
Hybrid-pi model
Encyclopedia
The hybrid-pi model is a popular circuit
model used for analyzing the small signal behavior of bipolar junction and field effect transistors. The model can be quite accurate for low-frequency circuits and can easily be adapted for higher frequency circuits with the addition of appropriate inter-electrode capacitance
s and other parasitic elements.
approximation to the BJT using the small-signal base-emitter voltage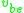 and collector-emitter voltage
and collector-emitter voltage 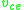 as independent variables, and the small-signal base current
as independent variables, and the small-signal base current 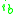 and collector current
and collector current 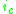 as dependent variables.
as dependent variables.
A basic, low-frequency hybrid-pi model for the bipolar transistor is shown in figure 1. The various parameters are as follows.
The reciprocal of gm is called the intrinsic resistance
is shown in figure 2. The various parameters are as follows.
is the transconductance
in siemens
, evaluated in the Shichman-Hodges model in terms of the Q-point drain current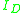 by (see Jaeger and Blalock):
by (see Jaeger and Blalock):
The combination:
often is called the overdrive voltage.
using the approximation for the channel length modulation parameter λ
Here VE is a technology-related parameter (about 4 V/μm for the 65 nm
technology node) and L is the length of the source-to-drain separation.
The reciprocal of the output resistance is named the drain conductance
Electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
model used for analyzing the small signal behavior of bipolar junction and field effect transistors. The model can be quite accurate for low-frequency circuits and can easily be adapted for higher frequency circuits with the addition of appropriate inter-electrode capacitance
Capacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
s and other parasitic elements.
Bipolar junction (BJT) parameters
The hybrid-pi model is a linearized two-port networkTwo-port network
A two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
approximation to the BJT using the small-signal base-emitter voltage
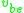 and collector-emitter voltage
and collector-emitter voltage 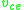 as independent variables, and the small-signal base current
as independent variables, and the small-signal base current 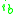 and collector current
and collector current 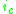 as dependent variables.
as dependent variables.A basic, low-frequency hybrid-pi model for the bipolar transistor is shown in figure 1. The various parameters are as follows.
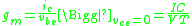 is the transconductanceTransconductanceTransconductance, also known as mutual conductance, is a property of certain electronic components. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance; transconductance, meanwhile, is the ratio of the current change at the output port to the voltage change at the input port. It is written as gm...
is the transconductanceTransconductanceTransconductance, also known as mutual conductance, is a property of certain electronic components. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance; transconductance, meanwhile, is the ratio of the current change at the output port to the voltage change at the input port. It is written as gm...
in siemensSiemens (unit)The siemens is the SI derived unit of electric conductance and electric admittance. Conductance and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance and impedance respectively, hence one siemens is equal to the reciprocal of one ohm, and is sometimes referred to as the mho. In English, the term...
, evaluated in a simple model
- where:
-
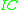 is the quiescent collector current (also called the collector bias or DC collector current)
is the quiescent collector current (also called the collector bias or DC collector current) -
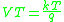 is the thermal voltage, calculated from Boltzmann's constant
is the thermal voltage, calculated from Boltzmann's constant 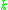 , the charge of an electronElementary chargeThe elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
, the charge of an electronElementary chargeThe elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
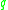 , and the transistor temperature in kelvinKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
, and the transistor temperature in kelvinKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s,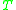 . At 295 K (approximately room temperature)
. At 295 K (approximately room temperature)  is about 25 mV (Google calculator).
is about 25 mV (Google calculator). -
 in ohms
in ohms
-
- where:
-
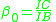 is the current gain at low frequencies (commonly called hFE). Here
is the current gain at low frequencies (commonly called hFE). Here 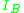 is the Q-point base current. This is a parameter specific to each transistor, and can be found on a datasheet;
is the Q-point base current. This is a parameter specific to each transistor, and can be found on a datasheet; 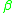 is a function of the choice of collector current.
is a function of the choice of collector current. 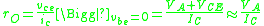 is the output resistance due to the Early effectEarly EffectThe Early effect is the variation in the width of the base in a bipolar junction transistor due to a variation in the applied base-to-collector voltage, named after its discoverer James M. Early...
is the output resistance due to the Early effectEarly EffectThe Early effect is the variation in the width of the base in a bipolar junction transistor due to a variation in the applied base-to-collector voltage, named after its discoverer James M. Early...
( is the Early voltage).
is the Early voltage).
-
Related terms
The reciprocal of the output resistance is named the output conductance .
.
The reciprocal of gm is called the intrinsic resistance
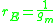 .
.
MOSFET parameters
A basic, low-frequency hybrid-pi model for the MOSFETMOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
is shown in figure 2. The various parameters are as follows.
is the transconductance
Transconductance
Transconductance, also known as mutual conductance, is a property of certain electronic components. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance; transconductance, meanwhile, is the ratio of the current change at the output port to the voltage change at the input port. It is written as gm...
in siemens
Siemens (unit)
The siemens is the SI derived unit of electric conductance and electric admittance. Conductance and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance and impedance respectively, hence one siemens is equal to the reciprocal of one ohm, and is sometimes referred to as the mho. In English, the term...
, evaluated in the Shichman-Hodges model in terms of the Q-point drain current
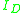 by (see Jaeger and Blalock):
by (see Jaeger and Blalock):-
-
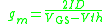 ,
,
-
- where:
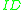 is the quiescent drain current (also called the drain bias or DC drain current)
is the quiescent drain current (also called the drain bias or DC drain current)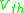 = threshold voltageThreshold voltageThe threshold voltage of a MOSFET is usually defined as the gate voltage where an inversion layer forms at the interface between the insulating layer and the substrate of the transistor. The purpose of the inversion layer's forming is to allow the flow of electrons through the gate-source junction...
= threshold voltageThreshold voltageThe threshold voltage of a MOSFET is usually defined as the gate voltage where an inversion layer forms at the interface between the insulating layer and the substrate of the transistor. The purpose of the inversion layer's forming is to allow the flow of electrons through the gate-source junction...
and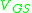 = gate-to-source voltage.
= gate-to-source voltage.
The combination:
often is called the overdrive voltage.
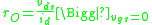 is the output resistance due to channel length modulationChannel length modulationOne of several short channel effects in MOSFET scaling, channel length modulation is a shortening of the length of the inverted channel region with increase in drain bias for large drain biases...
is the output resistance due to channel length modulationChannel length modulationOne of several short channel effects in MOSFET scaling, channel length modulation is a shortening of the length of the inverted channel region with increase in drain bias for large drain biases...
, calculated using the Shichman-Hodges model as
-
-
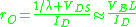 ,
,
-
using the approximation for the channel length modulation parameter λ
-
-
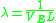 .
.
-
Here VE is a technology-related parameter (about 4 V/μm for the 65 nm
65 nanometer
The 65 nm process is an advanced lithographic node used in volume CMOS semiconductor fabrication. Printed linewidths can reach as low as 25 nm on a nominally 65 nm process, while the pitch between two lines may be greater than 130 nm.. For comparison, cellular ribosomes are...
technology node) and L is the length of the source-to-drain separation.
The reciprocal of the output resistance is named the drain conductance
 .
.
See also
- Small signal modelSmall signal modelSmall-signal modeling is a common analysis technique in electrical engineering which is used to approximate the behavior of nonlinear devices with linear equations...
- h-parameter model



