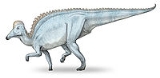
Amurosaurus
Encyclopedia
Amurosaurus is a genus
of lambeosaurine
hadrosaurid
dinosaur
found in the latest Cretaceous
period (65.5 million years ago) of eastern Asia
. Like most lambeosaurs, it would have been a primarily biped
al herbivore
with a "duckbill" shaped snout and a hollow crest on top of its head, although such a crest has not been found. Fossil
bones of adults are rare, but an adult would most likely have been at least 20 feet (6 m) long.
Russia
n paleontologists Yuri Bolotsky and Sergei Kurzanov
first described and named this dinosaur in 1991. The generic name is derived from the Amur River and the Greek
word sauros ("lizard"). The Amur (called Heilongjiang
or "Black Dragon River" in Chinese) forms the border of Russia and China
, and is near where this dinosaur's remains were found. There is one known species
(A. riabinini), named in honor of the late Russian paleontologist Anatoly Riabinin, who conducted the first Russian expeditions to recover dinosaur remains in the Amur region in 1916 and 1917.
All fossils of Amurosaurus have been recovered from a single bonebed locality, discovered in 1984 within the city limits of Blagoveschensk in the Amur Oblast
of far eastern Russia
. This bonebed is found in the Udurchukan Formation
, the oldest geologic formation
in the Tsagayan Group of far eastern Russia and northeastern China. This formation is thought to belong to the Maastrichtian
stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, which was deposited 65.5 million years ago in the equivalent of the Lancian
faunal stage of North America. The sediments were laid down in the floodplain
of a river
, which transported the fossils, but only a short distance, judging by the randomly assorted, disarticulated, but well-preserved bones within the bonebed, including fragile skull elements. Only a small section of the bonebed has been uncovered, but 90% of the remains found so far belong to lambeosaurines like Amurosaurus, mostly juveniles, with the rest belonging to other taxa, such as the hadrosaurine
Kerberosaurus
. Theropod teeth are also abundant, and there are many toothmarks on the bones, made by predators or scavenger
s.
The holotype
, or original specimen, consists of only a maxilla
(upper jaw bone), and a dentary
(lower jaw bone), both from the left side of the same individual. However, most of the other bones of the skull
and skeleton have also been preserved in the bonebed, albeit of many different individuals. This other material was described more recently, making Amurosaurus the most abundant and completely known Russian dinosaur (Godefroit et al., 2004).
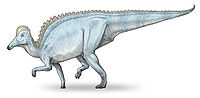 Amurosaurus is characterized by many autapomorphies
Amurosaurus is characterized by many autapomorphies
, or unique features, of the skull, as well as the sigmoid
al shape of the ulna
(a lower arm bone) when viewed from the front or side. Most other known lambeosaurines have hollow crests on the top of their skulls, and although the bones that would make up such a crest are unknown in this dinosaur, the bones of the roof of the skull are modified to support one, so it can be assumed that Amurosaurus was crested as well. As most of these features were described recently, as of early 2006, Amurosaurus has only been subjected to one cladistic analysis, which placed it as a basal
member of the lambeosaurine subfamily of hadrosaurs, but more derived than either Tsintaosaurus
or Jaxartosaurus
.
All known basal lambeosaurines come from Asia, which has led to the hypothesis
that lambeosaurines originated there and then later dispersed
across the Bering Strait
to North America
. Two derived
groups, the parasaurolophines (Parasaurolophus
, Charonosaurus
) and corythosaurs (Corythosaurus
, Nipponosaurus
) evolve
d later. As members of both groups are found in North America and Asia, there must have been further dispersal after their evolution, although in which direction that dispersal occurred is still unclear (Suzuki et al., 2004; Godefroit et al., 2004).
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of lambeosaurine
Lambeosaurinae
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.-Classification:Lambeosaurines have been split into Parasaurolophini and Corythosaurini . Corythosaurini and Parasaurolophini as terms entered the formal literature in Evans and Reisz's 2007 redescription of Lambeosaurus magnicristatus...
hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids or duck-billed dinosaurs are members of the family Hadrosauridae, and include ornithopods such as Edmontosaurus and Parasaurolophus. They were common herbivores in the Upper Cretaceous Period of what are now Asia, Europe and North America. They are descendants of the Upper...
dinosaur
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of animals of the clade and superorder Dinosauria. They were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates for over 160 million years, from the late Triassic period until the end of the Cretaceous , when the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event led to the extinction of...
found in the latest Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
period (65.5 million years ago) of eastern Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
. Like most lambeosaurs, it would have been a primarily biped
Biped
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs, or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning "two feet"...
al herbivore
Herbivore
Herbivores are organisms that are anatomically and physiologically adapted to eat plant-based foods. Herbivory is a form of consumption in which an organism principally eats autotrophs such as plants, algae and photosynthesizing bacteria. More generally, organisms that feed on autotrophs in...
with a "duckbill" shaped snout and a hollow crest on top of its head, although such a crest has not been found. Fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
bones of adults are rare, but an adult would most likely have been at least 20 feet (6 m) long.
Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n paleontologists Yuri Bolotsky and Sergei Kurzanov
Sergei Kurzanov
Sergei Kurzanov is a Russian paleontologist at the Paleontological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences. He is known mainly for his work in Mongolia and the ex-Soviet republics in Central Asia. In 1998, a species of iguanodont dinosaur from Mongolia was named Altirhinus kurzanovi in his...
first described and named this dinosaur in 1991. The generic name is derived from the Amur River and the Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
word sauros ("lizard"). The Amur (called Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang
For the river known in Mandarin as Heilong Jiang, see Amur River' is a province of the People's Republic of China located in the northeastern part of the country. "Heilongjiang" literally means Black Dragon River, which is the Chinese name for the Amur. The one-character abbreviation is 黑...
or "Black Dragon River" in Chinese) forms the border of Russia and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, and is near where this dinosaur's remains were found. There is one known species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
(A. riabinini), named in honor of the late Russian paleontologist Anatoly Riabinin, who conducted the first Russian expeditions to recover dinosaur remains in the Amur region in 1916 and 1917.
All fossils of Amurosaurus have been recovered from a single bonebed locality, discovered in 1984 within the city limits of Blagoveschensk in the Amur Oblast
Amur Oblast
Amur Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , situated about east of Moscow on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers. It shares its border with the Sakha Republic in the north, Khabarovsk Krai and the Jewish Autonomous Oblast in the east, People's Republic of China in the south, and Zabaykalsky...
of far eastern Russia
Russian Far East
Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean...
. This bonebed is found in the Udurchukan Formation
Udurchukan Formation
The Udurchukan Formation is a palaeontological formation located in Amur Region, Far East Russia. It dates to the Upper Cretaceous period....
, the oldest geologic formation
Geologic formation
A formation or geological formation is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy. A formation consists of a certain number of rock strata that have a comparable lithology, facies or other similar properties...
in the Tsagayan Group of far eastern Russia and northeastern China. This formation is thought to belong to the Maastrichtian
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, the latest age or upper stage of the Late Cretaceous epoch or Upper Cretaceous series, the Cretaceous period or system, and of the Mesozoic era or erathem. It spanned from 70.6 ± 0.6 Ma to 65.5 ± 0.3 Ma...
stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, which was deposited 65.5 million years ago in the equivalent of the Lancian
Lancian
-Geology:Terrestrial sedimentary strata from the Judithian to the Lancian are generally regressive through-out the entire sequence, so the preserved changes in fossil communities represent not only phylogenetic changes but ecological zones from the submontane habitats to near-sea level coastal...
faunal stage of North America. The sediments were laid down in the floodplain
Floodplain
A floodplain, or flood plain, is a flat or nearly flat land adjacent a stream or river that stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls and experiences flooding during periods of high discharge...
of a river
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
, which transported the fossils, but only a short distance, judging by the randomly assorted, disarticulated, but well-preserved bones within the bonebed, including fragile skull elements. Only a small section of the bonebed has been uncovered, but 90% of the remains found so far belong to lambeosaurines like Amurosaurus, mostly juveniles, with the rest belonging to other taxa, such as the hadrosaurine
Hadrosaurinae
Saurolophinae is a subfamily of hadrosaurid dinosaurs. Members of the subfamily derive from the Late Cretaceous of Antarctica, Argentina, Canada , China, Kazakhstan, Mexico, Russia, the United States and...
Kerberosaurus
Kerberosaurus
Kerberosaurus was a genus of hadrosaurine duckbill dinosaur from the late Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Tsagayan Formation of Blagoveschensk, Amur Region, Russia...
. Theropod teeth are also abundant, and there are many toothmarks on the bones, made by predators or scavenger
Scavenger
Scavenging is both a carnivorous and herbivorous feeding behavior in which individual scavengers search out dead animal and dead plant biomass on which to feed. The eating of carrion from the same species is referred to as cannibalism. Scavengers play an important role in the ecosystem by...
s.
The holotype
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example of an organism, known to have been used when the species was formally described. It is either the single such physical example or one of several such, but explicitly designated as the holotype...
, or original specimen, consists of only a maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
(upper jaw bone), and a dentary
Mandible
The mandible pronunciation or inferior maxillary bone forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place...
(lower jaw bone), both from the left side of the same individual. However, most of the other bones of the skull
Skull
The skull is a bony structure in the head of many animals that supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. A skull without a mandible is only a cranium. Animals that have skulls are called craniates...
and skeleton have also been preserved in the bonebed, albeit of many different individuals. This other material was described more recently, making Amurosaurus the most abundant and completely known Russian dinosaur (Godefroit et al., 2004).

Cladistics
Cladistics is a method of classifying species of organisms into groups called clades, which consist of an ancestor organism and all its descendants . For example, birds, dinosaurs, crocodiles, and all descendants of their most recent common ancestor form a clade...
, or unique features, of the skull, as well as the sigmoid
Sigmoid
Sigmoid means resembling the lower-case Greek letter sigma or the Latin letter S. Specific uses include:* Sigmoid function, a mathematical function* Sigmoid colon, part of the large intestine or colon...
al shape of the ulna
Ulna
The ulna is one of the two long bones in the forearm, the other being the radius. It is prismatic in form and runs parallel to the radius, which is shorter and smaller. In anatomical position The ulna is one of the two long bones in the forearm, the other being the radius. It is prismatic in form...
(a lower arm bone) when viewed from the front or side. Most other known lambeosaurines have hollow crests on the top of their skulls, and although the bones that would make up such a crest are unknown in this dinosaur, the bones of the roof of the skull are modified to support one, so it can be assumed that Amurosaurus was crested as well. As most of these features were described recently, as of early 2006, Amurosaurus has only been subjected to one cladistic analysis, which placed it as a basal
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, a basal clade is the earliest clade to branch in a larger clade; it appears at the base of a cladogram.A basal group forms an outgroup to the rest of the clade, such as in the following example:...
member of the lambeosaurine subfamily of hadrosaurs, but more derived than either Tsintaosaurus
Tsintaosaurus
Tsintaosaurus is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from China. It was about long, tall and weighed 3 tons. The type species is T. spinorhinus, first described by C. C...
or Jaxartosaurus
Jaxartosaurus
Jaxartosaurus is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur similar to Corythosaurus which lived during the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils were found in Kazakhstan and China. It had a large, helmet-like crest that it may have used for visual identification, or to vocalize with members of the same herd.The type...
.
All known basal lambeosaurines come from Asia, which has led to the hypothesis
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
that lambeosaurines originated there and then later dispersed
Biological dispersal
Biological dispersal refers to species movement away from an existing population or away from the parent organism. Through simply moving from one habitat patch to another, the dispersal of an individual has consequences not only for individual fitness, but also for population dynamics, population...
across the Bering Strait
Bering Strait
The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,...
to North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. Two derived
Derived
In phylogenetics, a derived trait is a trait that is present in an organism, but was absent in the last common ancestor of the group being considered. This may also refer to structures that are not present in an organism, but were present in its ancestors, i.e. traits that have undergone secondary...
groups, the parasaurolophines (Parasaurolophus
Parasaurolophus
Parasaurolophus is a genus of ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America during the Late Cretaceous Period, about 76.5–73 million years ago. It was an herbivore that walked both as a biped and a quadruped. Three species are recognized: P. walkeri , P. tubicen, and the...
, Charonosaurus
Charonosaurus
Charonosaurus |Charon]]'s lizard") is the name of a genus of dinosaur whose fossils were discovered by Godefroit, Zan & Jin in 2000 on the south bank of the Amur River, dividing China from Russia.-Description:...
) and corythosaurs (Corythosaurus
Corythosaurus
Corythosaurus is a genus of duck-billed dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period, about 77-76.5 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America...
, Nipponosaurus
Nipponosaurus
Nipponosaurus is a lambeosaurine hadrosaurid from Asia.The holotype was discovered in November 1934 during the construction of a hospital for the Kawakami colliery of the Mitsui Mining Company on Karafuto Prefecture , and additional material belonging to the specimen was recovered...
) evolve
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
d later. As members of both groups are found in North America and Asia, there must have been further dispersal after their evolution, although in which direction that dispersal occurred is still unclear (Suzuki et al., 2004; Godefroit et al., 2004).

