Alcoholic liver disease
Encyclopedia
Alcoholic liver disease is a term that encompasses the hepatic manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. It is the major cause of liver disease
in Western countries (in Asian countries, viral hepatitis
is the major cause - citation?). Although steatosis (fatty liver) will develop in any individual who consumes a large quantity of alcoholic beverages over a long period of time, this process is transient and reversible. Of all chronic heavy drinkers, only 15-20% develop hepatitis or cirrhosis, which can occur concomitantly or in succession.
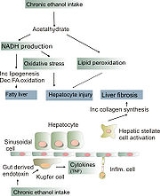
How alcohol damages the liver is not completely understood. 80% of alcohol passes through the liver to be detoxified. Chronic consumption of alcohol results in the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL6 and IL8), oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, and acetaldehyde toxicity. These factors cause inflammation, apoptosis and eventually fibrosis of liver cells. Why this occurs in only a few individuals is still unclear. Additionally, the liver has tremendous capacity to regenerate and can continue to function normally and even when 75% of hepatocytes are dead, it continues to function as normal.
is the accumulation of fatty acids in liver cells
. These can be seen as fatty globules under the microscope. Alcoholism
causes development of large fatty globules (macro
vesicular
steatosis) throughout the liver and can begin to occur after a few days of heavy drinking, (Dr. Darryl S. Inaba, Pharm D, and William E. Cohen, 2004). Alcohol is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) into acetaldehyde, then further metabolized by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) into acetic acid, which is finally oxidized into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). (Darryl S. Inaba, Pharm. D, and William E. Cohen, 2004:185). This process generates NADH, and increases the NADH/NAD+ ratio. A higher NADH concentration induces fatty acid synthesis while a decreased NAD level results in decreased fatty acid oxidation. Subsequently, the higher levels of fatty acids signal the liver cells to compound it to glycerol to form triglycerides. These triglycerides accumulate, resulting in fatty liver.
and the inflammation appears to predispose to liver fibrosis
. Inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL6 and IL8) are thought to be essential in the initiation and perpetuation of liver injury by inducing apoptosis and necrosis. One possible mechanism for the increased activity of TNF-α is the increased intestinal permeability due to liver disease. This facilitates the absorption of the gut-produced endotoxin into the portal circulation. The Kupffer cells of the liver then phagocytose endotoxin, stimulating the release of TNF-α. TNF-α then triggers apoptotic pathways through the activation of caspases, resulting in cell death.
is a late stage of serious liver disease marked by inflammation (swelling), fibrosis (cellular hardening) and damaged membranes preventing detoxification of chemicals in the body, ending in scarring and necrosis (cell death). Between 10% to 20% of heavy drinkers will develop cirrhosis of the liver.(NIAAA, 1993) Acetaldehyde may be responsible for alcohol-induced fibrosis by stimulating collagen deposition by hepatic stellate cells . The production of oxidants derived from NADPH oxi- dase and/or cytochrome P-450 2E1 and the formation of acetaldehyde-protein adducts damage the cell membrane.
Symptoms include jaundice (yellowing), liver enlargement, and pain and tenderness from the structural changes in damaged liver architecture. Without total abstinence from alcohol use, will eventually lead to liver failure
. Late complications of cirrhosis or liver failure include portal hypertension
(high blood pressure in the portal vein due to the increased flow resistance through the damaged liver), coagulation disorders
(due to impaired production of coagulation factors), ascites
(heavy abdominal swelling due to build up of fluids in the tissues) and other complications, including hepatic encephalopathy
and the hepatorenal syndrome
.
Cirrhosis can also result from other causes than alcohol abuse, such as viral hepatitis
and heavy exposure to toxin
s other than alcohol. The late stages of cirrhosis may look similar medically, regardless of cause. This phenomenon is termed the "final common pathway" for the disease.
Fatty change and alcoholic hepatitis with abstinence can be reversible. The later stages of fibrosis and cirrhosis tend to be irreversible, but can usually be contained with abstinence for long periods of time.
and a CT scan to assess liver damage. In some cases a liver biopsy
is performed. This minor procedure is done under local anesthesia
, and involves placing a small needle in the liver and obtaining a piece of tissue
. The tissue is then sent to the laboratory to be examined under a microscope
. The differential diagnoses for fatty liver non-alcoholic steatosis, drug-induced steatosis, include diabetes, obesity
and starvation
.
Other treatment for alcoholic hepatitis include:
interferes with alcohol metabolism. The diet is usually supplemented with vitamin
s and dietary minerals (including calcium
and iron
).
Many nutritionists recommend a diet high in protein, with frequent small meals eaten during the day , about 5-6 instead of the usual 3. Nutritionally, supporting the liver and supplementing with nutrients that enhance liver function is recommended. These include carnitine, which will help reverse fatty livers, and vitamin C, which is an antioxidant, aids in collagen synthesis, and increases the production of neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine and serotonin, as well as supplementing with the nutrients that have been depleted due to the alcohol consumption. Eliminating any food that may be manifesting as an intolerance and alkalizing the body is also important. There are some supplements that are recommended to help reduce cravings for alcohol, including choline, glutamine, and vitamin C. As research shows glucose increases the toxicity of centrilobular hepatotoxicants by inhibiting cell division and repair, it is suggested fatty acids are used by the liver instead of glucose as a fuel source to aid in repair; thus, it is recommended the patient consumes a diet high in protein and essential fatty acids, e.g. omega 3. Cessation of alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking, and increasing exercise are lifestyle recommendations to decrease the risk of liver disease caused by alcoholic stress.
and pentoxifylline), propylthiouracil
to modify metabolism and colchicine
to inhibit hepatic fibrosis.
routinely recommend natural antioxidant
supplements like milk thistle
. Currently, there exists no substantive clinical evidence to suggest that milk thistle
or other antioxidant
supplements are efficacious beyond placebo in treating liver disease caused by chronic alcohol consumption.
. While this is a viable option, liver transplant donors are scarce and usually there is a long waiting list in any given hospital. One of the criteria to become eligible for a liver transplant is to discontinue alcohol consumption for a minimum of six months.
s become noncompliant and narrow. This leads to increased pressure in blood vessels entering the liver. Over time, this causes a backlog of blood (portal hypertension), and is associated with massive bleeding
. Enlarged veins, also known as varicose veins
, also develop to bypass the blockages in the liver. These veins are very fragile and have a tendency to rupture and bleed. Variceal bleeding can be life-threatening and needs emergency treatment. Once the liver is damaged, fluid builds up in the abdomen and legs. The fluid buildup presses on the diaphragm and can make breathing very difficult. As liver damage progresses, the liver is unable to get rid of pigments like bilirubin
and both the skin and eyes turn yellow (jaundice
). The dark pigment also causes the urine to appear dark; however, the stools appear pale. Also with the progression of the disease, the liver can release toxic substances (including ammonia
) which then lead to brain damage
. This results in altered mental state, and may cause behavior and personality changes.
Liver disease
Liver disease is a broad term describing any single number of diseases affecting the liver.-Diseases:* Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons , autoimmunity or hereditary conditions...
in Western countries (in Asian countries, viral hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. The name is from the Greek hepar , the root being hepat- , meaning liver, and suffix -itis, meaning "inflammation"...
is the major cause - citation?). Although steatosis (fatty liver) will develop in any individual who consumes a large quantity of alcoholic beverages over a long period of time, this process is transient and reversible. Of all chronic heavy drinkers, only 15-20% develop hepatitis or cirrhosis, which can occur concomitantly or in succession.
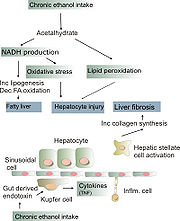
How alcohol damages the liver is not completely understood. 80% of alcohol passes through the liver to be detoxified. Chronic consumption of alcohol results in the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL6 and IL8), oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, and acetaldehyde toxicity. These factors cause inflammation, apoptosis and eventually fibrosis of liver cells. Why this occurs in only a few individuals is still unclear. Additionally, the liver has tremendous capacity to regenerate and can continue to function normally and even when 75% of hepatocytes are dead, it continues to function as normal.
Risk factors
The risk factors presently known are:- Quantity of alcohol taken: consumption of 60-80g per day for 20 years or more in men, or 20g/day for women significantly increases the risk of hepatitis and fibrosis by 7 to 47%, (and Mandayam S, Jamal MM, Morgan TR. Epidemiology of alcoholic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis 2004;24:217-232)
- Pattern of drinking: drinking outside of meal times increases up to 2.7 times the risk of alcoholic liver disease.
- Gender: females are twice as susceptible to alcohol related liver disease, and may develop alcoholic liver disease with shorter durations and doses of chronic consumption. The lesser amount of alcohol dehydrogenase secreted in the gut, higher proportion of body fat in women, and changes in fat absorption due to the with menstrual cycle may explain this phenomenon.
- Hepatitis C infection: a concomitant hepatitis C infection significantly accelerates the process of liver injury.
- Genetic factors: genetic factors predispose both to alcoholism and to alcoholic liver disease. Monozygotic twins are more likely to be alcoholics and to develop liver cirrhosis than dizygotic twins. Polymorphisms in the enzymes involved in the metabolism of alcohol, such as ADH, ALDH, CYP4502E1 , mitochondrial dysfunction, and cytokine polymorphism may partly explain this genetic component. However, no specific polymorphisms have currently been firmly linked to alcoholic liver disease.
- Iron overload (hematochromatosis)
- Diet: malnutrition, particularly vitamin A and E deficiencies, can worsen alcohol-induced liver damage by preventing regeneration of hepatocytes. This is particularly a concern as alcoholics are usually malnourished because of a poor diet, anorexia, and encephalopathy.
Pathophysiology

Fatty change
Fatty change, or steatosisSteatosis
In cellular pathology, steatosis is the process describing the abnormal retention of lipids within a cell. It reflects an impairment of the normal processes of synthesis and elimination of triglyceride fat. Excess lipid accumulates in vesicles that displace the cytoplasm...
is the accumulation of fatty acids in liver cells
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 70-80% of the liver's cytoplasmic mass.These cells are involved in:* Protein synthesis* Protein storage* Transformation of carbohydrates...
. These can be seen as fatty globules under the microscope. Alcoholism
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is a broad term for problems with alcohol, and is generally used to mean compulsive and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, usually to the detriment of the drinker's health, personal relationships, and social standing...
causes development of large fatty globules (macro
Macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or processes are of a size which is measurable and observable by the naked eye.When applied to phenomena and abstract objects, the macroscopic scale describes existence in the world as we perceive it, often in contrast to experiences or...
vesicular
Vesicle (biology)
A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
steatosis) throughout the liver and can begin to occur after a few days of heavy drinking, (Dr. Darryl S. Inaba, Pharm D, and William E. Cohen, 2004). Alcohol is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) into acetaldehyde, then further metabolized by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) into acetic acid, which is finally oxidized into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). (Darryl S. Inaba, Pharm. D, and William E. Cohen, 2004:185). This process generates NADH, and increases the NADH/NAD+ ratio. A higher NADH concentration induces fatty acid synthesis while a decreased NAD level results in decreased fatty acid oxidation. Subsequently, the higher levels of fatty acids signal the liver cells to compound it to glycerol to form triglycerides. These triglycerides accumulate, resulting in fatty liver.
Alcoholic hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is characterized by the inflammation of hepatocytes. Between 10% and 35% of heavy drinkers develop alcoholic hepatitis (NIAAA, 1993). While development of hepatitis is not directly related to the dose of alcohol, some people seem more prone to this reaction than others (citation?). This is called alcoholic steatonecrosisNecrosis
Necrosis is the premature death of cells in living tissue. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, toxins, or trauma. This is in contrast to apoptosis, which is a naturally occurring cause of cellular death...
and the inflammation appears to predispose to liver fibrosis
Fibrosis
Fibrosis is the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in an organ or tissue in a reparative or reactive process. This is as opposed to formation of fibrous tissue as a normal constituent of an organ or tissue...
. Inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL6 and IL8) are thought to be essential in the initiation and perpetuation of liver injury by inducing apoptosis and necrosis. One possible mechanism for the increased activity of TNF-α is the increased intestinal permeability due to liver disease. This facilitates the absorption of the gut-produced endotoxin into the portal circulation. The Kupffer cells of the liver then phagocytose endotoxin, stimulating the release of TNF-α. TNF-α then triggers apoptotic pathways through the activation of caspases, resulting in cell death.
Cirrhosis
CirrhosisCirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
is a late stage of serious liver disease marked by inflammation (swelling), fibrosis (cellular hardening) and damaged membranes preventing detoxification of chemicals in the body, ending in scarring and necrosis (cell death). Between 10% to 20% of heavy drinkers will develop cirrhosis of the liver.(NIAAA, 1993) Acetaldehyde may be responsible for alcohol-induced fibrosis by stimulating collagen deposition by hepatic stellate cells . The production of oxidants derived from NADPH oxi- dase and/or cytochrome P-450 2E1 and the formation of acetaldehyde-protein adducts damage the cell membrane.
Symptoms include jaundice (yellowing), liver enlargement, and pain and tenderness from the structural changes in damaged liver architecture. Without total abstinence from alcohol use, will eventually lead to liver failure
Liver failure
Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs of liver disease , and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage . The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis...
. Late complications of cirrhosis or liver failure include portal hypertension
Portal hypertension
In medicine, portal hypertension is hypertension in the portal vein and its tributaries.It is often defined as a portal pressure gradient of 10 mmHg or greater.-Causes:Causes can be divided into prehepatic, intrahepatic, and posthepatic...
(high blood pressure in the portal vein due to the increased flow resistance through the damaged liver), coagulation disorders
Coagulopathy
Coagulopathy is a condition in which the blood’s ability to clot is impaired. This condition can cause prolonged or excessive bleeding, which may occur spontaneously or following an injury or medical and dental procedures.The normal clotting process depends on the interplay of various proteins in...
(due to impaired production of coagulation factors), ascites
Ascites
Ascites is a gastroenterological term for an accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.The medical condition is also known as peritoneal cavity fluid, peritoneal fluid excess, hydroperitoneum or more archaically as abdominal dropsy. Although most commonly due to cirrhosis and severe liver...
(heavy abdominal swelling due to build up of fluids in the tissues) and other complications, including hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is the occurrence of confusion, altered level of consciousness and coma as a result of liver failure. In the advanced stages it is called hepatic coma or coma hepaticum...
and the hepatorenal syndrome
Hepatorenal syndrome
Hepatorenal syndrome is a life-threatening medical condition that consists of rapid deterioration in kidney function in individuals with cirrhosis or fulminant liver failure...
.
Cirrhosis can also result from other causes than alcohol abuse, such as viral hepatitis
Viral hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute or chronic forms. The most common causes of viral hepatitis are the five unrelated hepatotropic viruses Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D, and Hepatitis E...
and heavy exposure to toxin
Toxin
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
s other than alcohol. The late stages of cirrhosis may look similar medically, regardless of cause. This phenomenon is termed the "final common pathway" for the disease.
Fatty change and alcoholic hepatitis with abstinence can be reversible. The later stages of fibrosis and cirrhosis tend to be irreversible, but can usually be contained with abstinence for long periods of time.
Diagnosis
There are many tests to assess alcoholic liver damage. Besides blood examination, doctors use ultrasoundUltrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
and a CT scan to assess liver damage. In some cases a liver biopsy
Liver biopsy
Liver biopsy is the biopsy from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.-History:...
is performed. This minor procedure is done under local anesthesia
Anesthesia
Anesthesia, or anaesthesia , traditionally meant the condition of having sensation blocked or temporarily taken away...
, and involves placing a small needle in the liver and obtaining a piece of tissue
Tissue (biology)
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
. The tissue is then sent to the laboratory to be examined under a microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
. The differential diagnoses for fatty liver non-alcoholic steatosis, drug-induced steatosis, include diabetes, obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
and starvation
Starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy, nutrient and vitamin intake. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death...
.
Treatment
The first treatment of alcohol-induced liver disease is cessation of alcohol consumption. This is the only way to reverse liver damage or prevent liver injury from worsening. Without treatment, most patients with alcohol-induced liver damage will develop liver cirrhosis.Other treatment for alcoholic hepatitis include:
Early Treatments
In the 1920's, it was believed that a "Liver Exercise" could help with a large amount Alcohol Consumption.Nutrition
Doctors recommend a calorie-rich diet to help the liver in its regeneration process. Dietary fat must be reduced because fatFat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
interferes with alcohol metabolism. The diet is usually supplemented with vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
s and dietary minerals (including calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
and iron
Human iron metabolism
Human iron metabolism is the set of chemical reactions maintaining human homeostasis of iron. Iron is an essential element for most life on Earth, including human beings. The control of this necessary but potentially toxic substance is an important part of many aspects of human health and disease...
).
Many nutritionists recommend a diet high in protein, with frequent small meals eaten during the day , about 5-6 instead of the usual 3. Nutritionally, supporting the liver and supplementing with nutrients that enhance liver function is recommended. These include carnitine, which will help reverse fatty livers, and vitamin C, which is an antioxidant, aids in collagen synthesis, and increases the production of neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine and serotonin, as well as supplementing with the nutrients that have been depleted due to the alcohol consumption. Eliminating any food that may be manifesting as an intolerance and alkalizing the body is also important. There are some supplements that are recommended to help reduce cravings for alcohol, including choline, glutamine, and vitamin C. As research shows glucose increases the toxicity of centrilobular hepatotoxicants by inhibiting cell division and repair, it is suggested fatty acids are used by the liver instead of glucose as a fuel source to aid in repair; thus, it is recommended the patient consumes a diet high in protein and essential fatty acids, e.g. omega 3. Cessation of alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking, and increasing exercise are lifestyle recommendations to decrease the risk of liver disease caused by alcoholic stress.
Drugs
Abstinence from alcohol intake and nutritional modification form the backbone in the management of ALD. Symptom treatment can include: corticosteroids for severe cases, anticytokines (infliximabInfliximab
Infliximab is a monoclonal antibody against tumour necrosis factor alpha . It is used to treat autoimmune diseases. Remicade is marketed by Janssen Biotech, Inc...
and pentoxifylline), propylthiouracil
Propylthiouracil
Propylthiouracil or 6-n-Propylthiouracil is a thioamide drug used to treat hyperthyroidism by decreasing the amount of thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland...
to modify metabolism and colchicine
Colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used for gout. It is a toxic natural product and secondary metabolite, originally extracted from plants of the genus Colchicum...
to inhibit hepatic fibrosis.
Antioxidants
It is widely believed that alcohol-induced liver damage occurs via generation of oxidants. Thus alternative health care practitionersAlternative medicine
Alternative medicine is any healing practice, "that does not fall within the realm of conventional medicine." It is based on historical or cultural traditions, rather than on scientific evidence....
routinely recommend natural antioxidant
Antioxidant
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
supplements like milk thistle
Milk thistle
The milk thistle is a thistle of the genus Silybum Adans., a flowering plant of the daisy family . They are native to the Mediterranean regions of Europe, North Africa and the Middle East...
. Currently, there exists no substantive clinical evidence to suggest that milk thistle
Milk thistle
The milk thistle is a thistle of the genus Silybum Adans., a flowering plant of the daisy family . They are native to the Mediterranean regions of Europe, North Africa and the Middle East...
or other antioxidant
Antioxidant
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
supplements are efficacious beyond placebo in treating liver disease caused by chronic alcohol consumption.
Transplant
When all else fails and the liver is severely damaged, the only alternative is a liver transplantLiver transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with a healthy liver allograft. The most commonly used technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic location as the original...
. While this is a viable option, liver transplant donors are scarce and usually there is a long waiting list in any given hospital. One of the criteria to become eligible for a liver transplant is to discontinue alcohol consumption for a minimum of six months.
Complications and prognosis
As the liver scars, the blood vesselBlood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s become noncompliant and narrow. This leads to increased pressure in blood vessels entering the liver. Over time, this causes a backlog of blood (portal hypertension), and is associated with massive bleeding
Bleeding
Bleeding, technically known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging is the loss of blood or blood escape from the circulatory system...
. Enlarged veins, also known as varicose veins
Varicose veins
Varicose veins are veins that have become enlarged and tortuous. The term commonly refers to the veins on the leg, although varicose veins can occur elsewhere. Veins have leaflet valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards . Leg muscles pump the veins to return blood to the heart, against the...
, also develop to bypass the blockages in the liver. These veins are very fragile and have a tendency to rupture and bleed. Variceal bleeding can be life-threatening and needs emergency treatment. Once the liver is damaged, fluid builds up in the abdomen and legs. The fluid buildup presses on the diaphragm and can make breathing very difficult. As liver damage progresses, the liver is unable to get rid of pigments like bilirubin
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is the yellow breakdown product of normal heme catabolism. Heme is found in hemoglobin, a principal component of red blood cells. Bilirubin is excreted in bile and urine, and elevated levels may indicate certain diseases...
and both the skin and eyes turn yellow (jaundice
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellowish pigmentation of the skin, the conjunctival membranes over the sclerae , and other mucous membranes caused by hyperbilirubinemia . This hyperbilirubinemia subsequently causes increased levels of bilirubin in the extracellular fluid...
). The dark pigment also causes the urine to appear dark; however, the stools appear pale. Also with the progression of the disease, the liver can release toxic substances (including ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
) which then lead to brain damage
Brain damage
"Brain damage" or "brain injury" is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors...
. This results in altered mental state, and may cause behavior and personality changes.

