
Alveolar consonant
Encyclopedia

Alveolar ridge
An alveolar ridge is one of the two jaw ridges either on the roof of the mouth between the upper teeth and the hard palate or on the bottom of the mouth behind the lower teeth. The alveolar ridges contain the sockets of the teeth....
, which is called that because it contains the alveoli
Dental alveolus
Dental alveolus are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process of maxilla with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets...
(the sockets) of the superior teeth. Alveolar consonants may be articulated with the tip of the tongue (so-called apical consonant
Apical consonant
An apical consonant is a phone produced by obstructing the air passage with the apex of the tongue . This contrasts with laminal consonants, which are produced by creating an obstruction with the blade of the tongue .This is not a very common distinction, and typically applied only to fricatives...
s), as in English, or with the flat of the tongue just above the tip (the "blade" of the tongue; called laminal consonant
Laminal consonant
A laminal consonant is a phone produced by obstructing the air passage with the blade of the tongue, which is the flat top front surface just behind the tip of the tongue on the top. This contrasts with apical consonants, which are produced by creating an obstruction with the tongue apex only...
s), as in French and Spanish. The laminal alveolar articulation is often mistakenly called dental, because the tip of the tongue can be seen near to or touching the teeth. However, it is the rearmost point of contact that defines the place of articulation; this is where the oral cavity ends, and it is the resonant space of the oral cavity that gives consonants and vowels their characteristic timbre.
The International Phonetic Alphabet
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
(IPA) does not have separate symbols for the alveolar consonants. Rather, the same symbol is used for all coronal
Coronal consonant
Coronal consonants are consonants articulated with the flexible front part of the tongue. Only the coronal consonants can be divided into apical , laminal , domed , or subapical , as well as a few rarer orientations, because only the front of the tongue has such...
places of articulation which aren't palatalized
Palatalization
In linguistics, palatalization , also palatization, may refer to two different processes by which a sound, usually a consonant, comes to be produced with the tongue in a position in the mouth near the palate....
like English palato-alveolar
Palato-alveolar consonant
In phonetics, palato-alveolar consonants are postalveolar consonants, nearly always sibilants, that are weakly palatalized with a domed tongue...
sh, or retroflex. To disambiguate, the bridge ([s̪, t̪, n̪, l̪], etc.) may be used for a dental consonant, or the under-bar ([s̠, t̠, n̠, l̠], etc.) may be used for the postalveolar
Postalveolar consonant
Postalveolar consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the back of the alveolar ridge, further back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself, but not as far back as the hard palate...
s. Note that [s̪] differs from dental [θ] in being a sibilant
Sibilant consonant
A sibilant is a manner of articulation of fricative and affricate consonants, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the sharp edge of the teeth, which are held close together. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words sip, zip, ship, chip,...
, rather than a fricative. [s̠] differs from postalveolar [ʃ] in being unpalatalized.
The bare letters [s, t, n, l], etc. cannot be assumed to specifically represent alveolars. The language may not make such distinctions, such that two or more coronal places
Place of articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation of a consonant is the point of contact where an obstruction occurs in the vocal tract between an articulatory gesture, an active articulator , and a passive location...
are found allophonically
Allophone
In phonology, an allophone is one of a set of multiple possible spoken sounds used to pronounce a single phoneme. For example, and are allophones for the phoneme in the English language...
, or the transcription may simply be too broad to distinguish dental from alveolar. If it is necessary to specify a consonant as alveolar, a diacritic from the Extended IPA may be used: [s͇, t͇, n͇, l͇], etc.. Nonetheless, the symbols
(The Extended IPA diacritic was devised for speech pathology and is frequently used to mean 'alveolarized', as in the labioalveolar sounds [p͇, b͇, m͇, f͇, v͇], where the lower lip contacts the alveolar ridge.)
Alveolar consonants in IPA
The alveolar/coronal consonants identified by the IPA are:| IPA | Description | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Orthography | IPA | Meaning in English | ||
 |
alveolar nasal Alveolar nasal The alveolar nasal is a type of consonantal sound used in numerous spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar nasals is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is n.... |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
run | [ɹʷʌn] | run |
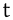 |
voiceless alveolar plosive Voiceless alveolar plosive The voiceless alveolar plosive is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar plosives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is t... |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
tap | [tʰæp] | tap Tap -Mechanical and electrical:* Tap , a device for controlling the release of a liquid or gas* Tap , part of an electrical device* A cutting tool, part of a tap and die set-Entertainment:* Tap dance... |
 |
voiced alveolar plosive Voiced alveolar plosive The voiced alveolar plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiced dental, alveolar, and postalveolar plosives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is d.-Features:Features of the voiced... |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
debt | [dɛt] | debt Debt A debt is an obligation owed by one party to a second party, the creditor; usually this refers to assets granted by the creditor to the debtor, but the term can also be used metaphorically to cover moral obligations and other interactions not based on economic value.A debt is created when a... |
 |
voiceless alveolar fricative Voiceless alveolar fricative The voiceless alveolar sibilant is a common consonant sound in spoken languages. It is the sound in English words such as sea and pass, and is represented in the International Phonetic Alphabet as . It has a characteristic high-pitched, highly perceptible hissing sound... |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
suit | [sjuːt] | suit |
 |
voiced alveolar fricative Voiced alveolar fricative The voiced alveolar fricatives are consonantal sounds. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents these sounds depends on whether a sibilant or non-sibilant fricative is being described.... |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
zoo | [zuː] | zoo Zoo A zoological garden, zoological park, menagerie, or zoo is a facility in which animals are confined within enclosures, displayed to the public, and in which they may also be bred.... |
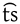 |
voiceless alveolar affricate Voiceless alveolar affricate The voiceless alveolar affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The sound is transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet with ⟨⟩ or ⟨⟩ . The voiceless alveolar affricate occurs in such languages as German, Cantonese, Italian, Russian, Japanese and Mandarin... |
German German language German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union.... |
Zeit | [t͡saɪt] | time Time Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects.... |
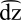 |
voiced alveolar affricate Voiced alveolar affricate The voiced alveolar affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The sound is transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet with ⟨⟩ or ⟨⟩ , and the equivalent X-SAMPA representation is ⟨dz⟩.-Features:... |
Italian Italian language Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia... |
zaino | [ˈd͡zaino] | backpack Backpack A backpack is, in its simplest form, a cloth sack carried on one's back and secured with two straps that go over the shoulders, but there can be exceptions... |
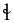 |
voiceless alveolar lateral fricative Voiceless alveolar lateral fricative The voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar fricatives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K... |
Welsh Welsh language Welsh is a member of the Brythonic branch of the Celtic languages spoken natively in Wales, by some along the Welsh border in England, and in Y Wladfa... |
Llwyd | [ɬʊɪd] | the name Lloyd or Floyd |
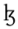 |
voiced alveolar lateral fricative | Zulu Zulu language Zulu is the language of the Zulu people with about 10 million speakers, the vast majority of whom live in South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa as well as being understood by over 50% of the population... |
dlala | [ˈɮálà] | to play |
| t͡ɬ | voiceless alveolar lateral affricate Voiceless alveolar lateral affricate The voiceless alveolar lateral affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is , and in Americanist phonetic notation it is .-Features:... |
Tsez Tsez language Tsez, also known as Dido is a Northeast Caucasian language with about 15,354 speakers spoken by the Tsez, a Muslim people in the mountainous Tsunta district of southern and western Dagestan in Russia. The name is said to derive from the Tsez word for "eagle", which is most likely a folk etymology... |
элIни | [ˈʔɛ̝t͡ɬni] | winter |
| d͡ɮ | voiced alveolar lateral affricate Voiced alveolar lateral affricate The voiced alveolar lateral affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is... |
Oowekyala | |||
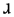 |
alveolar approximant | English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
red | [ɹʷɛd] | red Red Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye... |
 |
alveolar lateral approximant Alveolar lateral approximant The alveolar lateral approximant, also known as clear l, is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral approximants is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l.As a... |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
loop | [lup] | loop |
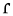 |
alveolar flap | Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
pero | [peɾo] | but |
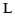 |
alveolar lateral flap | Venda Venda language Venda, also known as or , is a Bantu language and an official language of South Africa. The majority of Venda speakers live in the northern part of South Africa's Limpopo Province, but about 10% of speakers live in Zimbabwe. The Venda language is related to Kalanga which is spoken in Botswana... |
[vuɺa] | to open | |
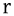 |
alveolar trill Alveolar trill The alveolar trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar trills is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r. It is commonly called the rolled R, rolling R, or trilled R... |
Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
perro | [pero] | dog Dog The domestic dog is a domesticated form of the gray wolf, a member of the Canidae family of the order Carnivora. The term is used for both feral and pet varieties. The dog may have been the first animal to be domesticated, and has been the most widely kept working, hunting, and companion animal in... |
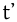 |
alveolar ejective Alveolar ejective The alveolar ejective is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is .-Features:Features of the aveolar ejective:-Occurrence:... |
Georgian Georgian language Georgian is the native language of the Georgians and the official language of Georgia, a country in the Caucasus.Georgian is the primary language of about 4 million people in Georgia itself, and of another 500,000 abroad... |
ტიტა | [tʼitʼa] | tulip |
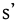 |
alveolar ejective fricative Alveolar ejective fricative The alveolar ejective fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is sʼ.-Features:Features of the alveolar ejective fricative:-Occurrence:... |
Amharic Amharic language Amharic is a Semitic language spoken in Ethiopia. It is the second most-spoken Semitic language in the world, after Arabic, and the official working language of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. Thus, it has official status and is used nationwide. Amharic is also the official or working... |
[sʼɛɡa] | grace | |
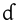 |
voiced alveolar implosive | Vietnamese Vietnamese language Vietnamese is the national and official language of Vietnam. It is the mother tongue of 86% of Vietnam's population, and of about three million overseas Vietnamese. It is also spoken as a second language by many ethnic minorities of Vietnam... |
đã | [ɗɐː] | Past tense indicator |
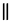 |
alveolar lateral click | Nama | î | [kǁĩĩ] | discussed |
Lack of alveolars
The alveolar or dental consonants [t] and [n] are, along with [k], the most common consonants in human languages. Nonetheless, there are a few languages which lack them. A few languages on Bougainville IslandBougainville Island
Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville of Papua New Guinea. This region is also known as Bougainville Province or the North Solomons. The population of the province is 175,160 , which includes the adjacent island of Buka and assorted outlying islands...
and around Puget Sound
Puget Sound
Puget Sound is a sound in the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins, with one major and one minor connection to the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Pacific Ocean — Admiralty Inlet being the major connection and...
, such as Makah
Makah language
The Makah language is the Indigenous language spoken by the Makah people. Makah has been extinct as a first language since 2002, when its last fluent native speaker died. However, it survives as a second language, and the Makah tribe is attempting to revive the language, including through preschool...
, lack nasals and therefore [n], but have [t]. Colloquial Samoan
Samoan language
Samoan Samoan Samoan (Gagana Sāmoa, is the language of the Samoan Islands, comprising the independent country of Samoa and the United States territory of American Samoa. It is an official language—alongside English—in both jurisdictions. Samoan, a Polynesian language, is the first language for most...
, however, lacks both [t] and [n], though it has a lateral alveolar approximant [l]. (Samoan words written with the letters t and n are pronounced with [k] and [ŋ] except in formal speech.)
Alveolar Switching
JapaneseJapanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
speakers often mix alveolar lateral approximant
Alveolar lateral approximant
The alveolar lateral approximant, also known as clear l, is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral approximants is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l.As a...
sounds in other languages with alveolar approximant sounds due to a lack of alveolar lateral approximants in their own language.

