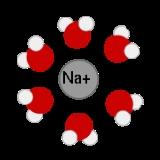
Aqueous solution
Encyclopedia
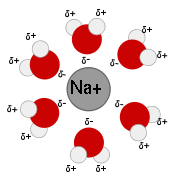
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
in which the solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
is water. It is usually shown in chemical equations by appending aq to the relevant formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
, such as NaCl(aq). The word aqueous means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved
Solvation
Solvation, also sometimes called dissolution, is the process of attraction and association of molecules of a solvent with molecules or ions of a solute...
in water. As water is an excellent solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
.
Substances which are hydrophobic ('water fearing') often do not dissolve well in water whereas those that hydrophilic ('water-loving') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance would be sodium chloride
Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaCl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of the ocean and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms...
(ordinary table salt). Acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
s and base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
s are aqueous solutions, as part of their Arrhenius definitions
Acid-base reaction theories
An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. Several concepts that provide alternative definitions for the reaction mechanisms involved and their application in solving related problems exist...
.
The ability of a substance to dissolve in water is determined by whether the substance can match or exceed the strong attractive forces that water molecules generate between themselves. If the substance lacks the ability to dissolve in water the molecules form a precipitate
Precipitation (chemistry)
Precipitation is the formation of a solid in a solution or inside anothersolid during a chemical reaction or by diffusion in a solid. When the reaction occurs in a liquid, the solid formed is called the precipitate, or when compacted by a centrifuge, a pellet. The liquid remaining above the solid...
.
Aqueous solutions that conduct electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
efficiently contain strong electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
s, while ones that conduct poorly are considered to have weak electrolytes. Those strong electrolytes are substances that are completely ionized
Ionization
Ionization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
in water, whereas the weak electrolytes exhibit only a small degree of ionization in water.
Nonelectrolytes are substances that dissolve in water, but which maintain their molecular integrity (do not dissociate into ions). Examples include sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
, urea
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
, glycerol
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids...
, and methylsulfonylmethane
Methylsulfonylmethane
Methylsulfonylmethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula 2SO2. It is also known by several other names including DMSO2, methyl sulfone, and dimethyl sulfone. This colorless solid features the sulfonyl functional group and is considered relatively inert chemically...
(MSM).
When performing calculations regarding the reacting
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
of one or more aqueous solutions, one generally must know the concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
, or molarity, of the aqueous solutions. Solution concentration is given in terms of the form of the solute prior to it dissolving.
See also
- SolubilitySolubilitySolubility is the property of a solid, liquid, or gaseous chemical substance called solute to dissolve in a solid, liquid, or gaseous solvent to form a homogeneous solution of the solute in the solvent. The solubility of a substance fundamentally depends on the used solvent as well as on...
- Dissociation (chemistry)Dissociation (chemistry)Dissociation in chemistry and biochemistry is a general process in which ionic compounds separate or split into smaller particles, ions, or radicals, usually in a reversible manner...
- Acid-base reaction theoriesAcid-base reaction theoriesAn acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. Several concepts that provide alternative definitions for the reaction mechanisms involved and their application in solving related problems exist...

