
Dynamic equilibrium
Encyclopedia
A dynamic equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction
ceases to change its ratio of reactants/products, but substances move between the chemicals at an equal rate, meaning there is no net change. It is a particular example of a system in a steady state
. In thermodynamics
a closed system
is in thermodynamic equilibrium
when reactions occur at such rates that the composition of the mixture does not change with time. Reactions do in fact occur, sometimes vigorously, but to such an extent that changes in composition cannot be observed. Equilibrium constants can be expressed in terms of the rate constants for elementary reactions.
in the liquid phase has a particular value. If half of the liquid is poured out and the bottle is sealed, carbon dioxide will leave the liquid phase at an ever decreasing rate and the partial pressure
of carbon dioxide in the gas phase will increase until equilibrium is reached. At that point a molecule of CO2 may leave the liquid phase, but then another molecule of CO2 will pass from the gas to the liquid. At equilibrium the rate of loss of CO2 is equal to the rate of gain. In this case, the equilibrium concentration of CO2 in the liquid is given by Henry's law
, which states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure
of that gas above the liquid. This relationship is written as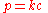
where k is a temperature-dependent constant, p is the partial pressure and c is the concentration of the dissolved gas in the liquid. Thus, the partial pressure of CO2 in the gas has increased until Henry's law is obeyed. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid has decreased and the drink has lost some of its fizz.
Henry's law may be derived by setting the chemical potential
s of carbon dioxide in the two phases to be equal to each other. Equality of chemical potential defines chemical equilibrium
. Other constants for dynamic equilibrium involving phase changes include partition coefficient
and solubility product. Raoult's law defines the equilibrium vapor pressure
of an ideal solution
.
Dynamic equilibria can also exist in a homogeneous system. A simple example occurs with acid-base equilibria such as the "dissociation" of acetic acid
, in aqueous solution.
At equilibrium the concentration quotient, K, the acid dissociation constant
, is constant (subject to some conditions)
In this case, the forward reaction involves the liberation of some proton
s from acetic acid molecules and the backward reaction involves the formation of acetic acid molecules when an acetate ion accepts a proton. Equilibrium is attained when the sum of chemical potentials of the species on the left-hand side of the equilibrium expression is equal to the sum of chemical potentials of the species on the right-hand side. At the same time the rates of forward and backward reactions are equal to each other. Equilibria involving the formation of chemical complexes are also dynamic equilibria and concentrations are governed by the stability constants of complexes
.
Dynamic equilibria can also occur in the gas phase as, for example, when nitrogen dioxide
dimerizes.
In the gas phase, square brackets are not used as these indicate a concentration, instead a capitalised P is used to indicate partial pressure.
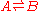
there are two reactions to consider, the forward reaction in which the species A is converted into B and the backward reaction in which B is converted into A. If both reactions are elementary reaction
s, then the rate of reaction is given by
where kf is the rate constant for the forward reaction and kb is the rate constant for the backward reaction and the square brackets, [..] denote concentration
. If only A is present at the beginning, time t=0, with a concentration [A]0, the sum of the two concentrations, [A]t and [B]t, at time t, will be equal to [A]0.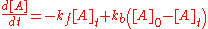
The solution to this differential equation is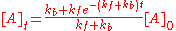
and is illustrated at the right. As time tends towards infinity, the concentrations [A]t and [B]t tend towards constant values. Let t approach infinity, that is, t→∞, in the expression above: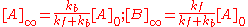
In practice, concentration changes will not be measurable after . Since the concentrations do not change thereafter, they are, by definition
. Since the concentrations do not change thereafter, they are, by definition
, equilibrium concentrations. Now, the equilibrium constant for the reaction is defined as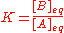
It follows that the equilibrium constant is numerically equal to the quotient of the rate constants.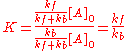
In general they may be more than one forward reaction and more than one backward reaction. Atkins states that, for a general reaction, the overall equilibrium constant is related to the rate constants of the elementary reactions by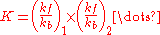
Reversible reaction
A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that results in an equilibrium mixture of reactants and products. For a reaction involving two reactants and two products this can be expressed symbolically as...
ceases to change its ratio of reactants/products, but substances move between the chemicals at an equal rate, meaning there is no net change. It is a particular example of a system in a steady state
Steady state
A system in a steady state has numerous properties that are unchanging in time. This implies that for any property p of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero:...
. In thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
a closed system
Closed system
-In physics:In thermodynamics, a closed system can exchange energy , but not matter, with its surroundings.In contrast, an isolated system cannot exchange any of heat, work, or matter with the surroundings, while an open system can exchange all of heat, work and matter.For a simple system, with...
is in thermodynamic equilibrium
Thermodynamic equilibrium
In thermodynamics, a thermodynamic system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium when it is in thermal equilibrium, mechanical equilibrium, radiative equilibrium, and chemical equilibrium. The word equilibrium means a state of balance...
when reactions occur at such rates that the composition of the mixture does not change with time. Reactions do in fact occur, sometimes vigorously, but to such an extent that changes in composition cannot be observed. Equilibrium constants can be expressed in terms of the rate constants for elementary reactions.
Examples
In a new bottle of cola the concentration of carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
in the liquid phase has a particular value. If half of the liquid is poured out and the bottle is sealed, carbon dioxide will leave the liquid phase at an ever decreasing rate and the partial pressure
Partial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
of carbon dioxide in the gas phase will increase until equilibrium is reached. At that point a molecule of CO2 may leave the liquid phase, but then another molecule of CO2 will pass from the gas to the liquid. At equilibrium the rate of loss of CO2 is equal to the rate of gain. In this case, the equilibrium concentration of CO2 in the liquid is given by Henry's law
Henry's law
In physics, Henry's law is one of the gas laws formulated by William Henry in 1803. It states that:An equivalent way of stating the law is that the solubility of a gas in a liquid at a particular temperature is proportional to the pressure of that gas above the liquid...
, which states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure
Partial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
of that gas above the liquid. This relationship is written as

where k is a temperature-dependent constant, p is the partial pressure and c is the concentration of the dissolved gas in the liquid. Thus, the partial pressure of CO2 in the gas has increased until Henry's law is obeyed. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid has decreased and the drink has lost some of its fizz.
Henry's law may be derived by setting the chemical potential
Chemical potential
Chemical potential, symbolized by μ, is a measure first described by the American engineer, chemist and mathematical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs. It is the potential that a substance has to produce in order to alter a system...
s of carbon dioxide in the two phases to be equal to each other. Equality of chemical potential defines chemical equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
. Other constants for dynamic equilibrium involving phase changes include partition coefficient
Partition coefficient
In chemistry and the pharmaceutical sciences, a partition- or distribution coefficient is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in the two phases of a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. The terms "gas/liquid partition coefficient" and "air/water partition coefficient" are...
and solubility product. Raoult's law defines the equilibrium vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
of an ideal solution
Ideal solution
In chemistry, an ideal solution or ideal mixture is a solution with thermodynamic properties analogous to those of a mixture of ideal gases. The enthalpy of solution is zero as is the volume change on mixing; the closer to zero the enthalpy of solution is, the more "ideal" the behavior of the...
.
Dynamic equilibria can also exist in a homogeneous system. A simple example occurs with acid-base equilibria such as the "dissociation" of acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
, in aqueous solution.
- CH3CO2H CH3CO2- + H+
At equilibrium the concentration quotient, K, the acid dissociation constant
Acid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
, is constant (subject to some conditions)

In this case, the forward reaction involves the liberation of some proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s from acetic acid molecules and the backward reaction involves the formation of acetic acid molecules when an acetate ion accepts a proton. Equilibrium is attained when the sum of chemical potentials of the species on the left-hand side of the equilibrium expression is equal to the sum of chemical potentials of the species on the right-hand side. At the same time the rates of forward and backward reactions are equal to each other. Equilibria involving the formation of chemical complexes are also dynamic equilibria and concentrations are governed by the stability constants of complexes
Stability constants of complexes
A stability constant is an equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex in solution. It is a measure of the strength of the interaction between the reagents that come together to form the complex...
.
Dynamic equilibria can also occur in the gas phase as, for example, when nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula it is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year. This reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor and is a prominent...
dimerizes.
- 2NO2 N2O4;
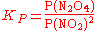
In the gas phase, square brackets are not used as these indicate a concentration, instead a capitalised P is used to indicate partial pressure.
Relationship between equilibrium and rate constants
In a simple reaction such as the isomerization:
there are two reactions to consider, the forward reaction in which the species A is converted into B and the backward reaction in which B is converted into A. If both reactions are elementary reaction
Elementary reaction
An elementary reaction is a chemical reaction in which one or more of the chemical species react directly to form products in a single reaction step and with a single transition state....
s, then the rate of reaction is given by

where kf is the rate constant for the forward reaction and kb is the rate constant for the backward reaction and the square brackets, [..] denote concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
. If only A is present at the beginning, time t=0, with a concentration [A]0, the sum of the two concentrations, [A]t and [B]t, at time t, will be equal to [A]0.
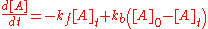
The solution to this differential equation is
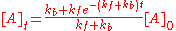
and is illustrated at the right. As time tends towards infinity, the concentrations [A]t and [B]t tend towards constant values. Let t approach infinity, that is, t→∞, in the expression above:
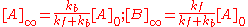
In practice, concentration changes will not be measurable after
 . Since the concentrations do not change thereafter, they are, by definition
. Since the concentrations do not change thereafter, they are, by definitionEquilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at...
, equilibrium concentrations. Now, the equilibrium constant for the reaction is defined as
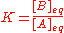
It follows that the equilibrium constant is numerically equal to the quotient of the rate constants.
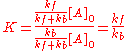
In general they may be more than one forward reaction and more than one backward reaction. Atkins states that, for a general reaction, the overall equilibrium constant is related to the rate constants of the elementary reactions by
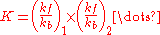
See also
- Equilibrium chemistryEquilibrium chemistryEquilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at...
- Static equilibrium
- Chemical equilibriumChemical equilibriumIn a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
- Radiative equilibriumRadiative equilibriumRadiative equilibrium is one of the several requirements for thermodynamic equilibrium, but it can occur in the absence of thermodynamic equilibrium. There are various types of radiative equilibrium, which is itself a kind of dynamic equilibrium....

