
Astronaut Group 5
Encyclopedia
NASA
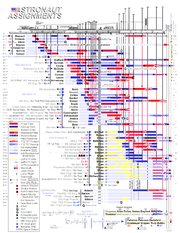
's Astronaut Group 5 (the 'Original 19') selected by NASA
in April 1966. Of the six Lunar Module Pilots that walked on the Moon, three came from Group 5. The group as a whole is roughly split between the half who flew to the Moon (nine in all) and the other half who flew Skylab
and Shuttle
, providing the core of Shuttle Commanders early in that program. This group is also distinctive in being the only time when NASA
hired a person into the astronaut corps who had already earned astronaut wings, X-15
pilot Joe Engle.
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
's Astronaut Group 5 (the 'Original 19') selected by NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
in April 1966. Of the six Lunar Module Pilots that walked on the Moon, three came from Group 5. The group as a whole is roughly split between the half who flew to the Moon (nine in all) and the other half who flew Skylab
Skylab
Skylab was a space station launched and operated by NASA, the space agency of the United States. Skylab orbited the Earth from 1973 to 1979, and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and other systems. It was launched unmanned by a modified Saturn V rocket, with a mass of...
and Shuttle
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
, providing the core of Shuttle Commanders early in that program. This group is also distinctive in being the only time when NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
hired a person into the astronaut corps who had already earned astronaut wings, X-15
North American X-15
The North American X-15 rocket-powered aircraft/spaceplane was part of the X-series of experimental aircraft, initiated with the Bell X-1, that were made for the USAAF/USAF, NACA/NASA, and the USN. The X-15 set speed and altitude records in the early 1960s, reaching the edge of outer space and...
pilot Joe Engle.

- Vance D. BrandVance D. BrandVance DeVoe Brand is an engineer and former test pilot and NASA astronaut. He served as command module pilot during the first U.S.-Soviet joint space flight in 1975, and as commander of three space shuttle missions....
, ex-USMC, (4 flights)
- Skylab RescueSkylab RescueBrand flew in 1975 during the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project as command module pilot, later commanding three Space Shuttle missions . Lind would wait another decade before he flew as a mission specialist on STS-51-B in 1985.-External links:* * * * * * *...
— never flown - Apollo-Soyuz Test ProjectApollo-Soyuz Test Project-Backup crew:-Crew notes:Jack Swigert had originally been assigned as the command module pilot for the ASTP prime crew, but prior to the official announcement he was removed as punishment for his involvement in the Apollo 15 postage stamp scandal.-Soyuz crew:...
— July 1975 — Command Module Pilot — First joint U.S./U.S.S.R. mission - STS-5STS-5STS-5 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission, the fifth shuttle mission overall and the fifth flight of the Space Shuttle Columbia. It was the first shuttle mission to deploy communications satellites into orbit...
— November 1982 — Commander — SBS-CSatellite Business SystemsSatellite Business Systems, abbreviated as SBS, was a company founded by IBM, Aetna, Comsat , that provided private professional satellite communications through its SBS fleet of FSS geosynchronous satellites, and was the first company to do so.SBS was founded on December 15, 1975 by the...
and Anik C-3Anik (satellite)The Anik satellites are geostationary communications satellites launched by Telesat Canada for television in Canada. In Inuktitut, Anik means "little brother".-The Satellites:-Anik A:...
satellite deployment mission - STS-41-BSTS-41-BSTS-41-B was the tenth NASA Space Shuttle mission, launching on 3 February 1984 and landing on 11 February. It was the fourth flight of the Space Shuttle Challenger. Following STS-9, the flight numbering system for the Space Shuttle program was changed...
— February 1984 — Commander — Westar 6WestarWestar was the name for the fleet of geosynchronous communications satellites operating in the C band which were launched by Western Union from 1974 to 1984. There were seven Westar satellites in all, with five of them launched and operating under the Westar name.In many international recognized...
and Palapa B2PalapaPalapa is a series of communication satellites owned by Indosat, an Indonesian telecommunication company.The name Palapa also alludes to "Sumpah Palapa" the oath taken by Gajah Mada, a 14th century Prime Minister of the Javanese Majapahit Empire described in the Pararaton...
satellite deployment mission - STS-35STS-35-Crew notes:Prior to the Challenger disaster, this mission was slated to launch in March 1986 as STS-61-E. Jon McBride was originally assigned to command this mission, which would have been his second spaceflight. He chose to retire from NASA in May 1989 and was replaced as mission commander by...
— December 1990 — Commander — SpacelabSpacelabSpacelab was a reusable laboratory used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory consisted of multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier and other related hardware housed in the Shuttle's cargo bay...
mission
- John S. Bull, USN
- Resigned from the astronaut corps after learning that he was suffering from pulmonary disease.
- Gerald P. CarrGerald P. CarrGerald Paul Carr is an engineer, retired United States Marine Corps colonel and former NASA astronaut. He was commander of Skylab 4, the third and final manned visit to the Skylab Orbital Workshop, from November 16, 1973 to February 8, 1974.-Biography:Carr was born in Denver, Colorado on August...
, USMC, (1 flight)
- Skylab 4Skylab 4Skylab 4 was the fourth Skylab mission and placed the third and final crew on board the space station. The mission started November 16, 1973 with the launch of three astronauts on a Saturn IB rocket, and lasted 84 days, 1 hour and 16 minutes...
— November 1973–February 1974 — Commander — Third crew of the SkylabSkylabSkylab was a space station launched and operated by NASA, the space agency of the United States. Skylab orbited the Earth from 1973 to 1979, and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and other systems. It was launched unmanned by a modified Saturn V rocket, with a mass of...
space stationSpace stationA space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing...
- Charles M. Duke, Jr, USAF, (1 flight)
- Apollo 16Apollo 16Young and Duke served as the backup crew for Apollo 13; Mattingly was slated to be the Apollo 13 command module pilot until being pulled from the mission due to his exposure to rubella through Duke.-Backup crew:...
— April 1972 — Lunar Module Pilot — Fifth manned lunar landing; tenth person to walk on the moon
- Joseph H. Engle, USAF, (2 flights + ALT)
- ALTApproach and Landing Tests-Crew 2:This crew later flew on STS-2.-Shuttle Carrier Aircraft:In addition to the two assigned shuttle crews, who would alternate crewing the orbiter, a single flight crew was attached to the Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft for the entire program:...
— February through October 1977 - STS-2STS-2STS-2 was a Space Shuttle mission conducted by NASA, using the Space Shuttle Columbia. The mission launched on 12 November 1981. It was the second shuttle mission overall, and was also the second mission for Columbia...
— November 1981 — Commander — Remote Manipulator System testing - STS-51-ISTS-51-ISTS-51-I was the twentieth mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program and the sixth flight of Space Shuttle Discovery. During the mission, Discovery deployed three communications satellites into orbit...
— August 1985 — Commander — AUSSAT-I, ASC-I, and Syncom IV-4SyncomSyncom started as a 1961 NASA program for active geosynchronous communication satellites, all of which were developed and manufactured by Hughes Space and Communications...
satellite deployment; Syncom IV-3 repair mission - Was replaced as the Lunar Module Pilot for Apollo 17Apollo 17Apollo 17 was the eleventh and final manned mission in the American Apollo space program. Launched at 12:33 a.m. EST on December 7, 1972, with a three-member crew consisting of Commander Eugene Cernan, Command Module Pilot Ronald Evans, and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt, Apollo 17 remains the...
by geologist Harrison SchmittHarrison SchmittHarrison Hagan "Jack" Schmitt is an American geologist, a retired NASA astronaut, university professor, and a former U.S. senator from New Mexico....
after Apollo 18Apollo 18Apollo 18 may refer to:* One of the canceled Apollo missions of the American Apollo lunar program* The officially unnumbered Apollo spacecraft used in the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project* Apollo 18 , a 1992 album by They Might Be Giants...
had been canceled. - Engle was the only shuttle pilot who had prior hypersonic flight experience, having earned his astronaut wings flying the X-15North American X-15The North American X-15 rocket-powered aircraft/spaceplane was part of the X-series of experimental aircraft, initiated with the Bell X-1, that were made for the USAAF/USAF, NACA/NASA, and the USN. The X-15 set speed and altitude records in the early 1960s, reaching the edge of outer space and...
rocket plane.
- Ronald E. Evans, JrRonald EvansRonald Ellwin Evans, Jr. was a NASA astronaut and one of only 24 people to have flown to the Moon. He also served as a captain in the United States Navy....
, USN, (1 flight)
- Apollo 17Apollo 17Apollo 17 was the eleventh and final manned mission in the American Apollo space program. Launched at 12:33 a.m. EST on December 7, 1972, with a three-member crew consisting of Commander Eugene Cernan, Command Module Pilot Ronald Evans, and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt, Apollo 17 remains the...
— December 1972 — Command Module Pilot — Last manned lunar landing
- Edward G. Givens, JrEdward GivensEdward Galen "Ed" Givens Jr was an United States Air Force officer and a NASA astronaut. He was selected in 1966 by NASA as a member of the 'Original 19' group....
, USAF
- Killed in automobile accident in 1967 after serving on the Apollo 7Apollo 7Apollo 7 was the first manned mission in the American Apollo space program, and the first manned US space flight after a cabin fire killed the crew of what was to have been the first manned mission, AS-204 , during a launch pad test in 1967...
support crew.
- Fred W. Haise, JrFred HaiseFred Wallace Haise, Jr. is an engineer and former NASA astronaut. He is one of only 24 people to have flown to the Moon. Having flown on Apollo 13, Haise was to be the sixth human to walk on the Moon, but the mission did not land due to a failure aboard the spacecraft.-Early life and...
, ex-USMC, (1 flight + ALT)
- Apollo 13Apollo 13Apollo 13 was the seventh manned mission in the American Apollo space program and the third intended to land on the Moon. The craft was launched on April 11, 1970, at 13:13 CST. The landing was aborted after an oxygen tank exploded two days later, crippling the service module upon which the Command...
— April 1970 — Lunar Module Pilot — Aborted lunar landing; would have been the sixth person to walk on the moon - Slated to land as Commander of Apollo 19
- ALTApproach and Landing Tests-Crew 2:This crew later flew on STS-2.-Shuttle Carrier Aircraft:In addition to the two assigned shuttle crews, who would alternate crewing the orbiter, a single flight crew was attached to the Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft for the entire program:...
— February through October 1977 - Was to command the original STS-2 flight to rescue SkylabSkylabSkylab was a space station launched and operated by NASA, the space agency of the United States. Skylab orbited the Earth from 1973 to 1979, and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and other systems. It was launched unmanned by a modified Saturn V rocket, with a mass of...
in 1979.
- James B. IrwinJames IrwinJames Benson Irwin was an American astronaut and engineer. He served as Lunar Module pilot for Apollo 15, the fourth human lunar landing; he was the eighth person to walk on the Moon.-Early life:...
, USAF, (1 flight)
- Apollo 15Apollo 15Apollo 15 was the ninth manned mission in the American Apollo space program, the fourth to land on the Moon and the eighth successful manned mission. It was the first of what were termed "J missions", long duration stays on the Moon with a greater focus on science than had been possible on previous...
— July 1971 — Lunar Module Pilot — Fourth manned lunar landing; eighth person to walk on the moon
- Don L. Lind, ex-USN, (1 flight)
- Skylab RescueSkylab RescueBrand flew in 1975 during the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project as command module pilot, later commanding three Space Shuttle missions . Lind would wait another decade before he flew as a mission specialist on STS-51-B in 1985.-External links:* * * * * * *...
— never flown - STS-51-BSTS-51-BSTS 51-B was the seventeenth flight of NASA's Space Shuttle program, and the seventh flight of Space Shuttle Challenger. The launch of Challenger on 29 April 1985 was delayed by 2 minutes and 18 seconds, due to a launch processing failure. Challenger was initially rolled out to the pad to launch on...
— April 1985 — Mission specialist — SpacelabSpacelabSpacelab was a reusable laboratory used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory consisted of multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier and other related hardware housed in the Shuttle's cargo bay...
mission - His first mission in 1985 came 19 years after being selected as an astronaut, longer than any other American astronaut.
- Jack R. Lousma, USMC, (2 flights)
- Skylab 3Skylab 3Skylab 3 was the second manned mission to Skylab. The Skylab 3 mission started July 28, 1973, with the launch of three astronauts on the Saturn IB rocket, and lasted 59 days, 11 hours and 9 minutes...
— July–September 1973 — Pilot — Second crew of the SkylabSkylabSkylab was a space station launched and operated by NASA, the space agency of the United States. Skylab orbited the Earth from 1973 to 1979, and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and other systems. It was launched unmanned by a modified Saturn V rocket, with a mass of...
space stationSpace stationA space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing... - STS-3STS-3STS-3 was NASA's third Space Shuttle mission, and was the third mission for the Space Shuttle Columbia. It was the first shuttle launch with an unpainted external tank, and the only mission to land at the White Sands Space Harbor near Las Cruces, New Mexico.-Crew:-Backup crew:-Mission...
— March 1982 — Commander — Research and development flight
- T. Kenneth Mattingly, II, USN, (3 flights)
- Apollo 16Apollo 16Young and Duke served as the backup crew for Apollo 13; Mattingly was slated to be the Apollo 13 command module pilot until being pulled from the mission due to his exposure to rubella through Duke.-Backup crew:...
— April 1972 — Command Module Pilot — Fifth manned lunar landing - STS-4STS-4STS-4 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission, using the Space Shuttle Columbia. The mission launched on 27 June 1982 and landed a week later on 4 July. STS-4 was the fourth shuttle mission overall, and was also the fourth mission for the Columbia.-Crew:...
— June 1982 — Commander — Research and development flight - STS-51-CSTS-51-CSTS-51-C was the 15th flight of NASA's Space Shuttle program, and the third flight of Space Shuttle Discovery. It was also the first shuttle mission to deploy a dedicated United States Department of Defense payload, and as such many mission details remain classified...
— January 1985 — Commander — United States Department of DefenseUnited States Department of DefenseThe United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
mission; deployed USA-8 (Magnum 1)Magnum (satellite)Magnum is the code name for a class of SIGINT spy satellites reportedly operated by the National Reconnaissance Office for the United States Central Intelligence Agency... - Was the original Command Module Pilot for Apollo 13Apollo 13Apollo 13 was the seventh manned mission in the American Apollo space program and the third intended to land on the Moon. The craft was launched on April 11, 1970, at 13:13 CST. The landing was aborted after an oxygen tank exploded two days later, crippling the service module upon which the Command...
, but was grounded due to exposure to rubellaRubellaRubella, commonly known as German measles, is a disease caused by the rubella virus. The name "rubella" is derived from the Latin, meaning little red. Rubella is also known as German measles because the disease was first described by German physicians in the mid-eighteenth century. This disease is...
, which he was not immune to.
- Bruce McCandless IIBruce McCandless IIBruce McCandless II is a former naval aviator with the United States Navy and former NASA astronaut. During the first of his two Space Shuttle missions he made the first ever untethered free flight, using the Manned Maneuvering Unit.-Education:McCandless is the son of Bruce McCandless, a decorated...
, USN, (2 flights)
- STS-41-BSTS-41-BSTS-41-B was the tenth NASA Space Shuttle mission, launching on 3 February 1984 and landing on 11 February. It was the fourth flight of the Space Shuttle Challenger. Following STS-9, the flight numbering system for the Space Shuttle program was changed...
— February 1984 — Mission specialist — Westar 6WestarWestar was the name for the fleet of geosynchronous communications satellites operating in the C band which were launched by Western Union from 1974 to 1984. There were seven Westar satellites in all, with five of them launched and operating under the Westar name.In many international recognized...
and Palapa B2PalapaPalapa is a series of communication satellites owned by Indosat, an Indonesian telecommunication company.The name Palapa also alludes to "Sumpah Palapa" the oath taken by Gajah Mada, a 14th century Prime Minister of the Javanese Majapahit Empire described in the Pararaton...
satellite deployment mission; first untethered EVAExtra-vehicular activityExtra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon... - STS-31STS-31STS-31 was the thirty-fifth mission of the American Space Shuttle program, which launched the Hubble Space Telescope astronomical observatory into Earth orbit...
— April 1990 — Mission specialist — Hubble Space TelescopeHubble Space TelescopeThe Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
deployment mission
- Edgar D. Mitchell, USN, (1 flight)
- Apollo 14Apollo 14Apollo 14 was the eighth manned mission in the American Apollo program, and the third to land on the Moon. It was the last of the "H missions", targeted landings with two-day stays on the Moon with two lunar EVAs, or moonwalks....
— January 1971 — Lunar Module Pilot — Third manned lunar landing; sixth person to walk on the moon
- William R. Pogue, USAF, (1 flight)
- Skylab 4Skylab 4Skylab 4 was the fourth Skylab mission and placed the third and final crew on board the space station. The mission started November 16, 1973 with the launch of three astronauts on a Saturn IB rocket, and lasted 84 days, 1 hour and 16 minutes...
— November 1973–February 1974 — Pilot — Third crew of the SkylabSkylabSkylab was a space station launched and operated by NASA, the space agency of the United States. Skylab orbited the Earth from 1973 to 1979, and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and other systems. It was launched unmanned by a modified Saturn V rocket, with a mass of...
space stationSpace stationA space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing...
- Stuart A. RoosaStuart RoosaStuart Allen Roosa was a NASA astronaut, who was the command module pilot for the Apollo 14 mission. The mission lasted from January 31 to February 9, 1971 and was the third mission to land astronauts on the Moon...
, USAF, (1 flight)
- Apollo 14Apollo 14Apollo 14 was the eighth manned mission in the American Apollo program, and the third to land on the Moon. It was the last of the "H missions", targeted landings with two-day stays on the Moon with two lunar EVAs, or moonwalks....
— January 1971 — Command Module Pilot — Third manned lunar landing
- John L. Swigert, JrJack SwigertHe later became staff director of the Committee on Science and Technology of the U.S. House of Representatives.Swigert was elected as a Republican to Colorado's newly created 6th congressional district in November 1982. He defeated Democrat Steve Hogan, 98,909 votes to 56,518...
, ex-USAF, (1 flight)
- Apollo 13Apollo 13Apollo 13 was the seventh manned mission in the American Apollo space program and the third intended to land on the Moon. The craft was launched on April 11, 1970, at 13:13 CST. The landing was aborted after an oxygen tank exploded two days later, crippling the service module upon which the Command...
— April 1970 — Command Module Pilot — Aborted lunar landing - Intended as Command Module Pilot on Apollo-Soyuz Test ProjectApollo-Soyuz Test Project-Backup crew:-Crew notes:Jack Swigert had originally been assigned as the command module pilot for the ASTP prime crew, but prior to the official announcement he was removed as punishment for his involvement in the Apollo 15 postage stamp scandal.-Soyuz crew:...
but was replaced by Vance Brand because of the Apollo 15 postage stamp incident
- Paul J. WeitzPaul J. WeitzPaul Joseph Weitz is an American former astronaut who flew in space twice.-Personal data:Born in Erie, Pennsylvania, on July 25, 1932. Married to the former Suzanne M. Berry of Harborcreek, Pennsylvania. Two children: Matthew and Cynthia. Hunting and fishing are among his hobbies. His mother, Mrs...
, USN, (2 flights)
- Skylab 2Skylab 2-Backup crew:-Support crew:*Robert L. Crippen*Richard H. Truly*Henry W. Hartsfield, Jr*William E. Thornton-Mission parameters:*Mass: 19,979 kg*Maximum Altitude: 440 km*Distance: 18,536,730.9 km...
— May–June 1973 — Pilot — First crew of the SkylabSkylabSkylab was a space station launched and operated by NASA, the space agency of the United States. Skylab orbited the Earth from 1973 to 1979, and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and other systems. It was launched unmanned by a modified Saturn V rocket, with a mass of...
space stationSpace stationA space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing... - STS-6STS-6STS-6 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission conducted using Space Shuttle Challenger, carrying the first Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-1, into orbit. Launched on 4 April 1983, STS-6 was the sixth shuttle mission and the first of the ten missions flown by Challenger...
— April 1983 — Commander — TDRS ATracking and Data Relay SatelliteA Tracking and Data Relay Satellite is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft,...
satellite deployment mission
- Alfred M. WordenAlfred WordenAlfred Merrill Worden is an American astronaut who was the command module pilot for the Apollo 15 Moon mission in July–August 1971. The son of Merrill and Helen Worden, he was born in Jackson, Michigan...
, USAF, (1 flight)
- Apollo 15Apollo 15Apollo 15 was the ninth manned mission in the American Apollo space program, the fourth to land on the Moon and the eighth successful manned mission. It was the first of what were termed "J missions", long duration stays on the Moon with a greater focus on science than had been possible on previous...
— July 1971 — Command Module Pilot — Fourth manned lunar landing

