
Dental consonant
Encyclopedia
A dental consonant is a consonant
articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as /t/, /d/, /n/, and /l/ in some languages. Dentals are primarily distinguished from sounds in which contact is made with the tongue
and the gum
ridge, as in English (see Alveolar consonant
), due to the acoustic similarity of the sounds and the fact that in the Roman alphabet they are generally written using the same symbols (t, d, n, and so on).
In the International Phonetic Alphabet
, the diacritic for dental consonant is 032A
, Irish
or Russian
, velarization
is generally associated with more dental articulations of coronal consonants so that velarized consonants (such as Albanian /ɫ/) tend to be dental or denti-alveolar while non-velarized consonants tend to be retracted to an alveolar position.
Sanskrit
, Hindi
and all other Indic languages have an entire set of dental plosives which occur phonemically as voiced and voiceless, and with or without aspiration. The nasal stop /n/ also exists in these languages, but is quite alveolar and apical in articulation. To the Indian speaker, the alveolar /t/ and /d/ of English sound more like the corresponding retroflex consonant
s of his own language than like the dentals.
Spanish
/t/ and /d/ are laminal denti-alveolar while /l/ and /n/ are prototypically alveolar but assimilate to the place of articulation
of a following consonant. Likewise, Italian
/t/, /d/, /t͡s/, /d͡z/ are denti-alveolar ([t̪], [d̪], [t̪͡s̪], and [d̪͡z̪] respectively) and /l/ and /n/ become denti-alveolar before a following dental consonant.
Although denti-alveolar consonants are often described as dental, it is the rear-most point of contact that is most relevant, for this is what defines the maximum acoustic space of resonance and will give a consonant its characteristic sound. In the case of French
, the rear-most contact is alveolar or sometimes slightly pre-alveolar.
are:
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as /t/, /d/, /n/, and /l/ in some languages. Dentals are primarily distinguished from sounds in which contact is made with the tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
and the gum
Gingiva
The gingiva , or gums, consists of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth.-General description:...
ridge, as in English (see Alveolar consonant
Alveolar consonant
Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth...
), due to the acoustic similarity of the sounds and the fact that in the Roman alphabet they are generally written using the same symbols (t, d, n, and so on).
In the International Phonetic Alphabet
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
, the diacritic for dental consonant is 032A
Dentals cross-linguistically
For many languages, such as AlbanianAlbanian language
Albanian is an Indo-European language spoken by approximately 7.6 million people, primarily in Albania and Kosovo but also in other areas of the Balkans in which there is an Albanian population, including western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, southern Serbia and northwestern Greece...
, Irish
Irish language
Irish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
or Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
, velarization
Velarization
Velarization is a secondary articulation of consonants by which the back of the tongue is raised toward the velum during the articulation of the consonant.In the International Phonetic Alphabet, velarization is transcribed by one of three diacritics:...
is generally associated with more dental articulations of coronal consonants so that velarized consonants (such as Albanian /ɫ/) tend to be dental or denti-alveolar while non-velarized consonants tend to be retracted to an alveolar position.
Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
, Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
and all other Indic languages have an entire set of dental plosives which occur phonemically as voiced and voiceless, and with or without aspiration. The nasal stop /n/ also exists in these languages, but is quite alveolar and apical in articulation. To the Indian speaker, the alveolar /t/ and /d/ of English sound more like the corresponding retroflex consonant
Retroflex consonant
A retroflex consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consonants, especially in Indology...
s of his own language than like the dentals.
Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
/t/ and /d/ are laminal denti-alveolar while /l/ and /n/ are prototypically alveolar but assimilate to the place of articulation
Place of articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation of a consonant is the point of contact where an obstruction occurs in the vocal tract between an articulatory gesture, an active articulator , and a passive location...
of a following consonant. Likewise, Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
/t/, /d/, /t͡s/, /d͡z/ are denti-alveolar ([t̪], [d̪], [t̪͡s̪], and [d̪͡z̪] respectively) and /l/ and /n/ become denti-alveolar before a following dental consonant.
Although denti-alveolar consonants are often described as dental, it is the rear-most point of contact that is most relevant, for this is what defines the maximum acoustic space of resonance and will give a consonant its characteristic sound. In the case of French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, the rear-most contact is alveolar or sometimes slightly pre-alveolar.
Dental consonants in the world's languages
The dental/denti-alveolar consonants as transcribed by the International Phonetic AlphabetInternational Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
are:
| IPA | Description | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Orthography | IPA | Meaning | ||
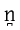 |
dental nasal Dental nasal The dental nasal is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is .-Features:Features of the dental nasal:- Occurrence :... |
Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
onda | [õn̪d̪a] | wave |
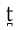 |
voiceless dental plosive Voiceless dental plosive The voiceless dental plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is t_d... |
Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
toro | [t̪oɾo] | bull |
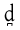 |
voiced dental plosive Voiced dental plosive The voiced dental plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is... |
Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
donde | [d̪õn̪d̪e] | where |
| s̪ | voiceless dental sibilant fricative | Polish Polish language Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries... |
kosa | [kɔs̪a] | scythe |
| z̪ | voiced dental sibilant fricative | Polish Polish language Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries... |
koza | [kɔz̪a] | goat |
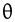 |
voiceless dental nonsibilant fricative Voiceless dental fricative The voiceless dental non-sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to English speakers as the 'th' in thing. Though rather rare as a phoneme in the world's inventory of languages, it is encountered in some of the most widespread and influential... (also often called "interdental") |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
thing | [θɪŋ] | thing |
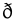 |
voiced dental nonsibilant fricative Voiced dental fricative The voiced dental non-sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound, eth, is . The symbol was taken from the Old English letter eth, which could stand for either a voiced or unvoiced... (also often called "interdental") |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
this | [ðɪs] | this |
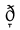 |
dental approximant | Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
codo | [koð̞o] | elbow |
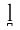 |
dental lateral approximant | Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
alto | [al̪t̪o] | tall |
 |
dental flap | Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
pero | [peɾ̪o] | but |
 |
dental trill | Marshallese Marshallese language The Marshallese language is a Malayo-Polynesian language of the Marshall Islands, and the principal language of the country... |
Ebadon | [ebˠɑr̪ˠon̪] | Ebadon |
 |
dental ejective Dental ejective The dental ejective is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is .-Features:Features of the dental ejective:-Occurrence:... |
||||
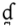 |
voiced dental implosive | ||||
 |
dental click release Dental click Dental clicks are a family of click consonants found, as constituents of words, only in Africa and in the Damin ritual jargon of Australia. The tut-tut! or tsk! tsk! sound used to express disapproval or pity is a dental click, although it isn't a speech sound in that context.The symbol in the... |
Xhosa Xhosa language Xhosa is one of the official languages of South Africa. Xhosa is spoken by approximately 7.9 million people, or about 18% of the South African population. Like most Bantu languages, Xhosa is a tonal language, that is, the same sequence of consonants and vowels can have different meanings when said... |
ukúcola | [ukʼúkǀola] | to grind fine |
See also
- Denti-alveolar consonant
- Place of articulationPlace of articulationIn articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation of a consonant is the point of contact where an obstruction occurs in the vocal tract between an articulatory gesture, an active articulator , and a passive location...
- List of phonetics topics

