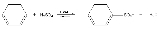
Aromatic sulfonation
Overview
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
in which a hydrogen atom on an arene
Aromatic hydrocarbon
An aromatic hydrocarbon or arene is a hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds between carbon atoms. The term 'aromatic' was assigned before the physical mechanism determining aromaticity was discovered, and was derived from the fact that many of the compounds have a sweet scent...
is replaced by a sulfonic acid
Sulfonic acid
Sulfonic acid usually refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula RS2–OH, where R is an alkyl or aryl. The formal part of acid, HS2–OH, are formally derivatives of the "parent" inorganic compound with the formula HSO2.-Preparation:Sulfonic acid is...
functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
in an electrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution EAS is an organic reaction in which an atom, usually hydrogen, appended to an aromatic system is replaced by an electrophile...
.
Sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. In the gaseous form, this species is a significant pollutant, being the primary agent in acid rain. It is prepared on massive scales as a precursor to sulfuric acid.-Structure and bonding:Gaseous SO3 is a trigonal planar molecule of...
is the electrophile
Electrophile
In general electrophiles are positively charged species that are attracted to an electron rich centre. In chemistry, an electrophile is a reagent attracted to electrons that participates in a chemical reaction by accepting an electron pair in order to bond to a nucleophile...
in this electrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution EAS is an organic reaction in which an atom, usually hydrogen, appended to an aromatic system is replaced by an electrophile...
generated from concentrated sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
(or fuming sulfuric acid) when heated. With benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
as substrate the reaction product is benzenesulfonic acid
Benzenesulfonic acid
Benzenesulfonic acid is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SO3H. It is the simplest aromatic sulfonic acid. It forms colorless deliquescent sheet crystals or a white waxy solid that is soluble in water and ethanol, slightly soluble in benzene and insoluble in carbon disulfide and diethyl...
.
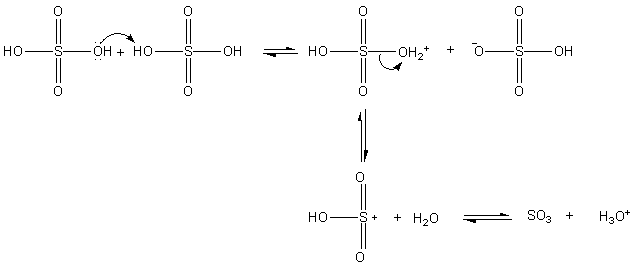
In contrast to aromatic nitration and other electrophilic aromatic substitutions this reaction is reversible
Reversible reaction
A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that results in an equilibrium mixture of reactants and products. For a reaction involving two reactants and two products this can be expressed symbolically as...
.

