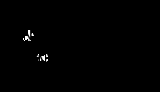
Aminophylline
Encyclopedia
Aminophylline is a bronchodilator
. It is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline
with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate
with the liberation of free theophylline. Its solutions are alkaline. One g dissolves in 25 mL of water to give a clear solution; 1 g dissolved in 5 mL of water crystallizes upon standing, but redissolves when a small amount of ethylenediamine is added. Insoluble in alcohol and in ether.
, aminophylline is both a
Aminophylline is less potent and shorter-acting than theophylline
. Its most common use is in the treatment of bronchial asthma.
Causes bronchodilatation, diuresis, CNS and cardiac stimulation, and gastric acid secretion by blocking phosphodiesterase which increases tissue concentrations of cyclic adenine monophosphate (cAMP) which in turn promotes catecholamine stimulation of lipolysis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis and induces release of epinephrine from adrenal medulla cells
Aminophylline has shown some promise as a bodyfat reducer when used as a topical cream (sometimes referred to as "cutting gel"). Aminophylline is also a treatment option for anaphylactic shock.
Bronchodilator
A bronchodilator is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be endogenous , or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties...
. It is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline
Theophylline
Theophylline, also known as dimethylxanthine, is a methylxanthine drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as COPD and asthma under a variety of brand names. Because of its numerous side-effects, the drug is now rarely administered for clinical use. As a member of the xanthine family, it...
with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate
Hydrate
Hydrate is a term used in inorganic chemistry and organic chemistry to indicate that a substance contains water. The chemical state of the water varies widely between hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understood....
Properties
It is more soluble in water than theophylline. White or slightly yellowish granules or powder, having a slight ammoniacal odor and a bitter taste. Upon exposure to air, it gradually loses ethylenediamine and absorbs carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
with the liberation of free theophylline. Its solutions are alkaline. One g dissolves in 25 mL of water to give a clear solution; 1 g dissolved in 5 mL of water crystallizes upon standing, but redissolves when a small amount of ethylenediamine is added. Insoluble in alcohol and in ether.
Mechanism of action
Like other methylated xanthine derivativesXanthine
Xanthine , is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids and in other organisms. A number of stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine and theobromine....
, aminophylline is both a
- competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitorPhosphodiesterase inhibitorA phosphodiesterase inhibitor is a drug that blocks one or more of the five subtypes of the enzyme phosphodiesterase , therefore preventing the inactivation of the intracellular second messengers cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic guanosine monophosphate by the respective PDE...
which raises intracellular cAMPCyclic adenosine monophosphateCyclic adenosine monophosphate is a second messenger important in many biological processes...
, activates PKACAMP-dependent protein kinaseIn cell biology, Protein kinase A refers to a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP . PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase...
, inhibits TNF-alphaTNF inhibitorTumor necrosis factor promotes the inflammatory response, which in turn causes many of the clinical problems associated with autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma. These disorders are...
and leukotrieneLeukotrieneLeukotrienes are fatty signaling molecules. They were first found in leukocytes . One of their roles is to trigger contractions in the smooth muscles lining the trachea; their overproduction is a major cause of inflammation in asthma and allergic rhinitis...
synthesis, and reduces inflammationAnti-inflammatoryAnti-inflammatory refers to the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs make up about half of analgesics, remedying pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system....
and innate immunity and - nonselective adenosine receptorAdenosine receptorThe adenosine receptors are a class of purinergic receptors, G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as endogenous ligand.-Pharmacology:...
antagonist.
Aminophylline is less potent and shorter-acting than theophylline
Theophylline
Theophylline, also known as dimethylxanthine, is a methylxanthine drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as COPD and asthma under a variety of brand names. Because of its numerous side-effects, the drug is now rarely administered for clinical use. As a member of the xanthine family, it...
. Its most common use is in the treatment of bronchial asthma.
Causes bronchodilatation, diuresis, CNS and cardiac stimulation, and gastric acid secretion by blocking phosphodiesterase which increases tissue concentrations of cyclic adenine monophosphate (cAMP) which in turn promotes catecholamine stimulation of lipolysis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis and induces release of epinephrine from adrenal medulla cells
Other uses
Aminophylline is used to reverse dypridamole or adenosine based infusions during nuclear cardiology stress testing.Aminophylline has shown some promise as a bodyfat reducer when used as a topical cream (sometimes referred to as "cutting gel"). Aminophylline is also a treatment option for anaphylactic shock.
Brand names
- Phyllocontin
- Truphylline
- Minomal R 175 mg tab
- Minomal R 350 mg tab
- Minomal SR 600 mg tab

