
Athlon 64
Encyclopedia
The Athlon 64 is an eighth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor
produced by AMD, released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon
, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. The second processor (after the Opteron
) to implement AMD64 architecture and the first 64-bit
processor targeted at the average consumer, it was AMD's primary consumer microprocessor, and competes primarily with Intel's Pentium 4
, especially the "Prescott" and "Cedar Mill" core revisions. It is AMD's first K8, eighth-generation processor core for desktop and mobile computers. Despite being natively 64-bit, the AMD64 architecture is backward-compatible with 32-bit x86 instructions. Athlon 64s have been produced for Socket 754
, Socket 939
, Socket 940
and Socket AM2
. The line was succeeded by the dual-core Athlon 64 X2
and Athlon X2 lines.
 The Athlon 64 was originally codenamed ClawHammer by AMD, and was referred to as such internally and in press releases. The first Athlon 64 FX was based on the first Opteron
The Athlon 64 was originally codenamed ClawHammer by AMD, and was referred to as such internally and in press releases. The first Athlon 64 FX was based on the first Opteron
core, SledgeHammer. Both cores, produced on a 130 nanometer process, were first introduced on September 23, 2003. The models first available were the FX-51, fitting Socket 940, and the 3200+, fitting Socket 754. Like the Opteron, on which it was based, the Athlon FX-51 required buffered RAM, increasing the final cost of an upgrade. The week of the Athlon 64's launch, Intel released the Pentium 4
Extreme Edition, a CPU designed to compete with the Athlon 64 FX. The Extreme Edition was widely considered a marketing ploy to draw publicity away from AMD, and was quickly nicknamed among some circles the "Emergency Edition". Despite a very strong demand for the chip, AMD experienced early manufacturing difficulties that made it difficult to deliver Athlon 64s in quantity. In the early months of the Athlon 64 lifespan, AMD could only produce 100,000 chips per month. However, it was very competitive in terms of performance to the Pentium 4, with magazine PC World
calling it the "fastest yet". "Newcastle" was released soon after ClawHammer, with half the Level 2 cache
.
On June 1, 2004, AMD released new versions of both the ClawHammer and Newcastle core revisions for the newly-introduced Socket 939
, an altered Socket 940
without the need for buffered memory. Socket 939 offered two main improvements over Socket 754: the memory controller
was altered with dual-channel architecture
, doubling peak memory bandwidth, and the HyperTransport
bus was increased in speed from 800 MHz to 1000 MHz. Socket 939 also was introduced in the FX series in the form of the FX-55. At the same time, AMD also began to ship the "Winchester" core, based on a 90 nanometer process.
Core revisions "Venice" and "San Diego" succeeded all previous revisions on April 15, 2005. Venice, the lower-end part, was produced for both Sockets 754 and 939, and included 512 KB
of L2 cache. San Diego, the higher-end chip, was produced only for Socket 939 and doubled Venice's L2 cache to 1 MB
. Both were produced on the 90 nm fabrication process. Both also included support for the SSE3
instruction set, a new feature that had been included in the rival Pentium 4
since the release of the Prescott core in February 2004. In addition, AMD overhauled the memory controller for this revision, resulting in performance improvements as well as support for newer DDR RAM.
. Released on May 31, 2005, it also initially had two different core revisions available to the public, Manchester and Toledo, the only appreciable difference between them being the amount of L2 cache. Both were released only for Socket 939. The Athlon 64 X2 was received very well by reviewers and the general public, with a general consensus emerging that AMD's implementation of multi-core
was superior to that of the competing Pentium D
. Some felt initially that the X2 would cause market confusion with regard to price points since the new processor was targeted at the same "enthusiast," US$350 and above market already occupied by AMD's existing socket 939 Athlon 64s. AMD's official breakdown of the chips placed the Athlon X2 aimed at a segment they called the "prosumer", along with digital media fans. The Athlon 64 was targeted at the mainstream consumer, and the Athlon FX at gamers. The Sempron
budget processor was targeted at value-conscious consumers. Following the launch of the Athlon 64 X2, AMD surpassed Intel in US retail sales for a period of time, although Intel retained overall market leadership because of its exclusive relationships with direct sellers such as Dell.
, an emerging technology that had been adopted much earlier by Intel. AMD's official position was that the CAS latency
on DDR2 had not progressed to a point where it would be advantageous for the consumer to adopt it. AMD finally remedied this gap with the "Orleans" core revision, the first Athlon 64 to fit Socket AM2
, released on May 23, 2006. "Windsor", an Athlon 64 X2 revision for Socket AM2, was released concurrently. Both Orleans and Windsor have either 512 KB
or 1 MB
of L2 cache per core. The Athlon 64 FX-62 was also released concurrently on the Socket AM2 platform. Socket AM2 also consumes less power than previous platforms, and supports AMD-V.
The memory controller used in all DDR2 SDRAM capable processors (Socket AM2), has extended column address range of 11 columns instead of conventional 10 columns, and the support of 16 KB page size, with at most 2048 individual entries supported. An OCZ unbuffered DDR2 kit, optimized for 64-bit
operating systems, was released to exploit the functionality provided by the memory controller in socket AM2 processors, allowing the memory controller to stay longer on the same page, thus benefitting graphics intensive applications.
market.
. Common among the Athlon 64 line are a variety of instruction sets including MMX, 3DNow!
, SSE
, SSE2
, and SSE3
. All Athlon 64s also support the NX bit
, a security feature named "Enhanced Virus Protection" by AMD. And as implementations of the AMD64 architecture, all Athlon 64 variants are able to run 16 bit, 32 bit x86, and AMD64 code
, through two different modes the processor can run in: "Legacy mode
" and "long mode". Legacy mode runs 16-bit and 32-bit programs natively, and long mode runs 64-bit programs natively, but also allows for 32-bit programs running inside a 64-bit operating system
. All Athlon 64 processors feature 128 Kilobyte
s of level 1 cache, and at least 512 KB of level 2 cache.
. Not only does this mean the controller runs at the same clock rate as the CPU itself, it also means the electrical signals have a shorter physical distance to travel compared to the old northbridge
interfaces. The result is a significant reduction in latency (response time) for access requests to main memory. The lower latency was often cited as one of the advantages of the Athlon 64's architecture over those of its competitors at the time.
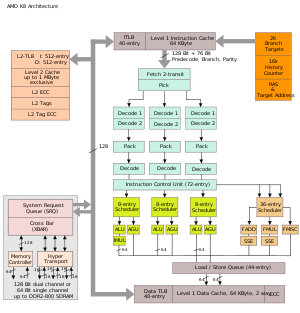
s (TLBs) have also been enlarged (40 4k/2M/4M entries in L1 cache, 512 4k entries), with reduced latencies and improved branch prediction, with four times the number of bimodal counters in the global history counter. This and other architectural enhancements, especially as regards SSE implementation, improve instruction per cycle (IPC) performance over the previous Athlon XP generation. To make this easier for consumers to understand, AMD has chosen to market the Athlon 64 using a PR (Performance Rating) system, where the numbers roughly map to Pentium 4 performance equivalents, rather than actual clock speed.
speed throttling technology branded Cool'n'Quiet
, a feature similar to Intel's SpeedStep
that can throttle the processor's clock speed back to facilitate lower power consumption and heat production. When the user is running undemanding applications and the load on the processor is light, the processor's clock speed and voltage are reduced. This in turn reduces its peak power consumption (max TDP set at 89 W by AMD) to as low as 32 W (stepping C0, clock speed reduced to 800 MHz) or 22W (stepping CG, clock speed reduced to 1 GHz). The Athlon 64 also has an Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) which prevents the CPU die from accidentally being damaged when mounting and unmounting heat sinks. With prior AMD CPUs a CPU shim
could be used by people worried about damaging the die.
supported by Windows XP
Service Pack 2 and future versions of Windows, Linux
2.6.8 and higher and FreeBSD
5.3 and higher is also included, for improved protection from malicious buffer overflow security threats. Hardware-set permission levels make it much more difficult for malicious code to take control of the system. It is intended to make 64-bit computing a more secure environment.
The Athlon 64 CPUs have been produced with 130 nm and 90 nm SOI
process technologies. All of the latest chips (Winchester, Venice and San Diego models) are on 90 nm. The Venice and San Diego models also incorporate dual stress liner technology (an amalgam of strained silicon
and 'squeezed silicon', the latter of which is not actually a technology) co-developed with IBM.
As the memory controller is integrated onto the CPU die, there is no FSB for the system memory to base its speed upon. Instead, system memory speed is obtained by using the following formula (using the ceiling function):
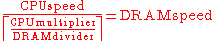
In simpler terms, the memory is always running at a set fraction of the CPU speed, with the divisor being a whole number. A 'FSB' figure is still used to determine the CPU speed, but the RAM speed is no longer directly related to this 'FSB' figure (known otherwise as the LDT).
To summarize, the Athlon 64 architecture features two buses from the CPU. One is the HT Bus
to the northbridge connecting the CPU to the chipset and device attachment bus (PCIe, AGP, PCI) and the other is the memory bus which connects the on-board memory controller to the bank of either DDR or DDR2 DRAM.
s. Unlike the standard Athlon 64, all of the Athlon 64 FX processors have their multipliers completely unlocked. The FX line is now dual-core, starting with the FX-60. The FX always has the highest clock speed of all Athlons at its release. From FX-70 onwards, the line of processors will also support dual-processor setup with NUMA
, named AMD Quad FX platform.
desktop
CPU
manufactured by AMD.
In 2007, AMD released two final Athlon 64 X2 versions: the AMD Athlon 64 X2 6400+ and 5000+ Black Editions. Both processors feature an unlocked multiplier, which allows for a large range of overclocked settings. The 6400+ is based on a 90 nm Windsor core (3.2 GHz, 2x1MB L2, 125W TDP) while the 5000+ is based on a 65 nm Brisbane core (2.6 GHz, 2x512KB L2, 65W TDP). These Black Edition processors are available at retail, but AMD does not include heatsinks in the retail package.
.jpg)
.jpg) Previously introduced as "Mobile Athlon 64", Turion 64 is now the brand name AMD applies to its 64-bit low-power consumption (mobile) processors
Previously introduced as "Mobile Athlon 64", Turion 64 is now the brand name AMD applies to its 64-bit low-power consumption (mobile) processors
. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2 processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the Pentium M
and currently the Intel Core
and Intel Core 2
processors.
Earlier Turion 64 processors are compatible with AMD's Socket 754
. The newer "Richmond" models are designed for AMD's Socket S1
. They are equipped with 512 or 1024 KB
of L2 cache, a 64-bit single channel on-die memory controller, and an 800 MHz HyperTransport
bus. Battery saving features, like PowerNow!
, are central to the marketing and usefulness of these CPUs.
. The first letter is M for single core processors and T for dual core Turion 64 X2 processors. The later in the alphabet that the second letter appears, the more the model has been designed for mobility (frugal power consumption). Take for instance, an MT-30 and an ML-34. Since the T in the MT-30 is later in the alphabet than the L in ML-34, the MT-30 consumes less power than the ML-34. But since 34 is greater than 30, the ML-34 is faster than the MT-30.
package, for smaller footprint to allow smaller designs for notebooks and lowering the cost. The clock of the processors is significantly lower than desktop and other mobile counterparts to reach a low TDP, at 15W maximum for a single core x86-64 CPU at 1.6 GHz. The Athlon Neo processors are equipped with 512 KB of L2 cache and HyperTransport 1.0 running at 800 MHz frequency.
At the introduction of Athlon 64 in September 2003, only Socket 754 and Socket 940 (Opteron) were ready and available. The onboard memory controller was not capable of running unbuffered (non-registered) memory in dual-channel mode at the time of release; as a stopgap measure, they introduced the Athlon 64 on Socket 754, and brought out a non-multiprocessor version of the Opteron called the Athlon 64 FX, as a multiplier unlocked enthusiast part for Socket 940, comparable to Intel's Pentium 4 Extreme Edition for the high end market.
In June 2004, AMD released Socket 939 as the mainstream Athlon 64 with dual-channel memory interface, leaving Socket 940 solely for the server market (Opterons), and relegating Socket 754 as a value/budget line, for Semprons and slower versions of the Athlon 64. Eventually Socket 754 replaced Socket A
for Semprons.
In May 2006, AMD released Socket AM2, which provided support for the DDR2 memory interface. Also, this marked the release of AMD-V.
In August 2006, AMD released Socket F for Opteron
server CPU which uses the LGA
chip form factor.
In November 2006, AMD released a specialized version of Socket F, called 1207 FX, for dual-socket, dual-core Athlon FX processors on the Quad FX platform. While Socket F Opterons already allowed for four processor cores, Quad FX allowed unbuffered RAM and expanded CPU/chipset configuration in the BIOS. Consequentially, Socket F and F 1207 FX are incompatible and require different processors, chipsets, and motherboards.
architecture in 2007, including but not limited to the Phenom and Phenom II processors. These successors feature higher core counts per CPU, as well as implement support for Hypertransport 3.0 and socket AM2+/AM3.
As of September 2010, Athlon64 X2 processors were still available for sale.
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
produced by AMD, released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon
Athlon
Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices . The original Athlon was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and, in a first, retained the initial performance lead it had over Intel's competing processors...
, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. The second processor (after the Opteron
Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
) to implement AMD64 architecture and the first 64-bit
64-bit
64-bit is a word size that defines certain classes of computer architecture, buses, memory and CPUs, and by extension the software that runs on them. 64-bit CPUs have existed in supercomputers since the 1970s and in RISC-based workstations and servers since the early 1990s...
processor targeted at the average consumer, it was AMD's primary consumer microprocessor, and competes primarily with Intel's Pentium 4
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the...
, especially the "Prescott" and "Cedar Mill" core revisions. It is AMD's first K8, eighth-generation processor core for desktop and mobile computers. Despite being natively 64-bit, the AMD64 architecture is backward-compatible with 32-bit x86 instructions. Athlon 64s have been produced for Socket 754
Socket 754
Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to succeed its Athlon XP platform . Socket 754 was the first socket developed by AMD to support their new consumer version of the 64 bit microprocessor family known as AMD64.-Technical specifications:Socket 754 was the original socket for...
, Socket 939
Socket 939
Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, Socket 940
Socket 940
Socket 940 is a 940-pin socket for 64-bit AMD server processors. This socket is entirely square in shape and pins are arranged in a grid with the exception of four key pins used to align the processor and the corners...
and Socket AM2
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
. The line was succeeded by the dual-core Athlon 64 X2
Athlon 64 X2
The Athlon 64 X2 is the first dual-core desktop CPU designed by AMD. It was designed from scratch as native dual-core by using an already multi-CPU enabled Athlon 64, joining it with another functional core on one die, and connecting both via a shared dual-channel memory controller/north bridge and...
and Athlon X2 lines.
Background

Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
core, SledgeHammer. Both cores, produced on a 130 nanometer process, were first introduced on September 23, 2003. The models first available were the FX-51, fitting Socket 940, and the 3200+, fitting Socket 754. Like the Opteron, on which it was based, the Athlon FX-51 required buffered RAM, increasing the final cost of an upgrade. The week of the Athlon 64's launch, Intel released the Pentium 4
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the...
Extreme Edition, a CPU designed to compete with the Athlon 64 FX. The Extreme Edition was widely considered a marketing ploy to draw publicity away from AMD, and was quickly nicknamed among some circles the "Emergency Edition". Despite a very strong demand for the chip, AMD experienced early manufacturing difficulties that made it difficult to deliver Athlon 64s in quantity. In the early months of the Athlon 64 lifespan, AMD could only produce 100,000 chips per month. However, it was very competitive in terms of performance to the Pentium 4, with magazine PC World
PC World (magazine)
PC World is a global computer magazine published monthly by IDG. It offers advice on various aspects of PCs and related items, the Internet, and other personal-technology products and services...
calling it the "fastest yet". "Newcastle" was released soon after ClawHammer, with half the Level 2 cache
Cache
In computer engineering, a cache is a component that transparently stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster. The data that is stored within a cache might be values that have been computed earlier or duplicates of original values that are stored elsewhere...
.
Single-core Athlon 64
All of the 64-bit processors sold by AMD so far have their genesis in the K8 or Hammer project.On June 1, 2004, AMD released new versions of both the ClawHammer and Newcastle core revisions for the newly-introduced Socket 939
Socket 939
Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, an altered Socket 940
Socket 940
Socket 940 is a 940-pin socket for 64-bit AMD server processors. This socket is entirely square in shape and pins are arranged in a grid with the exception of four key pins used to align the processor and the corners...
without the need for buffered memory. Socket 939 offered two main improvements over Socket 754: the memory controller
Memory controller
The memory controller is a digital circuit which manages the flow of data going to and from the main memory. It can be a separate chip or integrated into another chip, such as on the die of a microprocessor...
was altered with dual-channel architecture
Dual-channel architecture
Multi-channel architecture is a technology that increases the transfer speed of data between the RAM and the memory controller by adding more channels of communication between them. Theoretically this multiplies the data rate by exactly the number of channels present. Dual-channel memory employs...
, doubling peak memory bandwidth, and the HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
bus was increased in speed from 800 MHz to 1000 MHz. Socket 939 also was introduced in the FX series in the form of the FX-55. At the same time, AMD also began to ship the "Winchester" core, based on a 90 nanometer process.
Core revisions "Venice" and "San Diego" succeeded all previous revisions on April 15, 2005. Venice, the lower-end part, was produced for both Sockets 754 and 939, and included 512 KB
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
of L2 cache. San Diego, the higher-end chip, was produced only for Socket 939 and doubled Venice's L2 cache to 1 MB
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
. Both were produced on the 90 nm fabrication process. Both also included support for the SSE3
SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
instruction set, a new feature that had been included in the rival Pentium 4
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the...
since the release of the Prescott core in February 2004. In addition, AMD overhauled the memory controller for this revision, resulting in performance improvements as well as support for newer DDR RAM.
Dual-core Athlon 64
On April 21, 2005, less than a week after the release of Venice and San Diego, AMD announced its next addition to the Athlon 64 line, the Athlon 64 X2Athlon 64 X2
The Athlon 64 X2 is the first dual-core desktop CPU designed by AMD. It was designed from scratch as native dual-core by using an already multi-CPU enabled Athlon 64, joining it with another functional core on one die, and connecting both via a shared dual-channel memory controller/north bridge and...
. Released on May 31, 2005, it also initially had two different core revisions available to the public, Manchester and Toledo, the only appreciable difference between them being the amount of L2 cache. Both were released only for Socket 939. The Athlon 64 X2 was received very well by reviewers and the general public, with a general consensus emerging that AMD's implementation of multi-core
Multi-core (computing)
A multi-core processor is a single computing component with two or more independent actual processors , which are the units that read and execute program instructions...
was superior to that of the competing Pentium D
Pentium D
The Pentium D brand refers to two series of desktop dual-core 64-bit x86-64 microprocessors with the NetBurst microarchitecture manufactured by Intel. Each CPU comprised two dies, each containing a single core, residing next to each other on a multi-chip module package. The brand's first processor,...
. Some felt initially that the X2 would cause market confusion with regard to price points since the new processor was targeted at the same "enthusiast," US$350 and above market already occupied by AMD's existing socket 939 Athlon 64s. AMD's official breakdown of the chips placed the Athlon X2 aimed at a segment they called the "prosumer", along with digital media fans. The Athlon 64 was targeted at the mainstream consumer, and the Athlon FX at gamers. The Sempron
Sempron
Sempron has been the marketing name used by AMD for several different budget desktop CPUs, using several different technologies and CPU socket formats. The Sempron replaced the AMD Duron processor and competes against Intel's Celeron series of processors...
budget processor was targeted at value-conscious consumers. Following the launch of the Athlon 64 X2, AMD surpassed Intel in US retail sales for a period of time, although Intel retained overall market leadership because of its exclusive relationships with direct sellers such as Dell.
DDR2
The Athlon 64 had been maligned by some critics for some time because of its lack of support for DDR2 SDRAMDDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM is a double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory interface. It supersedes the original DDR SDRAM specification and has itself been superseded by DDR3 SDRAM...
, an emerging technology that had been adopted much earlier by Intel. AMD's official position was that the CAS latency
CAS Latency
Column Address Strobe latency, or CL, is the delay time between the moment a memory controller tells the memory module to access a particular memory column on a RAM memory module, and the moment the data from given array location is available on the module's output pins...
on DDR2 had not progressed to a point where it would be advantageous for the consumer to adopt it. AMD finally remedied this gap with the "Orleans" core revision, the first Athlon 64 to fit Socket AM2
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
, released on May 23, 2006. "Windsor", an Athlon 64 X2 revision for Socket AM2, was released concurrently. Both Orleans and Windsor have either 512 KB
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
or 1 MB
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
of L2 cache per core. The Athlon 64 FX-62 was also released concurrently on the Socket AM2 platform. Socket AM2 also consumes less power than previous platforms, and supports AMD-V.
The memory controller used in all DDR2 SDRAM capable processors (Socket AM2), has extended column address range of 11 columns instead of conventional 10 columns, and the support of 16 KB page size, with at most 2048 individual entries supported. An OCZ unbuffered DDR2 kit, optimized for 64-bit
64-bit
64-bit is a word size that defines certain classes of computer architecture, buses, memory and CPUs, and by extension the software that runs on them. 64-bit CPUs have existed in supercomputers since the 1970s and in RISC-based workstations and servers since the early 1990s...
operating systems, was released to exploit the functionality provided by the memory controller in socket AM2 processors, allowing the memory controller to stay longer on the same page, thus benefitting graphics intensive applications.
Moving to the subnotebook space
The Athlon architecture was further extended with the release of Athlon Neo processors on January 9, 2009. Based on the same architecture as the other Athlon 64 variants, the new processor features a small package footprint targeting Ultra-portable notebookSubnotebook
A subnotebook is a class of laptop computers that are smaller and lighter than a typical laptop....
market.
| AMD Athlon 64 processor family | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logo | Desktop Desktop computer A desktop computer is a personal computer in a form intended for regular use at a single location, as opposed to a mobile laptop or portable computer. Early desktop computers are designed to lay flat on the desk, while modern towers stand upright... |
Logo | Laptop Laptop A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit... |
||||
| Code-named | Core | Date released | Code-named | Core | Date released | ||
 |
ClawHammer Newcastle Winchester Venice Manchester * San Diego Toledo * |
130 nm 130 nm 90 nm 90 nm 90 nm 90 nm 90 nm |
Dec 2003 Dec 2003 Oct 2004 April 2005 May 2005 May 2005 May 2005 |
 |
ClawHammer Odessa Oakville Newark |
130 nm 130 nm 90 nm 90 nm |
Dec 2003 Feb 2004 Aug 2004 Apr 2005 |
 |
SledgeHammer ClawHammer San Diego |
130 nm 130 nm 90 nm |
Sep 2003 Jun 2004 Jun 2005 |
||||
 |
Orleans Lima |
65 nm 65 nm |
Feb 2007 May 2007 |
 |
Huron | 65 nm | Jan 2009 |
| * Athlon X2 with one cache disabled List of AMD Athlon 64 microprocessors |
|||||||
Features
There are four variants: Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Mobile Athlon 64 (later renamed "Turion 64") and the dual-core Athlon 64 X2Athlon 64 X2
The Athlon 64 X2 is the first dual-core desktop CPU designed by AMD. It was designed from scratch as native dual-core by using an already multi-CPU enabled Athlon 64, joining it with another functional core on one die, and connecting both via a shared dual-channel memory controller/north bridge and...
. Common among the Athlon 64 line are a variety of instruction sets including MMX, 3DNow!
3DNow!
3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSE
Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2
SSE2
SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, and SSE3
SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
. All Athlon 64s also support the NX bit
NX bit
The NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, a security feature named "Enhanced Virus Protection" by AMD. And as implementations of the AMD64 architecture, all Athlon 64 variants are able to run 16 bit, 32 bit x86, and AMD64 code
Machine code
Machine code or machine language is a system of impartible instructions executed directly by a computer's central processing unit. Each instruction performs a very specific task, typically either an operation on a unit of data Machine code or machine language is a system of impartible instructions...
, through two different modes the processor can run in: "Legacy mode
Legacy mode
In computing, legacy mode is a state in which a computer system, component, or software application behaves in a way different from its standard operation in order to support older software, data, or expected behavior...
" and "long mode". Legacy mode runs 16-bit and 32-bit programs natively, and long mode runs 64-bit programs natively, but also allows for 32-bit programs running inside a 64-bit operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
. All Athlon 64 processors feature 128 Kilobyte
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
s of level 1 cache, and at least 512 KB of level 2 cache.
On-die memory controller
The Athlon 64 features an on-die memory controller, a feature previously seen on only the Transmeta CrusoeTransmeta Crusoe
The Crusoe is a family of x86-compatible microprocessors developed by Transmeta. Crusoe was notable for its method of achieving x86 compatibility. Instead of the instruction set architecture being implemented in hardware, or translated by specialized hardware, the Crusoe runs a software abstraction...
. Not only does this mean the controller runs at the same clock rate as the CPU itself, it also means the electrical signals have a shorter physical distance to travel compared to the old northbridge
Northbridge (computing)
The northbridge has historically been one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a PC motherboard, the other being the southbridge. Increasingly these functions have migrated to the CPU chip itself, beginning with memory and graphics controllers. For Intel Sandy Bridge and AMD Fusion...
interfaces. The result is a significant reduction in latency (response time) for access requests to main memory. The lower latency was often cited as one of the advantages of the Athlon 64's architecture over those of its competitors at the time.
Translation Lookaside Buffers
Translation Lookaside BufferTranslation Lookaside Buffer
A translation lookaside buffer is a CPU cache that memory management hardware uses to improve virtual address translation speed. All current desktop and server processors use a TLB to map virtual and physical address spaces, and it is ubiquitous in any hardware which utilizes virtual memory.The...
s (TLBs) have also been enlarged (40 4k/2M/4M entries in L1 cache, 512 4k entries), with reduced latencies and improved branch prediction, with four times the number of bimodal counters in the global history counter. This and other architectural enhancements, especially as regards SSE implementation, improve instruction per cycle (IPC) performance over the previous Athlon XP generation. To make this easier for consumers to understand, AMD has chosen to market the Athlon 64 using a PR (Performance Rating) system, where the numbers roughly map to Pentium 4 performance equivalents, rather than actual clock speed.
Cool'n'Quiet
Athlon 64 also features CPUCentral processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
speed throttling technology branded Cool'n'Quiet
Cool'n'Quiet
Cool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, a feature similar to Intel's SpeedStep
SpeedStep
SpeedStep is a trademark for a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies built into some Intel microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be dynamically changed by software...
that can throttle the processor's clock speed back to facilitate lower power consumption and heat production. When the user is running undemanding applications and the load on the processor is light, the processor's clock speed and voltage are reduced. This in turn reduces its peak power consumption (max TDP set at 89 W by AMD) to as low as 32 W (stepping C0, clock speed reduced to 800 MHz) or 22W (stepping CG, clock speed reduced to 1 GHz). The Athlon 64 also has an Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) which prevents the CPU die from accidentally being damaged when mounting and unmounting heat sinks. With prior AMD CPUs a CPU shim
CPU shim
A CPU shim is a shim used between the CPU and the heat sink in a computer. Shims make it easier and less risky to mount a heatsink on the processor because it stabilizes the heatsink, preventing accidental damaging of the fragile CPU packaging...
could be used by people worried about damaging the die.
NX bit
The No Execute bit (NX bit)NX bit
The NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
supported by Windows XP
Windows XP
Windows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
Service Pack 2 and future versions of Windows, Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
2.6.8 and higher and FreeBSD
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free Unix-like operating system descended from AT&T UNIX via BSD UNIX. Although for legal reasons FreeBSD cannot be called “UNIX”, as the direct descendant of BSD UNIX , FreeBSD’s internals and system APIs are UNIX-compliant...
5.3 and higher is also included, for improved protection from malicious buffer overflow security threats. Hardware-set permission levels make it much more difficult for malicious code to take control of the system. It is intended to make 64-bit computing a more secure environment.
The Athlon 64 CPUs have been produced with 130 nm and 90 nm SOI
Silicon on insulator
Silicon on insulator technology refers to the use of a layered silicon-insulator-silicon substrate in place of conventional silicon substrates in semiconductor manufacturing, especially microelectronics, to reduce parasitic device capacitance and thereby improving performance...
process technologies. All of the latest chips (Winchester, Venice and San Diego models) are on 90 nm. The Venice and San Diego models also incorporate dual stress liner technology (an amalgam of strained silicon
Strained silicon
Strained silicon is a layer of silicon in which the silicon atoms are stretched beyond their normal interatomic distance. This can be accomplished by putting the layer of silicon over a substrate of silicon germanium...
and 'squeezed silicon', the latter of which is not actually a technology) co-developed with IBM.
As the memory controller is integrated onto the CPU die, there is no FSB for the system memory to base its speed upon. Instead, system memory speed is obtained by using the following formula (using the ceiling function):
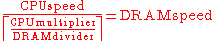
In simpler terms, the memory is always running at a set fraction of the CPU speed, with the divisor being a whole number. A 'FSB' figure is still used to determine the CPU speed, but the RAM speed is no longer directly related to this 'FSB' figure (known otherwise as the LDT).
To summarize, the Athlon 64 architecture features two buses from the CPU. One is the HT Bus
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
to the northbridge connecting the CPU to the chipset and device attachment bus (PCIe, AGP, PCI) and the other is the memory bus which connects the on-board memory controller to the bank of either DDR or DDR2 DRAM.
Athlon 64 FX
The Athlon 64 FX is positioned as a hardware enthusiast product, marketed by AMD especially toward gamerGamer
Historically, the term "gamer" usually referred to someone who played role-playing games and wargames. Since they became very popular, the term has included players of video games...
s. Unlike the standard Athlon 64, all of the Athlon 64 FX processors have their multipliers completely unlocked. The FX line is now dual-core, starting with the FX-60. The FX always has the highest clock speed of all Athlons at its release. From FX-70 onwards, the line of processors will also support dual-processor setup with NUMA
Non-Uniform Memory Access
Non-Uniform Memory Access is a computer memory design used in Multiprocessing, where the memory access time depends on the memory location relative to a processor...
, named AMD Quad FX platform.
Athlon 64 X2
The Athlon 64 X2 is the first dual-coreMulti-core (computing)
A multi-core processor is a single computing component with two or more independent actual processors , which are the units that read and execute program instructions...
desktop
Desktop computer
A desktop computer is a personal computer in a form intended for regular use at a single location, as opposed to a mobile laptop or portable computer. Early desktop computers are designed to lay flat on the desk, while modern towers stand upright...
CPU
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
manufactured by AMD.
In 2007, AMD released two final Athlon 64 X2 versions: the AMD Athlon 64 X2 6400+ and 5000+ Black Editions. Both processors feature an unlocked multiplier, which allows for a large range of overclocked settings. The 6400+ is based on a 90 nm Windsor core (3.2 GHz, 2x1MB L2, 125W TDP) while the 5000+ is based on a 65 nm Brisbane core (2.6 GHz, 2x512KB L2, 65W TDP). These Black Edition processors are available at retail, but AMD does not include heatsinks in the retail package.
Turion 64 (formerly Mobile Athlon 64)
.jpg)
.jpg)
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2 processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the Pentium M
Pentium M
The Pentium M brand refers to a family of mobile single-core x86 microprocessors introduced in March 2003 , and forming a part of the Intel Carmel notebook platform under the then new Centrino brand...
and currently the Intel Core
Intel Core
Yonah was the code name for Intel's first generation of 65 nm process mobile microprocessors, based on the Banias/Dothan-core Pentium M microarchitecture. SIMD performance has been improved through the addition of SSE3 instructions and improvements to SSE and SSE2 implementations, while integer...
and Intel Core 2
Intel Core 2
Core 2 is a brand encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single-die, whereas the quad-core models comprise two dies, each containing two cores, packaged in a...
processors.
Earlier Turion 64 processors are compatible with AMD's Socket 754
Socket 754
Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to succeed its Athlon XP platform . Socket 754 was the first socket developed by AMD to support their new consumer version of the 64 bit microprocessor family known as AMD64.-Technical specifications:Socket 754 was the original socket for...
. The newer "Richmond" models are designed for AMD's Socket S1
Socket S1
Socket S1 is the CPU socket type used by AMD for their Turion 64, Athlon 64 Mobile and later Sempron processors, which debuted with the dual core Turion 64 X2 CPUs on May 17, 2006.-Technical specifications:...
. They are equipped with 512 or 1024 KB
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
of L2 cache, a 64-bit single channel on-die memory controller, and an 800 MHz HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
bus. Battery saving features, like PowerNow!
PowerNow!
PowerNow! is speed throttling and power saving technology of AMD's processors used in laptops. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduce heat and noise...
, are central to the marketing and usefulness of these CPUs.
Model naming methodology
The model naming scheme does not make it obvious how to compare one Turion with another, or even an Athlon 64. The model name is two letters, a dash, and a two digit number (for example, ML-34). The two letters together designate a processor class, while the number represents a PR ratingPR rating
The PR system was developed by AMD in the mid-1990s as a method of comparing their x86 processors to those of rival Intel.-Branding:...
. The first letter is M for single core processors and T for dual core Turion 64 X2 processors. The later in the alphabet that the second letter appears, the more the model has been designed for mobility (frugal power consumption). Take for instance, an MT-30 and an ML-34. Since the T in the MT-30 is later in the alphabet than the L in ML-34, the MT-30 consumes less power than the ML-34. But since 34 is greater than 30, the ML-34 is faster than the MT-30.
Athlon Neo
With 27 mm × 27 mm in size and 2.5 mm in thickness, the Athlon Neo processors utilize a new package called "ASB1", essentially a BGABall grid array
A ball grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging used for integrated circuits.- Description :The BGA is descended from the pin grid array , which is a package with one face covered with pins in a grid pattern. These pins conduct electrical signals from the integrated circuit to the printed...
package, for smaller footprint to allow smaller designs for notebooks and lowering the cost. The clock of the processors is significantly lower than desktop and other mobile counterparts to reach a low TDP, at 15W maximum for a single core x86-64 CPU at 1.6 GHz. The Athlon Neo processors are equipped with 512 KB of L2 cache and HyperTransport 1.0 running at 800 MHz frequency.
Sockets
- Socket 754Socket 754Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to succeed its Athlon XP platform . Socket 754 was the first socket developed by AMD to support their new consumer version of the 64 bit microprocessor family known as AMD64.-Technical specifications:Socket 754 was the original socket for...
: The Athlon 64 value/budget line, 64-bit memory interface (Single-Channel) - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
: Athlon 64 performance line, Athlon 64 X2Athlon 64 X2The Athlon 64 X2 is the first dual-core desktop CPU designed by AMD. It was designed from scratch as native dual-core by using an already multi-CPU enabled Athlon 64, joining it with another functional core on one die, and connecting both via a shared dual-channel memory controller/north bridge and...
s, and newer Athlon 64 FXs, OpteronOpteronOpteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
, 128-bit memory interface (Dual-channel) - Socket 940Socket 940Socket 940 is a 940-pin socket for 64-bit AMD server processors. This socket is entirely square in shape and pins are arranged in a grid with the exception of four key pins used to align the processor and the corners...
: OpteronOpteronOpteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
and old Athlon 64 FX, 128-bit memory interface - requires registered DDR memory - Socket AM2Socket AM2The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
: Athlon 64/Athlon 64 FX/Athlon 64 X2/SempronSempronSempron has been the marketing name used by AMD for several different budget desktop CPUs, using several different technologies and CPU socket formats. The Sempron replaced the AMD Duron processor and competes against Intel's Celeron series of processors...
, 940 Pins (Not compatible with Socket 940); the first AMD socket to use DDR2 SDRAMDDR2 SDRAMDDR2 SDRAM is a double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory interface. It supersedes the original DDR SDRAM specification and has itself been superseded by DDR3 SDRAM...
. - Socket FSocket FSocket F is a CPU socket designed by AMD for its Opteron line of CPUs released on August 15, 2006. In 2010 Socket F was replaced by Socket C32 for entry-level servers and Socket G34 for high-end servers.-Technical specifications:...
: Opteron, 1207 Pins - Socket F (1207 FX): Athlon 64 FX on AMD Quad FX platform, also compatible for dual-processor OpteronOpteronOpteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
2200 series
At the introduction of Athlon 64 in September 2003, only Socket 754 and Socket 940 (Opteron) were ready and available. The onboard memory controller was not capable of running unbuffered (non-registered) memory in dual-channel mode at the time of release; as a stopgap measure, they introduced the Athlon 64 on Socket 754, and brought out a non-multiprocessor version of the Opteron called the Athlon 64 FX, as a multiplier unlocked enthusiast part for Socket 940, comparable to Intel's Pentium 4 Extreme Edition for the high end market.
In June 2004, AMD released Socket 939 as the mainstream Athlon 64 with dual-channel memory interface, leaving Socket 940 solely for the server market (Opterons), and relegating Socket 754 as a value/budget line, for Semprons and slower versions of the Athlon 64. Eventually Socket 754 replaced Socket A
Socket A
Socket A is the CPU socket used for AMD processors ranging from the Athlon Thunderbird to the Athlon XP/MP 3200+, and AMD budget processors including the Duron and Sempron. Socket A also supports AMD Geode NX embedded processors...
for Semprons.
In May 2006, AMD released Socket AM2, which provided support for the DDR2 memory interface. Also, this marked the release of AMD-V.
In August 2006, AMD released Socket F for Opteron
Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
server CPU which uses the LGA
Land grid array
The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit...
chip form factor.
In November 2006, AMD released a specialized version of Socket F, called 1207 FX, for dual-socket, dual-core Athlon FX processors on the Quad FX platform. While Socket F Opterons already allowed for four processor cores, Quad FX allowed unbuffered RAM and expanded CPU/chipset configuration in the BIOS. Consequentially, Socket F and F 1207 FX are incompatible and require different processors, chipsets, and motherboards.
Sledgehammer (130 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: C0, CG
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 1024 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, AMD64 - Socket 940Socket 940Socket 940 is a 940-pin socket for 64-bit AMD server processors. This socket is entirely square in shape and pins are arranged in a grid with the exception of four key pins used to align the processor and the corners...
, 800 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT800) - Registered DDR-SDRAM required
- VCore: 1.50/1.55 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 89 Watt max - First Release: September 23, 2003
- Clockrate: 2200 MHz (FX-51, C0), 2400 MHz (FX-53, C0 and CG)
Clawhammer (130 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: CG
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 1024 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, AMD64 - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.50 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 89 Watt (FX-55:104 Watt) - First Release: June 1, 2004
- Clockrate: 2400 MHz (FX-53), 2600 MHz (FX-55)
San Diego (90 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: E4, E6
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 1024 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors... - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.35 V or 1.40 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 104 Watt max - First Release: April 15, 2005
- Clockrate: 2600 MHz (FX-55), 2800 MHz (FX-57)
Toledo (90 nm SOI)
Dual-core CPU- CPU-Stepping: E6
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions), per core
- L2-Cache: 1024 KB fullspeed, per core
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors... - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.30 V - 1.35 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 110 Watt max - First Release: January 10, 2006
- Clockrate: 2600 MHz (FX-60)
Windsor (90 nm SOI)
Dual-core CPU- CPU-Stepping: F2, F3
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions), per core
- L2-Cache: 512 - 1024 KB fullspeed, per core
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM2Socket AM2The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.30 V - 1.40 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 125 Watt max - First Release: May 23, 2006
- Clockrate: 2000 - 3200 MHz (6400+)
Windsor (90 nm SOI) - Quad FX platform
Dual-core, dual CPUs (four cores total)- CPU-Stepping: F3
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions), per core
- L2-Cache: 1024 KB fullspeed, per core
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket F (1207 FX), 2000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT2000) - VCore: 1.35 V - 1.40 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 125 Watt max per CPU - First Release: November 30, 2006
- Clockrate: 2600 MHz (FX-70), 2800 MHz (FX-72), 3000 MHz (FX-74)
Clawhammer (130 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: C0, CG
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 1024 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX Bit (only CG)NX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors... - Socket 754Socket 754Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to succeed its Athlon XP platform . Socket 754 was the first socket developed by AMD to support their new consumer version of the 64 bit microprocessor family known as AMD64.-Technical specifications:Socket 754 was the original socket for...
, 800 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT800) - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.50 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 89 Watt max - First Release: September 23, 2003
- Clockrate: 2000–2600 MHz
Newcastle (130 nm SOI)
Also possible: ClawHammer-512 (Clawhammer with partially disabled L2-Cache)- CPU-Stepping: CG
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 512 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors... - Socket 754Socket 754Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to succeed its Athlon XP platform . Socket 754 was the first socket developed by AMD to support their new consumer version of the 64 bit microprocessor family known as AMD64.-Technical specifications:Socket 754 was the original socket for...
, 800 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT800) - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.50 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 89 Watt max - First Release: 2004
- Clockrate: 1800–2400 MHz
Winchester (90 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: D0
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 512 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors... - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.40 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 67 Watt max - First Release: 2004
- Clockrate: 1800–2200 MHz
Venice (90 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: E3, E6
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 512 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors... - Socket 754Socket 754Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to succeed its Athlon XP platform . Socket 754 was the first socket developed by AMD to support their new consumer version of the 64 bit microprocessor family known as AMD64.-Technical specifications:Socket 754 was the original socket for...
, 800 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT800) - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.35 V or 1.40 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 89 Watt max - First Release: April 4, 2005
- Clockrate: 1800–2400 MHz
San Diego (90 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: E4, E6
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 1024 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors... - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.35 V or 1.40 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 89 Watt max - First Release: April 15, 2005
- Clockrate: 2200–2600 MHz
Manchester (90 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: F1
- L1-Cache: 2 x 64 + 2 x 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 2 x 512 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors... - Socket 939Socket 939Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.35 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 89 Watt max - First Release: April 15, 2005
- Clockrate: 2200–2600 MHz
Orleans (90 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: F2, F3
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 512 KB, 1M
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM2Socket AM2The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.25 V or 1.40 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 62 Watt max - First Release: May 23, 2006
- Clockrate: 1800–2600 MHz
Lima (65 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: G1
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 512 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM2Socket AM2The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
, 1000 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT1000) - VCore: 1.25/1.35/1.40V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 45 Watt max - First Release: February 20, 2007
- Clockrate: 2000–2800 MHz
Huron (65 nm SOI)
- CPU-Stepping: G2
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 512 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - ASB1 package (BGABall grid arrayA ball grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging used for integrated circuits.- Description :The BGA is descended from the pin grid array , which is a package with one face covered with pins in a grid pattern. These pins conduct electrical signals from the integrated circuit to the printed...
), 800 MHz HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
(HT800) - VCore: 1.1 V
- Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 15 Watt max - First Release: January 8, 2009
- Clockrate: 1600 MHz
Athlon X2 Dual Core Processor L310
- Generation: K8
- 65 nm SOI
- CPU-Stepping: G
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 512 KB, fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
(?), NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 13 Watt max - PowerNow: No
- P-States: 1
- Clockrate: 1200 MHz
Athlon X2 Dual Core Processor L335
- Generation: K8
- 65 nm SOI
- CPU-Stepping: G
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: (2*256 KB), fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
(?), NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 18 Watt max - PowerNow: Yes
- Clockrate: 1600 MHz
Turion Neo X2 Dual Core Processor L625
- Generation: K8
- 65 nm SOI
- CPU-Stepping: G2
- L1-Cache: 64 + 64 KB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: (2*512 KB), fullspeed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX BitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Power Consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 18 Watt max - PowerNow: Yes
- Clockrate: 1600 MHz
Successors
The Athlon 64 was succeeded by the K10AMD K10
The AMD Family 10h is a microprocessor microarchitecture by AMD. Though there were once reports that the K10 had been canceled, the first third-generation Opteron products for servers were launched on September 10, 2007, with the Phenom processors for desktops following and launching on November...
architecture in 2007, including but not limited to the Phenom and Phenom II processors. These successors feature higher core counts per CPU, as well as implement support for Hypertransport 3.0 and socket AM2+/AM3.
As of September 2010, Athlon64 X2 processors were still available for sale.
See also
- 64-bit64-bit64-bit is a word size that defines certain classes of computer architecture, buses, memory and CPUs, and by extension the software that runs on them. 64-bit CPUs have existed in supercomputers since the 1970s and in RISC-based workstations and servers since the early 1990s...
- List of AMD Athlon 64 microprocessors
- List of AMD Sempron microprocessors
- List of AMD Turion microprocessors

