
Atomic nanoscope
Encyclopedia
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
is used as the probing atom) is an imaging system which is expected to provide resolution at the nanometer scale.
History
The resolution of optical microscopes is limited to a few hundred nanometers by the wave properties of the light.The idea of imaging with atoms instead of light is widely discussed in the literature since the past century. Atom optics
Atom optics
Atom optics is the area of physics which deals with beams of cold, slowly moving neutral atoms, as a special case of a particle beam....
using neutral atoms instead of light could provide resolution as good as the electron microscope
Electron microscope
An electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons to illuminate the specimen and produce a magnified image. Electron microscopes have a greater resolving power than a light-powered optical microscope, because electrons have wavelengths about 100,000 times shorter than...
and be completely non-destructive, because short wavelengths on the order of a nanometer can be realized at low energy of the probing particles. "It follows that a helium microscope with nanometer resolution is possible. A helium atom microscope will be [a] unique non-destructive tool for reflection of transmission microscopy."
Focusing of neutral atoms
Currently, the atom-optic imaging systems are not competitive with electron microscopy and various methods of near-field probe. The main problem in the optics of atomic beamAtomic beam
Atomic beam is special case of particle beam; it is the collimated flux of neutral atoms.The imaging systems using the slow atomic beams can use the Fresnel zone plate of a Fresnel diffraction mirror as focusing element. The imaging system with atomic beam could provide the sub-micrometre...
s for an imaging system is the focusing element. There is no material transparent to the beam of low-energy atoms. A Fresnel zone plate
and evanescent field lens
were suggested, as well as various atomic mirrors.
Such mirrors use the quantum reflection
Quantum reflection
Quantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
by Casimir–van der Waals potential tails.
Ridged mirrors
Recently, the performance of solid-state atomic mirrorAtomic mirror (physics)
In physics, an atomic mirror is a device which reflects neutral atoms in the similar way as the conventional mirror reflects visible light. Atomic mirrors can be made of electric fields or magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves or just silicon wafer; in the last case, atoms are reflected by the...
s was greatly enhanced with so-called ridged mirror
Ridged mirror
In atomic physics, a ridged mirror is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles coming at the grazing incidence angle, characterised in the following: in order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this...
s (or Fresnel diffraction
Fresnel diffraction
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction, is an approximation of Kirchhoff-Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field....
mirrors). The specular reflection
Specular reflection
Specular reflection is the mirror-like reflection of light from a surface, in which light from a single incoming direction is reflected into a single outgoing direction...
of an atomic wave from a ridged mirror
Ridged mirror
In atomic physics, a ridged mirror is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles coming at the grazing incidence angle, characterised in the following: in order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this...
can be interpreted as spatial Zeno effect.
At the appropriate ellipsoidal profile, such a mirror could be used for focusing of an atomic beam
Atomic beam
Atomic beam is special case of particle beam; it is the collimated flux of neutral atoms.The imaging systems using the slow atomic beams can use the Fresnel zone plate of a Fresnel diffraction mirror as focusing element. The imaging system with atomic beam could provide the sub-micrometre...
into a spot of some tens of nanometers; the scattering of atoms from this spot brings the image of the object, like in the scanning confocal microscope, scanning electron microscope
Scanning electron microscope
A scanning electron microscope is a type of electron microscope that images a sample by scanning it with a high-energy beam of electrons in a raster scan pattern...
, or scanning probe microscopy
Scanning probe microscopy
Scanning Probe Microscopy is a branch of microscopy that forms images of surfaces using a physical probe that scans the specimen. An image of the surface is obtained by mechanically moving the probe in a raster scan of the specimen, line by line, and recording the probe-surface interaction as a...
.
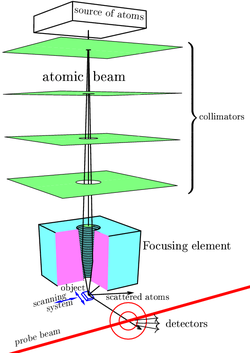
The scheme shown in the picture is one possibility. A similar scheme is posted at the homepage of the University of Cambridge; see an additional list of references there. Such an imaging system could also be realized with holographic
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows the light scattered from an object to be recorded and later reconstructed so that when an imaging system is placed in the reconstructed beam, an image of the object will be seen even when the object is no longer present...
, Fresnel diffraction
Fresnel diffraction
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction, is an approximation of Kirchhoff-Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field....
, and evanescent wave
Evanescent wave
An evanescent wave is a nearfield standing wave with an intensity that exhibits exponential decay with distance from the boundary at which the wave was formed. Evanescent waves are a general property of wave-equations, and can in principle occur in any context to which a wave-equation applies...
systems. Some of such systems may become competitive with established methods of visualization and measuring of nano-objects. See the overview at Nanowiki (Nanotechnology).
See also
- Atom opticsAtom opticsAtom optics is the area of physics which deals with beams of cold, slowly moving neutral atoms, as a special case of a particle beam....
- Atomic mirrorAtomic mirror (physics)In physics, an atomic mirror is a device which reflects neutral atoms in the similar way as the conventional mirror reflects visible light. Atomic mirrors can be made of electric fields or magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves or just silicon wafer; in the last case, atoms are reflected by the...
- Quantum reflectionQuantum reflectionQuantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
- Ridged mirrorRidged mirrorIn atomic physics, a ridged mirror is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles coming at the grazing incidence angle, characterised in the following: in order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this...
- Grazing angle
- Zeno effect
- Matter wave

