
Astronomical Netherlands Satellite
Encyclopedia
The Astronomical Netherlands Satellite (ANS; also known as Astronomische Nederlandse Satelliet) was a space-based
X-ray
and ultraviolet
telescope
. It was launched into Earth orbit on 30 August 1974 at 14:07:39 UTC in a Scout rocket
from Vandenberg Air Force Base
, United States
. The mission ran for 20 months until June 1976, and was jointly funded by the Netherlands Institute for Space Research
and NASA
. ANS was the first Dutch
satellite, and the Main Belt asteroid 9996 ANS
was named after it.
The telescope had an initial orbit of with a periapsis of 266 kilometres (165.3 mi), an apoapsis of 1176 kilometres (730.7 mi), with inclination
98.0° and eccentricity
0.064048, giving it a period of 99.2 minutes. The orbit was sun-synchronous, and the altitude of the spacecraft could be controlled via magnetic coils that interacted with the Earth
's magnetic field
, as well as by reaction wheels. The satellite also had two masses that were ejected early in the mission, which removed most of the satellite's angular momentum
. The altitude could be measured by a variety of techniques, including solar sensors, horizon
sensors, star sensors and a magnetometer
.
ANS could measure X-ray
photons in the energy range 2 to 30 KeV
, with a 60 cm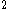 detector, and was used to find the positions of galactic
detector, and was used to find the positions of galactic
and extragalactic X-ray sources. It also measured their spectra
, and looked at their variations over time. It discovered X-ray bursts, and also detected X-rays from Capella
.
ANS also observed in the ultraviolet
part of the spectrum, with a 22 cm (260 cm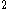 ) Cassegrain
) Cassegrain
telescope. The wavelength
s of the observe photons were between 150 and 330 nm, with the detector split into five channels with central wavelengths of 155, 180, 220, 250 and 330 nm. At these frequencies it took over 18,000 measurements of around 400 objects.
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
and ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
. It was launched into Earth orbit on 30 August 1974 at 14:07:39 UTC in a Scout rocket
Scout (rocket)
The Scout family of rockets were launch vehicles designed to place small satellites into orbit around the Earth. The Scout multistage rocket was the first orbital launch vehicle to be entirely composed of solid fuel stages....
from Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg Air Force Base is a United States Air Force Base, located approximately northwest of Lompoc, California. It is under the jurisdiction of the 30th Space Wing, Air Force Space Command ....
, United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. The mission ran for 20 months until June 1976, and was jointly funded by the Netherlands Institute for Space Research
Netherlands Institute for Space Research
SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research is the Dutch expertise institute for space research. The Institute develops and uses innovative technology for groundbreaking research in space, focusing on astrophysical research, Earth science and planetary research...
and NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
. ANS was the first Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
satellite, and the Main Belt asteroid 9996 ANS
9996 ANS
9996 ANS is a C-type main belt asteroid. It orbits the Sun once every 4.68 years.Discovered on October 17, 1960 by C. J. van Houten and I. van Houten-Groeneveld on archived photographic plates made by T. Gehrels, it was given the provisional designation 9070 P-L...
was named after it.
The telescope had an initial orbit of with a periapsis of 266 kilometres (165.3 mi), an apoapsis of 1176 kilometres (730.7 mi), with inclination
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
98.0° and eccentricity
Orbital eccentricity
The orbital eccentricity of an astronomical body is the amount by which its orbit deviates from a perfect circle, where 0 is perfectly circular, and 1.0 is a parabola, and no longer a closed orbit...
0.064048, giving it a period of 99.2 minutes. The orbit was sun-synchronous, and the altitude of the spacecraft could be controlled via magnetic coils that interacted with the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
, as well as by reaction wheels. The satellite also had two masses that were ejected early in the mission, which removed most of the satellite's angular momentum
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
. The altitude could be measured by a variety of techniques, including solar sensors, horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
sensors, star sensors and a magnetometer
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a measuring instrument used to measure the strength or direction of a magnetic field either produced in the laboratory or existing in nature...
.
ANS could measure X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
photons in the energy range 2 to 30 KeV
Kev
Kev can refer to:*Kev Hawkins, a fictional character.*Kevin, a given name occasionally shortened to "Kev".*Kiloelectronvolt, a unit of energy who symbol is "KeV".* Krefelder Eislauf-VereinKEV can refer to:...
, with a 60 cm
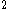 detector, and was used to find the positions of galactic
detector, and was used to find the positions of galacticMilky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
and extragalactic X-ray sources. It also measured their spectra
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
, and looked at their variations over time. It discovered X-ray bursts, and also detected X-rays from Capella
Capella (star)
Capella is the brightest star in the constellation Auriga, the sixth brightest star in the night sky and the third brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus and Vega. Although it appears to be a single star to the naked eye, it is actually a star system of four stars in...
.
ANS also observed in the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
part of the spectrum, with a 22 cm (260 cm
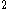 ) Cassegrain
) CassegrainCassegrain reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas....
telescope. The wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
s of the observe photons were between 150 and 330 nm, with the detector split into five channels with central wavelengths of 155, 180, 220, 250 and 330 nm. At these frequencies it took over 18,000 measurements of around 400 objects.

