
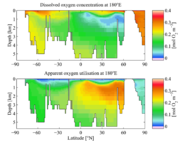
Apparent oxygen utilisation
Encyclopedia
Freshwater
Fresh water is naturally occurring water on the Earth's surface in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, bogs, ponds, lakes, rivers and streams, and underground as groundwater in aquifers and underground streams. Fresh water is generally characterized by having low concentrations of dissolved salts and...
or marine
Marine (ocean)
Marine is an umbrella term. As an adjective it is usually applicable to things relating to the sea or ocean, such as marine biology, marine ecology and marine geology...
systems apparent oxygen utilisation (AOU) is the difference between the measured dissolved oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
concentration and its equilibrium
Dynamic equilibrium
A dynamic equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction ceases to change its ratio of reactants/products, but substances move between the chemicals at an equal rate, meaning there is no net change. It is a particular example of a system in a steady state...
saturation
Oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation or dissolved oxygen is a relative measure of the amount of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water.It has particular significance in medicine and...
concentration in water with the same physical and chemical properties. Such differences typically occur when biological activity acts to change the ambient concentration of oxygen. For example, primary production
Primary production
400px|thumb|Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September [[1997]] to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential, and not an actual estimate of it...
liberates oxygen and increases its concentration, while respiration
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate , and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that involve...
consumes it and decreases its concentration.
Consequently, the AOU of a water sample represents the sum of the biological activity that the sample has experienced since it was last in equilibrium with the atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
.
In shallow water systems (e.g. lake
Lake
A lake is a body of relatively still fresh or salt water of considerable size, localized in a basin, that is surrounded by land. Lakes are inland and not part of the ocean and therefore are distinct from lagoons, and are larger and deeper than ponds. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams,...
s), the full water column is generally in close contact with the atmosphere, so oxygen concentrations are typically close to saturation: AOU values are low.
In deep water systems (e.g. ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
s), water can be out of contact with the atmosphere for extremely long periods of time (years, decades, centuries) and large AOU values are possible.
See also
- Biological pumpBiological pumpIn oceanic biogeochemistry, the biological pump is the sum of a suite of biologically-mediated processes that transport carbon from the surface euphotic zone to the ocean's interior.-Overview:...
- EutrophicationEutrophicationEutrophication or more precisely hypertrophication, is the movement of a body of water′s trophic status in the direction of increasing plant biomass, by the addition of artificial or natural substances, such as nitrates and phosphates, through fertilizers or sewage, to an aquatic system...
- HypoxiaHypoxia (environmental)Hypoxia, or oxygen depletion, is a phenomenon that occurs in aquatic environments as dissolved oxygen becomes reduced in concentration to a point where it becomes detrimental to aquatic organisms living in the system...
- RemineralisationRemineralisationIn biogeochemistry, remineralisation refers to the transformation of organic molecules to inorganic forms, typically mediated by biological activity....
- World Ocean AtlasWorld Ocean AtlasThe World Ocean Atlas is a data product of the Ocean Climate Laboratory of the National Oceanographic Data Center . The WOA consists of a climatology of fields of in situ ocean properties for the World Ocean...

