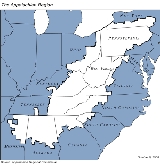
Appalachia
Overview
Appalachia is a term used to describe a cultural region in the eastern United States
that stretches from the Southern Tier
of New York
state to northern Alabama
, Mississippi
, and Georgia
. While the Appalachian Mountains
stretch from Belle Isle
in Canada
to Cheaha Mountain
in the U.S. state of Alabama
, the cultural region of Appalachia typically refers only to the central and southern portions of the range. As of 2005, the region was home to approximately 23 million people.
Since its recognition as a distinctive region in the late 19th century, Appalachia has been a source of enduring myths and distortions regarding the isolation, temperament, and behavior of its inhabitants.
Eastern United States
The Eastern United States, the American East, or simply the East is traditionally defined as the states east of the Mississippi River. The first two tiers of states west of the Mississippi have traditionally been considered part of the West, but can be included in the East today; usually in...
that stretches from the Southern Tier
Southern Tier
The Southern Tier is a geographical term that refers to the counties of New York State west of the Catskill Mountains along the northern border of Pennsylvania. It is a loosely defined term that generally includes the counties that border Pennsylvania west of Delaware County inclusive...
of New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
state to northern Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
, Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
, and Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
. While the Appalachian Mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
stretch from Belle Isle
Belle Isle (Newfoundland and Labrador)
Belle Isle is an uninhabited island just off the coast of Labrador and north of Newfoundland at the Atlantic entrance to the Strait of Belle Isle which takes its name...
in Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
to Cheaha Mountain
Cheaha Mountain
Cheaha Mountain , often called Mount Cheaha, is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Alabama. It is located a few miles north-west of the town of Delta in scenic Cheaha State Park, which contains a lodge, restaurant, and other amenities....
in the U.S. state of Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
, the cultural region of Appalachia typically refers only to the central and southern portions of the range. As of 2005, the region was home to approximately 23 million people.
Since its recognition as a distinctive region in the late 19th century, Appalachia has been a source of enduring myths and distortions regarding the isolation, temperament, and behavior of its inhabitants.

