y-parameters of a network are related to its S-Parameters by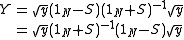
and
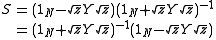
where
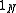 is the identity matrix
is the identity matrixIdentity matrix
In linear algebra, the identity matrix or unit matrix of size n is the n×n square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. It is denoted by In, or simply by I if the size is immaterial or can be trivially determined by the context...
,
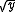 is a diagonal matrix
is a diagonal matrixDiagonal matrix
In linear algebra, a diagonal matrix is a matrix in which the entries outside the main diagonal are all zero. The diagonal entries themselves may or may not be zero...
having the square root of the characteristic admittance (the reciprocal of the characteristic impedance
Characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
) at each port as its non-zero elements,
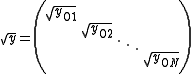
and
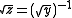 is the corresponding diagonal matrix of square roots of characteristic impedance
is the corresponding diagonal matrix of square roots of characteristic impedanceCharacteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
s. In these expressions the matrices represented by the bracketed factors commute
Commute
Commute, commutation or commutative may refer to:* Commuting, the process of travelling between a place of residence and a place of work* Commutative property, a property of a mathematical operation...
and so, as shown above, may be written in either order.Any square matrix commutes with itself and with the identity matrix, and if two matrices A and B commute, then so do A and B-1 (since AB-1 = B-1BAB-1 = B-1ABB-1 = B-1A)
Two port
In the special case of a two-port network, with the same characteristic admittance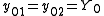 at each port, the above expressions reduce to
at each port, the above expressions reduce to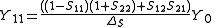
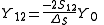
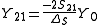
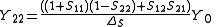
Where
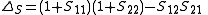
The above expressions will generally use complex numbers for
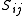 and
and 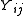 . Note that the value of
. Note that the value of 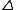 can become 0 for specific values of
can become 0 for specific values of 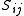 so the division by
so the division by 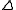 in the calculations of
in the calculations of 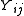 may lead to a division by 0.
may lead to a division by 0.The two-port S-parameters may also be obtained from the equivalent two-port Y-parameters by means of the following expressions.
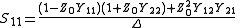
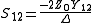
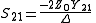
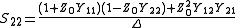
where
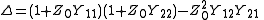
and
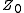 is the characteristic impedance
is the characteristic impedanceCharacteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
at each port (assumed the same for the two ports).
Relation to Z-parameters
Conversion from Z-parameters to Y-parameters is much simpler, as the Y-parameter matrix is just the inverse of the Z-parameter matrix. The following expressions show the applicable relations: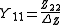
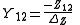
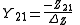
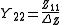
Where
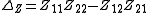
In this case
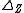 is the determinant
is the determinantDeterminant
In linear algebra, the determinant is a value associated with a square matrix. It can be computed from the entries of the matrix by a specific arithmetic expression, while other ways to determine its value exist as well...
of the Z-parameter matrix.
Vice versa the Y-parameters can be used to determine the Z-parameters, essentially using the
same expressions since
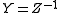
And
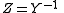
See also
- Scattering parametersScattering parametersScattering parameters or S-parameters describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks when undergoing various steady state stimuli by electrical signals....
- Impedance parametersImpedance parametersImpedance parameters or Z-parameters are properties used in electrical engineering, electronic engineering, and communication systems engineering to describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks. They are also used to describe the small-signal response of non-linear networks...
- Two-port networkTwo-port networkA two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
- Hybrid-pi modelHybrid-pi modelThe hybrid-pi model is a popular circuit model used for analyzing the small signal behavior of bipolar junction and field effect transistors. The model can be quite accurate for low-frequency circuits and can easily be adapted for higher frequency circuits with the addition of appropriate...
- Power gainPower gainThe power gain of an electrical network is the ratio of an output power to an input power. Unlike other signal gains, such as voltage and current gain, "power gain" may be ambiguous as the meaning of terms "input power" and "output power" is not always clear. Three important power gains are...

