
Banksia ser. Crocinae
Encyclopedia
Banksia ser. Crocinae is a taxonomic
series (botany)
in the genus
Banksia
. It consists of four closely related species, all of which are endemic to Western Australia
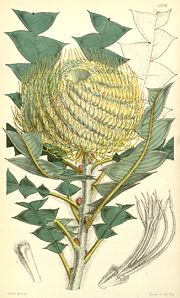
; namely B. prionotes
(Acorn Banksia), B. burdettii
(Burdett's Banksia), B. hookeriana
(Hooker's Banksia) and B. victoriae
(Woolly Orange Banksia). The series was first published by Alex George
in 1981, but discarded by Kevin Thiele
and Pauline Ladiges in 1996, and finally reinstated by George in 1999. Recent Cladistic
analyses suggest that it is monophyletic
or nearly so.
. George grouped the four species into a series on the grounds that they are "remarkably similar especially in floral morphology", giving the series the name B. ser. Crocinae from the Latin
crocinus ("rich orange"), in reference to the bright orange inflorescence
s. He also remarked that "the series is probably derived from the Orthostylis, which can in hingsight be read as an admission of paraphyly
.
The placement and circumscription of B. ser. Crocinae in George's 1981 arrangement may be summarised as follows:
and Pauline Ladiges undertook a cladistic
analysis of morphological
characters of Banksia, which yielded a phylogeny somewhat at odds with George's taxonomic arrangement. Their cladogram
included a clade
consisting of the members of George's B. ser. Banksia, together with the four members of B. ser. Crocinae:
B. ser. Crocinae was found to be monophyletic, but B. ser. Banksia was paraphyletic
with respect to it. To resolve this, Thiele and Ladiges abandoned B. ser. Crocinae, transferring its four taxa into B. ser. Banksia. They then divided B. ser. Banksia, into two subseries, with the species belonging to George's B. ser. Crocinae endind up in B. subser. Cratistylis
.
series of monographs was published. This was essentially a revision of George's 1981 arrangement, which took into account some of Thiele and Ladiges' data, but rejected their overall arrangement. With respect to B. ser. Cyrtostylis, George's 1999 arrangement was identical to his 1981 arrangement, except that B. burdettii and B. victoriae were exchanged in phyletic order.
 Since 1998, Austin Mast
Since 1998, Austin Mast
has been publishing results of ongoing cladistic analyses of DNA sequence
data for the subtribe Banksiinae. His analyses suggest a phylogeny that is rather different to previous taxonomic arrangements. B. ser. Crocinae is monophyletic or nearly so, occurring in a polytomous clade with B. menziesii
; this clade is sister to a clade containing B. sceptrum
(Sceptre Banksia) and B. ashbyi
(Ashby's Banksia), and a clade containing Banksia lindleyana
(Porcupine Banksia):
Early in 2007 Mast and Thiele initiated a rearrangement of Banksia by transferring Dryandra into it, and publishing B. subg. Spathulatae
for the species having spoon-shaped cotyledon
s; in this way they also redefined the autonym
B. subg. Banksia
. All members of B. ser. Crocinae fall within Mast and Thiele's B. subg. Banksia, but no further details have been published. Mast and Thiele have foreshadowed publishing a full arrangement once DNA sampling of Dryandra is complete.
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
series (botany)
Series (botany)
Series is a low-level taxonomic rank below that of section but above that of species.In botany, a series is a subdivision of a genus...
in the genus
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
Banksia
Banksia
Banksia is a genus of around 170 species in the plant family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes and fruiting "cones" and heads. When it comes to size, banksias range from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up...
. It consists of four closely related species, all of which are endemic to Western Australia
Western Australia
Western Australia is a state of Australia, occupying the entire western third of the Australian continent. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Great Australian Bight and Indian Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east and South Australia to the south-east...
; namely B. prionotes
Banksia prionotes
Banksia prionotes, commonly known as Acorn Banksia or Orange Banksia, is a species of shrub or tree of the genus Banksia in the family Proteaceae. It is native to the southwest of Western Australia and can reach up to 10 m in height. It can be much smaller in more exposed areas or in the...
(Acorn Banksia), B. burdettii
Banksia burdettii
Burdett's Banksia is a species of large shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs on sandplain country north of Gingin, Western Australia....
(Burdett's Banksia), B. hookeriana
Banksia hookeriana
The Hooker's Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs on sandplain shrubland between Arrowsmith and Eneabba in Western Australia. Seeds do not require any treatment, and take 23 to 49 days to germinate....
(Hooker's Banksia) and B. victoriae
Banksia victoriae
Banksia victoriae, commonly known as Woolly Orange Banksia, is a species of large shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia...
(Woolly Orange Banksia). The series was first published by Alex George
Alex George
Alexander Segger George is a Western Australian botanist. He is the authority on the plant genera Banksia and Dryandra...
in 1981, but discarded by Kevin Thiele
Kevin Thiele
Kevin R. Thiele is curator of the Western Australian Herbarium. His research interests include the systematics of the plant families Proteaceae, Rhamnaceae and Violaceae, and the conservation ecology of grassy woodland ecosystems...
and Pauline Ladiges in 1996, and finally reinstated by George in 1999. Recent Cladistic
Cladistics
Cladistics is a method of classifying species of organisms into groups called clades, which consist of an ancestor organism and all its descendants . For example, birds, dinosaurs, crocodiles, and all descendants of their most recent common ancestor form a clade...
analyses suggest that it is monophyletic
Monophyly
In common cladistic usage, a monophyletic group is a taxon which forms a clade, meaning that it contains all the descendants of the possibly hypothetical closest common ancestor of the members of the group. The term is synonymous with the uncommon term holophyly...
or nearly so.
George 1981
B. ser. Banksia originated in the 1981 arrangement of George, published in his classic monograph The genus Banksia L.f. (Proteaceae)The genus Banksia L.f. (Proteaceae)
The genus Banksia L.f. is a 1981 monograph by Alex George on the taxonomy of the plant genus Banksia. Published by the Western Australian Herbarium as Nuytsia 3, it presented George's taxonomic arrangement of Banksia, the first major taxonomic revision of the genus since George Bentham published...
. George grouped the four species into a series on the grounds that they are "remarkably similar especially in floral morphology", giving the series the name B. ser. Crocinae from the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
crocinus ("rich orange"), in reference to the bright orange inflorescence
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Strictly, it is the part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed and which is accordingly modified...
s. He also remarked that "the series is probably derived from the Orthostylis, which can in hingsight be read as an admission of paraphyly
Paraphyly
A group of taxa is said to be paraphyletic if the group consists of all the descendants of a hypothetical closest common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups of descendants...
.
The placement and circumscription of B. ser. Crocinae in George's 1981 arrangement may be summarised as follows:
- Banksia
- B. subg. BanksiaBanksia subg. BanksiaBanksia subg. Banksia is a valid botanic name for a subgenus of Banksia. As an autonym, it necessarily contains the type species of Banksia, B. serrata . Within this constraint, however, there have been various circumscriptions.-Banksia verae:B. subg...
- B. sect. BanksiaBanksia sect. BanksiaBanksia sect. Banksia is one of four sections of Banksia subgenus Banksia. It contains those species of subgenus Banksia with straight or sometimes curved but not hooked styles. These species all have cylindrical inflorescences and usually exhibit a bottom-up sequence of flower anthesis...
- B. ser. SalicinaeBanksia ser. SalicinaeBanksia ser. Salicinae is a valid botanic name for a series of Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Meissner:...
(9 species) - B. ser. GrandesBanksia ser. GrandesBanksia ser. Grandes is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of two closely related species in section Banksia, both endemic to Western Australia. These are B. grandis and B. solandri ....
(2 species) - B. ser. QuercinaeBanksia ser. QuercinaeBanksia ser. Quercinae is avalid botanic name for a series of Banksia. First published by Carl Meissner in 1856, the name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Meissner:...
(3 species) - B. ser. Orthostylis (4 species)
- B. ser. Crocinae
- B. prionotesBanksia prionotesBanksia prionotes, commonly known as Acorn Banksia or Orange Banksia, is a species of shrub or tree of the genus Banksia in the family Proteaceae. It is native to the southwest of Western Australia and can reach up to 10 m in height. It can be much smaller in more exposed areas or in the...
- B. victoriaeBanksia victoriaeBanksia victoriae, commonly known as Woolly Orange Banksia, is a species of large shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia...
- B. hookerana (now spelled B. hookerianaBanksia hookerianaThe Hooker's Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs on sandplain shrubland between Arrowsmith and Eneabba in Western Australia. Seeds do not require any treatment, and take 23 to 49 days to germinate....
) - B. burdettiiBanksia burdettiiBurdett's Banksia is a species of large shrub or small tree in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs on sandplain country north of Gingin, Western Australia....
- B. prionotes
- B. ser. CyrtostylisBanksia ser. CyrtostylisBanksia ser. Cyrtostylis is a valid botanic name for a taxonomic series within the plant genus Banksia. First published at sectional rank by George Bentham in 1870, it was demoted to a series by Alex George in 1981. The name has had three circumscriptions.-According to Bentham:Bentham published B....
(12 species) - B. ser. ProstrataeBanksia ser. ProstrataeBanksia ser. Prostratae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of six closely related species in section Banksia, all endemic to Western Australia, with a prostrate habit.Banksia ser...
(6 species) - B. ser. TetragonaeBanksia ser. TetragonaeBanksia ser. Tetragonae is a taxonomic series in the genus Banksia. It consists of three closely related species of erect shrub with pendulous inflorescences in section Banksia. These are B. lemanniana , B. caleyi and B. aculeata ....
(3 species) - B. ser. Coccineae (1 species)
- B. ser. Salicinae
- B. sect. OncostylisBanksia sect. OncostylisBanksia sect. Oncostylis is one of four sections of subgenus Banksia subg. Banksia. It contains those Banksia species with hooked pistils. All of the species in Oncostylis also exhibit a top-down sequence of flower anthesis, except for Banksia nutans which is bottom-up.Banksia sect...
(3 series, 21 species)
- B. sect. Banksia
- B. subg. IsostylisBanksia subg. IsostylisBanksia subg. Isostylis is a subgenus of Banksia. It contains three closely related species, all of which occur only in Southwest Western Australia. Members of subgenus Isostylis have dome-shaped flower heads that are superficially similar to those of B. ser...
(2 species)
- B. subg. Banksia
Thiele and Ladiges 1996
In 1996, Kevin ThieleKevin Thiele
Kevin R. Thiele is curator of the Western Australian Herbarium. His research interests include the systematics of the plant families Proteaceae, Rhamnaceae and Violaceae, and the conservation ecology of grassy woodland ecosystems...
and Pauline Ladiges undertook a cladistic
Cladistics
Cladistics is a method of classifying species of organisms into groups called clades, which consist of an ancestor organism and all its descendants . For example, birds, dinosaurs, crocodiles, and all descendants of their most recent common ancestor form a clade...
analysis of morphological
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
characters of Banksia, which yielded a phylogeny somewhat at odds with George's taxonomic arrangement. Their cladogram
Cladogram
A cladogram is a diagram used in cladistics which shows ancestral relations between organisms, to represent the evolutionary tree of life. Although traditionally such cladograms were generated largely on the basis of morphological characters, DNA and RNA sequencing data and computational...
included a clade
Clade
A clade is a group consisting of a species and all its descendants. In the terms of biological systematics, a clade is a single "branch" on the "tree of life". The idea that such a "natural group" of organisms should be grouped together and given a taxonomic name is central to biological...
consisting of the members of George's B. ser. Banksia, together with the four members of B. ser. Crocinae:

B. ser. Crocinae was found to be monophyletic, but B. ser. Banksia was paraphyletic
Paraphyly
A group of taxa is said to be paraphyletic if the group consists of all the descendants of a hypothetical closest common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups of descendants...
with respect to it. To resolve this, Thiele and Ladiges abandoned B. ser. Crocinae, transferring its four taxa into B. ser. Banksia. They then divided B. ser. Banksia, into two subseries, with the species belonging to George's B. ser. Crocinae endind up in B. subser. Cratistylis
Banksia subser. Cratistylis
Banksia subser. Cratistylis is a valid botanic name for a subseries of Banksia. It was first published by Kevin Thiele in 1996, but discarded by Alex George in 1999.-Cladistics:...
.
George 1999
Thiele and Ladiges' arrangement remained current only until 1999, when George's treatment of the genus for the Flora of AustraliaFlora of Australia (series)
The Flora of Australia is a 59 volume series describing the vascular plants, bryophytes and lichens present in Australia and its external territories...
series of monographs was published. This was essentially a revision of George's 1981 arrangement, which took into account some of Thiele and Ladiges' data, but rejected their overall arrangement. With respect to B. ser. Cyrtostylis, George's 1999 arrangement was identical to his 1981 arrangement, except that B. burdettii and B. victoriae were exchanged in phyletic order.
Recent developments

Austin Mast
Austin R. Mast is a research botanist. Born in 1972, he obtained a Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 2000. He is currently an associate professor within the Department of Biological Science at Florida State University , and has been director of FSU's since August 2003.One of his...
has been publishing results of ongoing cladistic analyses of DNA sequence
DNA sequence
The sequence or primary structure of a nucleic acid is the composition of atoms that make up the nucleic acid and the chemical bonds that bond those atoms. Because nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are unbranched polymers, this specification is equivalent to specifying the sequence of...
data for the subtribe Banksiinae. His analyses suggest a phylogeny that is rather different to previous taxonomic arrangements. B. ser. Crocinae is monophyletic or nearly so, occurring in a polytomous clade with B. menziesii
Banksia menziesii
Banksia menziesii, commonly known as firewood banksia, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Banksia. It is a gnarled tree up to 10 m tall, or a lower spreading 1–3 m shrub in the more northern parts of its range. The serrated leaves are dull green with new growth a paler grey...
; this clade is sister to a clade containing B. sceptrum
Banksia sceptrum
Banksia sceptrum, the Sceptre Banksia, occurs in Western Australia near the central west coast from Geraldton north through Kalbarri to Hamelin Pool. It extends inland almost to Mullewa....
(Sceptre Banksia) and B. ashbyi
Banksia ashbyi
The Ashby's Banksia is a species of shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It occurs in heath and spinifex country along the coast of Western Australia between Geraldton and Exmouth.-Description:...
(Ashby's Banksia), and a clade containing Banksia lindleyana
Banksia lindleyana
Banksia lindleyana, commonly known as the Porcupine Banksia, is a species of woody shrub in the genus Banksia of the family Proteaceae. It generally grows as a small shrub to 1 m high with long narrow serrated leaves, and bright yellow oval or round inflorescences...
(Porcupine Banksia):
Early in 2007 Mast and Thiele initiated a rearrangement of Banksia by transferring Dryandra into it, and publishing B. subg. Spathulatae
Banksia subg. Spathulatae
Banksia subg. Spathulatae is a valid botanic name for a subgenus of Banksia. It was published in 2007 by Austin Mast and Kevin Thiele, and defined as containing all those Banksia species having spathulate cotyledons...
for the species having spoon-shaped cotyledon
Cotyledon
A cotyledon , is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Upon germination, the cotyledon may become the embryonic first leaves of a seedling. The number of cotyledons present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants...
s; in this way they also redefined the autonym
Autonym (botany)
In botanical nomenclature, autonyms are automatically created names, as regulated by the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature . Autonyms are cited without an author. Relevant provisions are in articles 6.8, 22.1-3 and 26.1-3....
B. subg. Banksia
Banksia subg. Banksia
Banksia subg. Banksia is a valid botanic name for a subgenus of Banksia. As an autonym, it necessarily contains the type species of Banksia, B. serrata . Within this constraint, however, there have been various circumscriptions.-Banksia verae:B. subg...
. All members of B. ser. Crocinae fall within Mast and Thiele's B. subg. Banksia, but no further details have been published. Mast and Thiele have foreshadowed publishing a full arrangement once DNA sampling of Dryandra is complete.

