
Auditory fatigue
Encyclopedia
Auditory fatigue is defined as a temporary loss of hearing after exposure to sound. This results in a temporary shift of the auditory threshold known as a temporary threshold shift (TTS). The damage can become permanent (permanent threshold shift, PTS) if sufficient recovery time is not allowed for before continued sound exposure. When the hearing loss is rooted from a traumatic occurrence, it may be classified as noise-induced hearing loss, or NIHL.
There are two main types of auditory fatigue, short-term and long-term. These are distinguished from each other by several characteristics listed individually below.
Short-term fatigue
Long-term fatigue
is extensive, and can be divided into the inner ear
and outer ear
.
The remainder of this article mainly references the cochlea
, outer hair cells, and Organ of Corti
.
In general, structural damages to any anatomical part of the ear can cause hearing-related problems. Usually, minor bending of the stereocilia (inner ear) is associated with temporary hearing loss and is involved in auditory fatigue. Complete loss of the stereocilia causes permanent hearing damage and is more associated with noise-induced hearing loss and other auditory diseases.
The outer hair cells, or OHCs, can be thought of as microamplifiers that provide stimulation to the inner hair cells. The OHCs are the most fragile of the hair cells, hence their involvement in auditory fatigue and other hearing impairments.
described below. Auditory fatigue can be explained by the relative activity of the active process at low-level stimulation (<30dB).
There are two different systems associated with the mechanics of the cochlea
: the classical passive system and an active process. The passive system works to stimulate the inner hair cells directly and works at levels above 40dB. At stimulation levels that prevent the excitation of the passive system, prolonged noise exposure results in a decrease in the loudness heard over time, even when the actual intensity of the noise has not changed. This is caused by the exhaustion of the active process.
The active process is also known as the cochlear amplifier. This amplification increases vibrations of the basilar membrane through energy obtained from the Organ of Corti. As the stimulation increases, it is assumed that basilar membrane
displacement, caused by the traveling wave, becomes continually more basal in regards to the cochlea. A sustained low-level stimulus can cause an energetic exhaustion of the active system which in turn prevents the passive system from activating.
is required in order to maintain the electrochemical gradients used in mechano-electrical and electro-mechanical transduction during noise exposure and sound recognition. The metabolic activity is associated with active displacements which are components of the sound-induced vibration involving prestin
, a motor protein that causes OHC motility. Excess vibrations require increased metabolic energy.
In addition, these extra vibrations can cause the formation of free radicals known as reactive oxygen species
or ROS. Elevated levels of ROS continue to increase the metabolic demands of the system. These increasing demands fatigue the system and eventually lead to structural damages to the Organ of Corti.
and return threshold levels to their baseline values. There is currently no way to estimate the amount of time needed to recover from auditory fatigue because it is not usually detectable until after the injury has already occurred. Studies that measured recovery time have noted that the time required is related to the magnitude of the initial hearing loss. The most significant recovery was found to occur during the first 15 minutes following cessation of the noise exposure. When sufficient recovery time is not allotted, the effects become permanent and cause acquired noise-induced hearing loss. Up to 120 minutes of recovery time can be required of noises of only 95 dB. For comparison, common items that can produce noise at this level are motorcycles and subways.
and salicylic acid
are considered ototoxic at certain doses. Research has been done to determine their ability to protect against auditory fatigue and permanent damage through toughening phenomena, a state described by reduced active cochlear displacements. Although limited research has been done with these two substances in terms of protective drug regimes because of their associated risks, both have shown positive results in reducing auditory fatigue by the decrease in ROS formation through individual mechanisms described below.
Furosemide injections prior to noise exposure have been shown to decrease the endocochlear potential
. This decrease results in a reduction of active cochlear displacements and it is believed that the protection by furosemide stems from the limitation of excessive vibrations while the cochlear amplifier is depressed.
Salicylic acid competitively interferes with anion binding to OHC prestin which thereby reduces motility. This reduction in active displacement is again associated with depression of the cochlear amplifier which decreases the excessive vibrations experienced during noise-exposure.
Antioxidant
Vitamins A
, C
and E
have been shown to be 'free radical scavengers
' by studies looking for protective tendencies of antioxidants. In addition, NAC, or N-acetyl-L-cysteine (acetylcysteine), has been shown to reduce ROS formation associated with the excessive vibrations induced by the noise exposure.
Although auditory fatigue and NIHL protective measures would be helpful for those who are constantly exposed to long and loud noises, current research is limited due to the negative associations with the substances. Furosemide
is used in congestive heart failure treatments because of its diuretic
properties. Salicylic acid
is a compound most frequently used in anti-acne washes, but is also an anticoagulant
. Further uses of these substances would need to be personalized to the individual and only under close monitoring. Antioxidants do not have these negative effects and therefore are the most commonly researched substance for the purpose of protecting against auditory fatigue. However, at this time there has been no marketed application. In addition, no synergistic relationships between the drugs on the degree of reduction of auditory fatigue have been discovered at this time.
There are several factors that may not be harmful to the auditory system by themselves, but when paired with an extended noise exposure duration have been shown to increase the risk of auditory fatigue. This is important because humans will remove themselves from a noisy environment if it passes their pain threshold. However, when paired with other factors that may not physically recognizable as damaging, TTS may be greater even with less noise exposure. One such factor is physical exercise. Although this is generally good for the body, combined noise exposure during highly physical activities was shown to produce a greater TTS than just the noise exposure alone. This could be related to the amount of ROS being produced by the excessive vibrations further increasing the metabolic activity required, which is already increased during physical exercise. However, a person can decrease their susceptibility to TTS by improving their cardiovascular fitness overall.
Heat exposure is another risk factor. As blood temperature rises, TTS increases when paired with high-frequency noise exposure. It is hypothesized that hair cells for high-frequency transduction require a greater oxygen supply than others, and the two simultaneous metabolic processes can deplete any oxygen reserves of the cochlea. In this case, the auditory system undergoes temporary changes caused by a decrease in the oxygen tension of the cochlear endolymph that leads to vasoconstriction
of the local vessels. Further research could be done to see if this is a reason for the increased TTS during physical exercise that is during continued noise-exposure as well.
Another factor that may not show signs of being harmful is the current workload of a person. Exposure to noise greater than 95dB in individuals with heavy workloads was shown to cause severe TTS. In addition, the workload was a driving factor in the amount of recovery time required to return threshold levels to their baselines. In contrast, a factor that is harmful to the body, but not normally directly to the auditory system is smoking. This common lifestyle habit has also been shown to increase temporary threshold shifts that occur from noise exposure damages.
There are some factors that are known to directly affect the auditory system. Contact with ototoxic chemicals such as styrene, toluene
and carbon disulfide
heighten the risk of auditory damages. Those individuals in work environments are more likely to experience the noise and chemical combination that can increase the likelihood of auditory fatigue. Individually, styrene is known to cause structural damages of the cochlea without actually interfering with functional capabilities. This explains the synergistic interaction between noise and styrene because the cochlea will be increasingly damaged with the excessive vibrations of the noise plus the damage caused by the chemical itself. Specifically, noise damage typically damages the first layer of the outer hair cells. The combined effects of styrene and noise exposure shows damages to all three rows instead, reinforcing previous results. Also, the combined effects of these chemicals and the noise produce greater auditory fatigue than when an individual is exposed to one factor immediately followed by the next.
It is important to understand that noise exposure itself is the main influential factor in threshold shifts and auditory fatigue, but that individuals may be at greater risk when synergistic effects take place during interactions with the above factors.
There are two main types of auditory fatigue, short-term and long-term. These are distinguished from each other by several characteristics listed individually below.
Short-term fatigue
- full recovery from TTS can be achieved in approximately two minutes
- the TTS is relatively independent of exposure duration
- TTS is maximal at the exposure frequency of the sound
Long-term fatigue
- recovery requires a minimum of several minutes but can take up to days
- dependent on exposure duration and noise level
Affected anatomy
Note: The complete anatomy of the earEar
The ear is the organ that detects sound. It not only receives sound, but also aids in balance and body position. The ear is part of the auditory system....
is extensive, and can be divided into the inner ear
Inner ear
The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:...
and outer ear
Outer ear
The outer ear is the external portion of the ear, which consists of the pinna, concha, and external auditory meatus. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum . One consequence of the configuration of the external ear is to selectively boost the sound pressure 30- to 100-fold for...
.
The remainder of this article mainly references the cochlea
Cochlea
The cochlea is the auditory portion of the inner ear. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, making 2.5 turns around its axis, the modiolus....
, outer hair cells, and Organ of Corti
Organ of Corti
The organ of Corti is the organ in the inner ear of mammals that contains auditory sensory cells, or "hair cells."The organ was named after the Italian anatomist Marquis Alfonso Giacomo Gaspare Corti , who conducted microscopic research of the mammaliean auditory system.-Structure and function:The...
.
In general, structural damages to any anatomical part of the ear can cause hearing-related problems. Usually, minor bending of the stereocilia (inner ear) is associated with temporary hearing loss and is involved in auditory fatigue. Complete loss of the stereocilia causes permanent hearing damage and is more associated with noise-induced hearing loss and other auditory diseases.
The outer hair cells, or OHCs, can be thought of as microamplifiers that provide stimulation to the inner hair cells. The OHCs are the most fragile of the hair cells, hence their involvement in auditory fatigue and other hearing impairments.
 |
 |
|
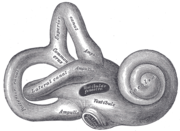
| Depiction of inner ear Inner ear The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:... showing Cochlea Cochlea The cochlea is the auditory portion of the inner ear. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, making 2.5 turns around its axis, the modiolus.... |
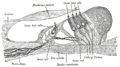
Depiction of Cochlea showing Organ of Corti Organ of Corti The organ of Corti is the organ in the inner ear of mammals that contains auditory sensory cells, or "hair cells."The organ was named after the Italian anatomist Marquis Alfonso Giacomo Gaspare Corti , who conducted microscopic research of the mammaliean auditory system.-Structure and function:The... |
Organ of Corti showing hair cells |
Traveling wave theory
Temporary threshold shifts related to auditory fatigue are related to the amplitude of a stimulus-driven traveling wave. This is believed to be true because the vibration propagated by the active process is not usually at the center of the maximum amplitude of this wave. Instead, it is located much further down and the differences associated between them explain the shift in threshold. The TTS that is experienced is the exhaustion of the active system located at the locus of the traveling wave driven by the cochlear amplifierCochlear amplifier
The cochlear amplifier was first proposed in 1948 by T. Gold. This was around the time when Georg von Békésy was publishing articles observing the propagation of passive travelling waves in the dead Cochlea....
described below. Auditory fatigue can be explained by the relative activity of the active process at low-level stimulation (<30dB).
Classical passive system
There are two different systems associated with the mechanics of the cochlea
Cochlea
The cochlea is the auditory portion of the inner ear. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, making 2.5 turns around its axis, the modiolus....
: the classical passive system and an active process. The passive system works to stimulate the inner hair cells directly and works at levels above 40dB. At stimulation levels that prevent the excitation of the passive system, prolonged noise exposure results in a decrease in the loudness heard over time, even when the actual intensity of the noise has not changed. This is caused by the exhaustion of the active process.
Active process
The active process is also known as the cochlear amplifier. This amplification increases vibrations of the basilar membrane through energy obtained from the Organ of Corti. As the stimulation increases, it is assumed that basilar membrane
Basilar membrane
The basilar membrane within the cochlea of the inner ear is a stiff structural element that separates two liquid-filled tubes that run along the coil of the cochlea, the scala media and the scala tympani .-Function:...
displacement, caused by the traveling wave, becomes continually more basal in regards to the cochlea. A sustained low-level stimulus can cause an energetic exhaustion of the active system which in turn prevents the passive system from activating.
Excessive vibrations
Currently it is believed that auditory fatigue and NIHL are related to excessive vibrations of the inner ear which may cause structural damages. Metabolic activityMetabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
is required in order to maintain the electrochemical gradients used in mechano-electrical and electro-mechanical transduction during noise exposure and sound recognition. The metabolic activity is associated with active displacements which are components of the sound-induced vibration involving prestin
Prestin
Prestin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A5 gene.Prestin is the motor protein of the outer hair cells of the inner ear of the mammalian cochlea. It is highly expressed in the outer hair cells, and is not expressed in the nonmotile inner hair cells...
, a motor protein that causes OHC motility. Excess vibrations require increased metabolic energy.
In addition, these extra vibrations can cause the formation of free radicals known as reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen. Examples include oxygen ions and peroxides. Reactive oxygen species are highly reactive due to the presence of unpaired valence shell electrons....
or ROS. Elevated levels of ROS continue to increase the metabolic demands of the system. These increasing demands fatigue the system and eventually lead to structural damages to the Organ of Corti.
Recovery
In all cases of auditory fatigue, sufficient recovery time should allow full correction of the hearing impairmentHearing impairment
-Definition:Deafness is the inability for the ear to interpret certain or all frequencies of sound.-Environmental Situations:Deafness can be caused by environmental situations such as noise, trauma, or other ear defections...
and return threshold levels to their baseline values. There is currently no way to estimate the amount of time needed to recover from auditory fatigue because it is not usually detectable until after the injury has already occurred. Studies that measured recovery time have noted that the time required is related to the magnitude of the initial hearing loss. The most significant recovery was found to occur during the first 15 minutes following cessation of the noise exposure. When sufficient recovery time is not allotted, the effects become permanent and cause acquired noise-induced hearing loss. Up to 120 minutes of recovery time can be required of noises of only 95 dB. For comparison, common items that can produce noise at this level are motorcycles and subways.
Toughening and energy spread
Two protective measures have been investigated related to the amount of noise exposure and the duration of that exposure. Although these would be hard to regulate in spontaneous occurrences, they may could have a positive effect on work conditions if guidelines could be set for machining times or for other systems that produce loud noises over a long period of time. The toughening effect is put in place by increasing the system's resistance to noise over time. Currently, the specific mechanisms that cause the cochlear toughening are not known. However, the OHCs and related processes are known to play a role.The other toughening measure is to spread a given amount of energy to the system over a longer amount of time. This would allow recovery processes to take place during the quiet interludes that are gained by increasing the exposure duration. So far, studies have not shown a direct correlation between the amount of toughening and the amount of threshold shift experienced. This suggests that even a toughened cochlea may not be completely protected.Substances
Both furosemideFurosemide
Furosemide or frusemide is a loop diuretic used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and edema. It is most commonly marketed by Sanofi-Aventis under the brand name Lasix...
and salicylic acid
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid and a beta hydroxy acid. This colorless crystalline organic acid is widely used in organic synthesis and functions as a plant hormone. It is derived from the metabolism of salicin...
are considered ototoxic at certain doses. Research has been done to determine their ability to protect against auditory fatigue and permanent damage through toughening phenomena, a state described by reduced active cochlear displacements. Although limited research has been done with these two substances in terms of protective drug regimes because of their associated risks, both have shown positive results in reducing auditory fatigue by the decrease in ROS formation through individual mechanisms described below.
Furosemide
Furosemide injections prior to noise exposure have been shown to decrease the endocochlear potential
Endocochlear potential
The endocochlear potential is the main resting potential in the cochlea. It is a positive direct current of 80mV which can be recorded from the endolymph with electrodes. When a sound is presented, the endocochlear potential changes either positive or negative in the endolymph, depending on the...
. This decrease results in a reduction of active cochlear displacements and it is believed that the protection by furosemide stems from the limitation of excessive vibrations while the cochlear amplifier is depressed.
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid competitively interferes with anion binding to OHC prestin which thereby reduces motility. This reduction in active displacement is again associated with depression of the cochlear amplifier which decreases the excessive vibrations experienced during noise-exposure.
AntioxidantAntioxidantAn antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
s
Vitamins A
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a vitamin that is needed by the retina of the eye in the form of a specific metabolite, the light-absorbing molecule retinal, that is necessary for both low-light and color vision...
, C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
and E
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is used to refer to a group of fat-soluble compounds that include both tocopherols and tocotrienols. There are many different forms of vitamin E, of which γ-tocopherol is the most common in the North American diet. γ-Tocopherol can be found in corn oil, soybean oil, margarine and dressings...
have been shown to be 'free radical scavengers
Scavenger (chemistry)
A scavenger in chemistry is a chemical substance added to a mixture in order to remove or inactivate impurities or unwanted reaction products. Their use is wide-ranged:...
' by studies looking for protective tendencies of antioxidants. In addition, NAC, or N-acetyl-L-cysteine (acetylcysteine), has been shown to reduce ROS formation associated with the excessive vibrations induced by the noise exposure.
Limitations
Although auditory fatigue and NIHL protective measures would be helpful for those who are constantly exposed to long and loud noises, current research is limited due to the negative associations with the substances. Furosemide
Furosemide
Furosemide or frusemide is a loop diuretic used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and edema. It is most commonly marketed by Sanofi-Aventis under the brand name Lasix...
is used in congestive heart failure treatments because of its diuretic
Diuretic
A diuretic provides a means of forced diuresis which elevates the rate of urination. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way.- Medical uses :...
properties. Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid and a beta hydroxy acid. This colorless crystalline organic acid is widely used in organic synthesis and functions as a plant hormone. It is derived from the metabolism of salicin...
is a compound most frequently used in anti-acne washes, but is also an anticoagulant
Anticoagulant
An anticoagulant is a substance that prevents coagulation of blood. A group of pharmaceuticals called anticoagulants can be used in vivo as a medication for thrombotic disorders. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as test tubes, blood transfusion bags, and renal dialysis...
. Further uses of these substances would need to be personalized to the individual and only under close monitoring. Antioxidants do not have these negative effects and therefore are the most commonly researched substance for the purpose of protecting against auditory fatigue. However, at this time there has been no marketed application. In addition, no synergistic relationships between the drugs on the degree of reduction of auditory fatigue have been discovered at this time.
Risk increasing factors
- Physical exercise
- Heat exposure
- Workload
- Smoking
- Ototoxic chemicals
There are several factors that may not be harmful to the auditory system by themselves, but when paired with an extended noise exposure duration have been shown to increase the risk of auditory fatigue. This is important because humans will remove themselves from a noisy environment if it passes their pain threshold. However, when paired with other factors that may not physically recognizable as damaging, TTS may be greater even with less noise exposure. One such factor is physical exercise. Although this is generally good for the body, combined noise exposure during highly physical activities was shown to produce a greater TTS than just the noise exposure alone. This could be related to the amount of ROS being produced by the excessive vibrations further increasing the metabolic activity required, which is already increased during physical exercise. However, a person can decrease their susceptibility to TTS by improving their cardiovascular fitness overall.
Heat exposure is another risk factor. As blood temperature rises, TTS increases when paired with high-frequency noise exposure. It is hypothesized that hair cells for high-frequency transduction require a greater oxygen supply than others, and the two simultaneous metabolic processes can deplete any oxygen reserves of the cochlea. In this case, the auditory system undergoes temporary changes caused by a decrease in the oxygen tension of the cochlear endolymph that leads to vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, particularly the large arteries, small arterioles and veins. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in...
of the local vessels. Further research could be done to see if this is a reason for the increased TTS during physical exercise that is during continued noise-exposure as well.
Another factor that may not show signs of being harmful is the current workload of a person. Exposure to noise greater than 95dB in individuals with heavy workloads was shown to cause severe TTS. In addition, the workload was a driving factor in the amount of recovery time required to return threshold levels to their baselines. In contrast, a factor that is harmful to the body, but not normally directly to the auditory system is smoking. This common lifestyle habit has also been shown to increase temporary threshold shifts that occur from noise exposure damages.
There are some factors that are known to directly affect the auditory system. Contact with ototoxic chemicals such as styrene, toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
and carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide is a colorless volatile liquid with the formula CS2. The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non-polar solvent...
heighten the risk of auditory damages. Those individuals in work environments are more likely to experience the noise and chemical combination that can increase the likelihood of auditory fatigue. Individually, styrene is known to cause structural damages of the cochlea without actually interfering with functional capabilities. This explains the synergistic interaction between noise and styrene because the cochlea will be increasingly damaged with the excessive vibrations of the noise plus the damage caused by the chemical itself. Specifically, noise damage typically damages the first layer of the outer hair cells. The combined effects of styrene and noise exposure shows damages to all three rows instead, reinforcing previous results. Also, the combined effects of these chemicals and the noise produce greater auditory fatigue than when an individual is exposed to one factor immediately followed by the next.
It is important to understand that noise exposure itself is the main influential factor in threshold shifts and auditory fatigue, but that individuals may be at greater risk when synergistic effects take place during interactions with the above factors.

