
Alleghenian orogeny
Encyclopedia
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
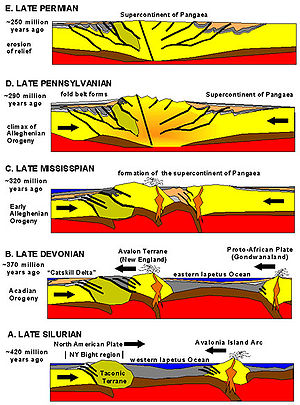
-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
and Allegheny Mountains
Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range , also spelled Alleghany, Allegany and, informally, the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the eastern United States and Canada...
. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 1957.
The Alleghenian orogeny occurred approximately 350 million to 300 million years ago, in the Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
period. The orogeny was caused by Africa colliding with North America. At the time, these continents did not exist in their current forms: North America was part of the Euramerica
Euramerica
Euramerica was a minor supercontinent created in the Devonian as the result of a collision between the Laurentian, Baltica, and Avalonia cratons .300 million years ago in the Late Carboniferous tropical rainforests lay over the equator of Euramerica...
super-continent, while Africa was part of Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
. This collision formed the super-continent Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
, which contained all major continental land masses. The collision provoked the orogeny: it exerted massive stress on what is today the Eastern Seaboard
Eastern seaboard
An Eastern seaboard can mean any easternmost part of a continent, or its countries, states and/or cities.Eastern seaboard may also refer to:* East Coast of Australia* East Coast of the United States* Eastern Seaboard of Thailand-See also:...
of North America, forming a wide and high mountain chain. Evidence for the Alleghenian orogeny stretches for many hundreds of miles on the surface from Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
to New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
and can be traced further subsurface to the southwest. In the north, the Alleghenian deformation extends northeast to Newfoundland. Subsequent erosion wore down the mountain chain and spread sediments both to the east and to the west.
Continental collision
The immense region involved in the continental collision, the vast temporal length of the orogeny and the thickness of the pile of sediments and igneous rocks known to have been involved are evidence that at the peak of the mountain-building process, the Appalachians could have risen as high or perhaps even higher than the present-day Himalaya.As the continents collided, the rock material trapped in-between was crushed and forced upward. With nowhere to go, rocks along the eastern margin of the North American continent were shoved far inland (the same occurred in the opposite direction along the margin of the African continent, forming the Atlas Mountains
Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains is a mountain range across a northern stretch of Africa extending about through Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. The highest peak is Toubkal, with an elevation of in southwestern Morocco. The Atlas ranges separate the Mediterranean and Atlantic coastlines from the Sahara Desert...
of Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
and the western Sahara
Sahara
The Sahara is the world's second largest desert, after Antarctica. At over , it covers most of Northern Africa, making it almost as large as Europe or the United States. The Sahara stretches from the Red Sea, including parts of the Mediterranean coasts, to the outskirts of the Atlantic Ocean...
). Close to the boundary between the colliding plates, tectonic stresses contributed to the metamorphosizing of the rock (i.e. the transformation of igneous
Igneous rock
Igneous rock is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic rock. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava...
and sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution....
into metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
).
The sedimentary rock in the eastern Appalachian Basin region was squeezed into great folds that ran perpendicular to the direction of forces. The greatest amount of deformation associated with the Alleghenian orogeny occurred in the Southern Appalachians (North Carolina
North Carolina
North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
, Tennessee
Tennessee
Tennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area...
, Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
, and West Virginia
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian and Southeastern regions of the United States, bordered by Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Ohio to the northwest, Pennsylvania to the northeast and Maryland to the east...
). In that region, a series of great faults developed in addition to the folds. As the two continents collided, large belts of rock bounded by thrust fault
Thrust fault
A thrust fault is a type of fault, or break in the Earth's crust across which there has been relative movement, in which rocks of lower stratigraphic position are pushed up and over higher strata. They are often recognized because they place older rocks above younger...
s piled one on top another, shortening of the crust along the eastern edge of North America in the North Carolina and Tennessee region by as much as 200 miles (321.9 km). The relative amount of deformation gradually diminishes northward. The fold belt extends northward through Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
and gradually peters in the vicinity of the New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
border. The Kittatinny Mountains
Kittatinny Mountains
The Kittatinny Mountains are a long ridge traversing across northwestern New Jersey running in a northeast-southwest axis. It is the first major ridge in the far northeastern extension of the Ridge and Valley province of the Appalachian Mountains...
in northwestern New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
mark the northeastern-most extension of the high ridges of the Valley and Ridge Province
Ridge-and-valley Appalachians
The Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also called the Ridge and Valley Province or the Valley and Ridge Appalachians, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division and are also a belt within the Appalachian Mountains extending from southeastern New York through northwestern New...
. The influence of Alleghenian deformation on the regions east of the Valley and Ridge Province must have be even more intense, however, there is little evidence preserved. Rocks of Mississippian, Pennsylvanian
Pennsylvanian
The Pennsylvanian is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two subperiods of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain...
, and Permian
Permian
The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian...
age are missing along the Eastern Seaboard.
Subsequent erosion

Piedmont (United States)
The Piedmont is a plateau region located in the eastern United States between the Atlantic Coastal Plain and the main Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New Jersey in the north to central Alabama in the south. The Piedmont province is a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division...
. Sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
s that were carried eastward formed the coastal plain
Coastal plain
A coastal plain is an area of flat, low-lying land adjacent to a seacoast and separated from the interior by other features. One of the world's longest coastal plains is located in eastern South America. The southwestern coastal plain of North America is notable for its species diversity...
and part of the continental shelf
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
. Thus, the coastal plain and Piedmont are largely the byproducts of erosion that took place from 150+ million years ago to the present.
Sediments that were carried westward formed the Allegheny
Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau is a large dissected plateau area in western and central New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Ohio...
and Cumberland Plateau
Cumberland Plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and western West Virginia, part of Tennessee, and a small portion of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia . The terms "Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the...
, which in some areas are popularly called mountains, but are actually simply uplifted and eroded plateaus
Dissected plateau
A dissected plateau is a plateau area that has been severely eroded so that the relief is sharp. Such an area may be referred to as mountainous, but dissected plateaus are distinguishable from orogenic mountain belts by the lack of folding, metamorphism, extensive faulting, or magmatic activity...
. Carbonate
Carbonate
In chemistry, a carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, . The name may also mean an ester of carbonic acid, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C2....
s and fine sediments from the Alleghenian orogeny were carried farther west to form limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
rocks in a shallow sea that was later uplifted and forms the bulk of Tennessee
Tennessee
Tennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area...
, Kentucky
Kentucky
The Commonwealth of Kentucky is a state located in the East Central United States of America. As classified by the United States Census Bureau, Kentucky is a Southern state, more specifically in the East South Central region. Kentucky is one of four U.S. states constituted as a commonwealth...
, Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
, and Indiana
Indiana
Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
.
A portion of the Alleghenian mountain system departed with Africa when Pangaea broke up and the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
began to form. Today, this forms the Anti-Atlas
Anti-Atlas
The Anti-Atlas or Lesser Atlas or Little Atlas, is a mountain range in Morocco, a part of the Atlas mountains in the northwest of Africa. The Anti-Atlas extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the southwest toward the northeast, to the heights of Ouarzazate and further east to the city of Tafilalt,...
mountains of Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
. The Anti-Atlas have been geologically uplifted in relatively recent times, and are today much more rugged than their Alleghenian relatives.

