
Band-stop filter
Encyclopedia
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
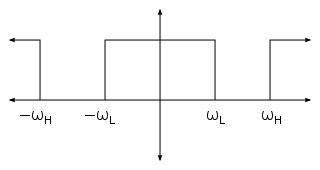
, a band-stop filter or band-rejection filter is a filter
Filter (signal processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
that passes most frequencies
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
unaltered, but attenuates those in a specific range to very low levels. It is the opposite of a band-pass filter
Band-pass filter
A band-pass filter is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects frequencies outside that range.Optical band-pass filters are of common usage....
. A notch filter is a band-stop filter with a narrow stopband
Stopband
A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level...
(high Q factor
Q factor
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, or equivalently, characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency....
).
Narrow notch filters (optical) are used in Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique used to study vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system.It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range...
, live sound reproduction (public address systems, or PA systems) and in instrument amplifier
Instrument amplifier
An instrument amplifier is an electronic amplifier that converts the often barely audible or purely electronic signal from musical instruments such as an electric guitar, an electric bass, or an electric keyboard into an electronic signal capable of driving a loudspeaker that can be heard by the...
s (especially amplifiers or preamplifier
Preamplifier
A preamplifier is an electronic amplifier that prepares a small electrical signal for further amplification or processing. A preamplifier is often placed close to the sensor to reduce the effects of noise and interference. It is used to boost the signal strength to drive the cable to the main...
s for acoustic instruments such as acoustic guitar
Acoustic guitar
An acoustic guitar is a guitar that uses only an acoustic sound board. The air in this cavity resonates with the vibrational modes of the string and at low frequencies, which depend on the size of the box, the chamber acts like a Helmholtz resonator, increasing or decreasing the volume of the sound...
, mandolin
Mandolin
A mandolin is a musical instrument in the lute family . It descends from the mandore, a soprano member of the lute family. The mandolin soundboard comes in many shapes—but generally round or teardrop-shaped, sometimes with scrolls or other projections. A mandolin may have f-holes, or a single...
, bass instrument amplifier
Double bass
The double bass, also called the string bass, upright bass, standup bass or contrabass, is the largest and lowest-pitched bowed string instrument in the modern symphony orchestra, with strings usually tuned to E1, A1, D2 and G2...
, etc.) to reduce or prevent audio feedback
Audio feedback
Audio feedback is a special kind of positive feedback which occurs when a sound loop exists between an audio input and an audio output...
, while having little noticeable effect on the rest of the frequency spectrum (electronic
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
or software
Computer software
Computer software, or just software, is a collection of computer programs and related data that provide the instructions for telling a computer what to do and how to do it....
filters). Other names include 'band limit filter', 'T-notch filter', 'band-elimination filter', and 'band-reject filter'.
Typically, the width of the stopband is less than 1 to 2 decade
Decade (log scale)
One decade is a factor of 10 difference between two numbers measured on a logarithmic scale. It is especially useful when referring to frequencies and when describing frequency response of electronic systems, such as audio amplifiers and filters.-Calculations:The factor-of-ten in a decade can be...
s (that is, the highest frequency attenuated is less than 10 to 100 times the lowest frequency attenuated). In the audio
Audio frequency
An audio frequency or audible frequency is characterized as a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human...
band, a notch filter uses high and low frequencies that may be only semitone
Semitone
A semitone, also called a half step or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically....
s apart.
Audio example 1: Anti-hum filter for countries using 60 Hz power lines
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
- Low Freq: 59 HzHertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
- High Freq: 61 HzHertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
This means that the filter passes all frequencies, except for the range of 59–61 Hz. This would be used to filter out the mains hum
Mains hum
Mains hum, electric hum, or power line hum is an audible oscillation of alternating current at the frequency of the mains electricity, which is usually 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the local power line frequency...
from the 60 Hz power line, though its higher harmonics could still be present. The common European version of the filter would have a 49–51 Hz range.
Audio example 2: Anti-presence filter
- Low Freq: 1 kHz
- High Freq: 4 kHz
RF example 1: Non-linearities of power amplifiers
For instance, when measuring non-linearities of power amplifiers a very narrow notch filter could be very useful to avoid the carrier so maximum input power of e.g. a spectrum analyser used to detect spurious content will not be exceeded.
RF example 2: Wave trap
A notch filter, usually a simple LC circuit, used to remove a specific interfering frequency. This is a technique used with radio receivers that are so close to a transmitter that it swamps all other signals. The wave trap is used to remove, or greatly reduce, the signal from the local transmitter.
Optical notch filters sometimes rely on destructive interference.
See also
- Band-pass filterBand-pass filterA band-pass filter is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects frequencies outside that range.Optical band-pass filters are of common usage....
- High-pass filterHigh-pass filterA high-pass filter is a device that passes high frequencies and attenuates frequencies lower than its cutoff frequency. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system...
- Low-pass filterLow-pass filterA low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
- Mains humMains humMains hum, electric hum, or power line hum is an audible oscillation of alternating current at the frequency of the mains electricity, which is usually 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the local power line frequency...
- Parametric equalizer
- Bass instrument amplificationBass instrument amplificationBass instrument amplification, used for the bass guitar, double bass and similar instruments, is distinct from other types of amplification systems due to the particular challenges associated with low-frequency sound reproduction. This distinction affects the design of the loudspeakers, the speaker...
(discusses use of notch filter to prevent feedback)

