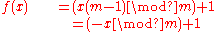Atbash
Encyclopedia
Atbash is a simple substitution cipher
for the Hebrew alphabet
. It consists in substituting aleph
(the first letter) for tav
(the last), beth (the second) for shin
(one before last), and so on, reversing the alphabet
. In the Book of Jeremiah
, Lev Kamai (51:1) is Atbash for Kasdim (Chaldeans
), and Sheshakh (25:26; 51:41) is Atbash for Bavel (Babylon
). It has been associated with the esoteric methodologies of Jewish mysticism's interpretations of Hebrew religious texts as in the Kabbalah
.
The Atbash cipher for the modern Hebrew alphabet would be:
Plain: אבגדהוזחטיכלמנסעפצקרשת
Cipher: תשרקצפעסנמלכיטחזוהדגבא
An Atbash cipher for the Roman alphabet would be as follows:
Plain: abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
Cipher: ZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
An easier, simpler and faster way of doing this is:
First 13 letters: A|B|C|D|E|F|G|H|I|J|K|L|M
Last 13 Letters: Z|Y|X|W|V|U|T|S|R|Q|P|O|N
Atbash can also be used to mean the same thing in any other alphabet as well. This is a very simple substitution cipher.
For example, in Atbash, the letters "nlmvb" indicate the word "money".
A few English words 'Atbash' into other English words. For example, "hob"="sly", "hold"="slow", "holy"="slob", "horn"="slim", "zoo"="all", "irk"="rip", "low"="old", "glow"="told", and "grog"="tilt".
It is a very weak cipher because it only has one possible key, and it is a simple monoalphabetic substitution cipher. However, this may not have been an issue in the cipher's time.
.
If you define the first letter of the alphabet to be 0, the second letter to be 1 and so on up to the last letter of the alphabet being the number of letters in the alphabet-1; then the Atbash cipher may be enciphered & deciphered using the encryption function for an Affine cipher:

Where, for the Atbash cipher: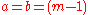 in which m is the number of letters in the alphabet (
in which m is the number of letters in the alphabet ( for monocase English
for monocase English
).
This may be simplified to:
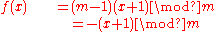
If, instead, the first letter of the alphabet is defined to be 1, the second letter to be 2 and so on, the encryption function for the Affine Cipher becomes:
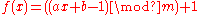
Where, for the Atbash cipher: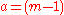 ,
,  in which m is the length of the alphabet.
in which m is the length of the alphabet.
This may be simplified to:
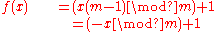
Substitution cipher
In cryptography, a substitution cipher is a method of encryption by which units of plaintext are replaced with ciphertext according to a regular system; the "units" may be single letters , pairs of letters, triplets of letters, mixtures of the above, and so forth...
for the Hebrew alphabet
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
. It consists in substituting aleph
Aleph
* Aleph or Alef is the first letter of the Semitic abjads descended from Proto-Canaanite, Arabic alphabet, Phoenician alphabet, Hebrew alphabet, Syriac alphabet-People:*Aleph , an Italo disco artist and alias of Dave Rodgers...
(the first letter) for tav
Taw (letter)
Taw, Tav or Taf is the twenty-second and last letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Taw and Arabic alphabet .Its original sound value is ....
(the last), beth (the second) for shin
Shin (letter)
Shin literally means "Sharp" ; It is the twenty-first letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic/Hebrew , and Arabic ....
(one before last), and so on, reversing the alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
. In the Book of Jeremiah
Book of Jeremiah
The Book of Jeremiah is the second of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, following the book of Isaiah and preceding Ezekiel and the Book of the Twelve....
, Lev Kamai (51:1) is Atbash for Kasdim (Chaldeans
Chaldean Christians
Chaldean Christians are ethnic Assyrian adherents of the Chaldean Catholic Church, most of whom entered communion with the Catholic Church from the Church of the East, which was already Catholic, but most wanted to stray away from the Catholic Church, causing the split in the 17th and 18th...
), and Sheshakh (25:26; 51:41) is Atbash for Bavel (Babylon
Babylon
Babylon was an Akkadian city-state of ancient Mesopotamia, the remains of which are found in present-day Al Hillah, Babil Province, Iraq, about 85 kilometers south of Baghdad...
). It has been associated with the esoteric methodologies of Jewish mysticism's interpretations of Hebrew religious texts as in the Kabbalah
Kabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
.
The Atbash cipher for the modern Hebrew alphabet would be:
Plain: אבגדהוזחטיכלמנסעפצקרשת
Cipher: תשרקצפעסנמלכיטחזוהדגבא
An Atbash cipher for the Roman alphabet would be as follows:
Plain: abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
Cipher: ZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
An easier, simpler and faster way of doing this is:
First 13 letters: A|B|C|D|E|F|G|H|I|J|K|L|M
Last 13 Letters: Z|Y|X|W|V|U|T|S|R|Q|P|O|N
Atbash can also be used to mean the same thing in any other alphabet as well. This is a very simple substitution cipher.
For example, in Atbash, the letters "nlmvb" indicate the word "money".
A few English words 'Atbash' into other English words. For example, "hob"="sly", "hold"="slow", "holy"="slob", "horn"="slim", "zoo"="all", "irk"="rip", "low"="old", "glow"="told", and "grog"="tilt".
It is a very weak cipher because it only has one possible key, and it is a simple monoalphabetic substitution cipher. However, this may not have been an issue in the cipher's time.
The Atbash Cipher as an Affine cipher
The Atbash cipher can be seen as a special case of the Affine cipherAffine cipher
The affine cipher is a type of monoalphabetic substitution cipher, wherein each letter in an alphabet is mapped to its numeric equivalent, encrypted using a simple mathematical function, and converted back to a letter...
.
If you define the first letter of the alphabet to be 0, the second letter to be 1 and so on up to the last letter of the alphabet being the number of letters in the alphabet-1; then the Atbash cipher may be enciphered & deciphered using the encryption function for an Affine cipher:

Where, for the Atbash cipher:
 in which m is the number of letters in the alphabet (
in which m is the number of letters in the alphabet ( for monocase English
for monocase EnglishEnglish language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
).
This may be simplified to:
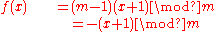
If, instead, the first letter of the alphabet is defined to be 1, the second letter to be 2 and so on, the encryption function for the Affine Cipher becomes:
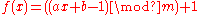
Where, for the Atbash cipher:
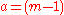 ,
,  in which m is the length of the alphabet.
in which m is the length of the alphabet.This may be simplified to: