
DNA sequence
Encyclopedia
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biological molecules essential for life, and include DNA and RNA . Together with proteins, nucleic acids make up the most important macromolecules; each is found in abundance in all living things, where they function in encoding, transmitting and expressing genetic information...
and the chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
s that bond those atoms. Because nucleic acids, such as DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
and RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
, are unbranched polymers, this specification is equivalent to specifying the sequence of nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
s that comprise the molecule. This sequence is written as a succession of letters representing a real or hypothetical nucleic acid molecule or strand. By convention, the primary structure of a DNA or RNA molecule is reported from the 5' end to the 3' end.
The sequence has capacity to represent information
Information
Information in its most restricted technical sense is a message or collection of messages that consists of an ordered sequence of symbols, or it is the meaning that can be interpreted from such a message or collection of messages. Information can be recorded or transmitted. It can be recorded as...
. Biological DNA represents the information which directs the functions of a living thing. In that context, the term genetic sequence is often used. Sequences can be read from the biological raw material through DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
methods.
Nucleic acids also have a secondary structure
Secondary structure
In biochemistry and structural biology, secondary structure is the general three-dimensional form of local segments of biopolymers such as proteins and nucleic acids...
and tertiary structure
Tertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
. Primary structure is sometimes mistakenly referred to as primary sequence. Conversely, there is no parallel concept of secondary or tertiary sequence.
Nucleotides

Nucleic acids consist of a chain of linked units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of three subunits: a phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
group and a sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
(ribose
Ribose
Ribose is an organic compound with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide with linear form H––4–H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection....
in the case of RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
, deoxyribose
Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, more, precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H---3-H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom...
in DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
) make up the backbone of the nucleic acid strand, and attached to the sugar is one of a set of nucleobase
Nucleobase
Nucleobases are a group of nitrogen-based molecules that are required to form nucleotides, the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nucleobases provide the molecular structure necessary for the hydrogen bonding of complementary DNA and RNA strands, and are key components in the formation of stable...
s. The nucleobases are important in base pair
Base pair
In molecular biology and genetics, the linking between two nitrogenous bases on opposite complementary DNA or certain types of RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds is called a base pair...
ing of strands to form higher-level secondary
Nucleic acid secondary structure
The secondary structure of a nucleic acid molecule refers to the basepairing interactions within a single molecule or set of interacting molecules, and can be represented as a list of bases which are paired in a nucleic acid molecule....
and tertiary structure
Nucleic acid tertiary structure
300px|thumb|upright|alt = Colored dice with checkered background|Example of a large catalytic RNA. The self-splicing group II intron from Oceanobacillus iheyensis....
such as the famed double helix
Nucleic acid double helix
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its...
.
The possible letters are A, C, G, and T, representing the four nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
bases
Nucleobase
Nucleobases are a group of nitrogen-based molecules that are required to form nucleotides, the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nucleobases provide the molecular structure necessary for the hydrogen bonding of complementary DNA and RNA strands, and are key components in the formation of stable...
of a DNA strand — adenine
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide , and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA...
, cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
, guanine
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
, thymine
Thymine
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at...
— covalently linked to a phosphodiester
Phosphodiester bond
A phosphodiester bond is a group of strong covalent bonds between a phosphate group and two 5-carbon ring carbohydrates over two ester bonds. Phosphodiester bonds are central to all known life, as they make up the backbone of each helical strand of DNA...
backbone. In the typical case, the sequences are printed abutting one another without gaps, as in the sequence AAAGTCTGAC, read left to right in the 5' to 3'
Directionality (molecular biology)
Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. The chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide sugar-ring numerically gives rise to a 5′-end and a 3′-end...
direction. With regards to transcription, a sequence is on the coding strand if it has the same order as the transcribed RNA.
One sequence can be complementary
Complementarity (molecular biology)
In molecular biology, complementarity is a property of double-stranded nucleic acids such as DNA, as well as DNA:RNA duplexes. Each strand is complementary to the other in that the base pairs between them are non-covalently connected via two or three hydrogen bonds...
to another sequence, meaning that they have the base on each position is the complementary (i.e. A to T, C to G) and in the reverse order. For example, the complementary sequence to TTAC is GTAA. If one strand of the double-stranded DNA is considered the sense
Sense (molecular biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, sense is a concept used to compare the polarity of nucleic acid molecules, such as DNA or RNA, to other nucleic acid molecules...
strand, then the other strand, considered the antisense strand, will have the complementary sequence to the sense strand.
Notation
While A, T, C, and G represent a particular nucleotide at a position, there are also letters that represent ambiguity which are used when more than one kind of nucleotide could occur at that position. The rules of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) are as follows:- A = adenine
- C = cytosine
- G = guanine
- T = thymine
- R = G A (purine)
- Y = T C (pyrimidine)
- K = G T (keto)
- M = A C (amino)
- S = G C (strong bonds)
- W = A T (weak bonds)
- B = G T C (all but A)
- D = G A T (all but C)
- H = A C T (all but G)
- V = G C A (all but T)
- N = A G C T (any)
These symbols are also valid for RNA, except with U (uracil) replacing T (thymine).
Apart from adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T) and uracil (U), DNA and RNA also contain bases that have been modified after the nucleic acid chain has been formed. In DNA, the most common modified base is 5-methylcytidine (m5C). In RNA, there are many modified bases, including pseudouridine (Ψ), dihydrouridine (D), inosine (I), ribothymidine (rT) and 7-methylguanosine (m7G). Hypoxanthine
Hypoxanthine
Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative. It is occasionally found as a constituent of nucleic acids where it is present in the anticodon of tRNA in the form of its nucleoside inosine. It has a tautomer known as 6-Hydroxypurine. Hypoxanthine is a necessary additive in certain cell,...
and xanthine
Xanthine
Xanthine , is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids and in other organisms. A number of stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine and theobromine....
are two of the many bases created through mutagen
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens...
presence, both of them through deamination (replacement of the amine-group with a carbonyl-group). Hypoxanthine is produced from adenine
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide , and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA...
, xanthine from guanine
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
. Similarly, deamination of cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
results in uracil
Uracil
Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. The others are adenine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine.Uracil is a common and...
.
Biological significance
In biological systems, nucleic acids contain information which is used by a living cellCell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
to construct specific protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. The sequence of nucleobase
Nucleobase
Nucleobases are a group of nitrogen-based molecules that are required to form nucleotides, the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nucleobases provide the molecular structure necessary for the hydrogen bonding of complementary DNA and RNA strands, and are key components in the formation of stable...
s on a nucleic acid strand is translated
Translation (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the third stage of protein biosynthesis . In translation, messenger RNA produced by transcription is decoded by the ribosome to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide, that will later fold into an active protein...
by cell machinery into a sequence of amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
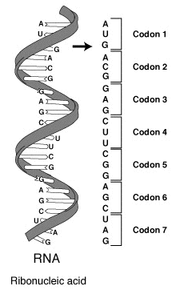
s making up a protein strand. Each group of three bases, called a codon, corresponds to a single amino acid, and there is a specific genetic code
Genetic code
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins by living cells....
by which each possible combination of three bases corresponds to a specific amino acid.
The central dogma of molecular biology
Central dogma of molecular biology
The central dogma of molecular biology was first articulated by Francis Crick in 1958 and re-stated in a Nature paper published in 1970:In other words, the process of producing proteins is irreversible: a protein cannot be used to create DNA....
outlines the mechanism by which proteins are constructed using information contained in nucleic acids. DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
is transcribed
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
into mRNA molecules, which travels to the ribosome
Ribosome
A ribosome is a component of cells that assembles the twenty specific amino acid molecules to form the particular protein molecule determined by the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule....
where the mRNA is used as a template for the construction of the protein strand. Since nucleic acids can bind to molecules with complementary
Complementarity (molecular biology)
In molecular biology, complementarity is a property of double-stranded nucleic acids such as DNA, as well as DNA:RNA duplexes. Each strand is complementary to the other in that the base pairs between them are non-covalently connected via two or three hydrogen bonds...
sequences, there is a distinction between "sense
Sense (molecular biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, sense is a concept used to compare the polarity of nucleic acid molecules, such as DNA or RNA, to other nucleic acid molecules...
" sequences which code for proteins, and the complementary "antisense" sequence which is by itself nonfunctional, but can bind to the sense strand.
Sequence determination
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleotideNucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
sequence of a given DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
fragment. The sequence of the DNA of a living thing encodes the necessary information for that living thing to survive and reproduce. Therefore, determining the sequence is useful in fundamental research into why and how organisms live, as well as in applied subjects. Because of the importance of DNA to living things, knowledge of a DNA sequence may be useful in practically any biological research
Research
Research can be defined as the scientific search for knowledge, or as any systematic investigation, to establish novel facts, solve new or existing problems, prove new ideas, or develop new theories, usually using a scientific method...
. For example, in medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
it can be used to identify, diagnose
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of anything. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines with variations in the use of logics, analytics, and experience to determine the cause and effect relationships...
and potentially develop treatments for genetic diseases. Similarly, research into pathogens may lead to treatments for contagious diseases. Biotechnology
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, technology, medicine and other fields requiring bioproducts. Biotechnology also utilizes these products for manufacturing purpose...
is a burgeoning discipline, with the potential for many useful products and services.
RNA is not sequenced directly. Instead, it is copied to a DNA by reverse transcriptase
Reverse transcriptase
In the fields of molecular biology and biochemistry, a reverse transcriptase, also known as RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, is a DNA polymerase enzyme that transcribes single-stranded RNA into single-stranded DNA. It also helps in the formation of a double helix DNA once the RNA has been reverse...
, and this DNA is then sequenced.
Current sequencing methods rely on the discriminatory ability of DNA polymerases, and therefore can only distinguish four bases. An inosine (created from adenosine during RNA editing
RNA editing
The term RNA editing describes those molecular processes in which the information content in an RNA molecule is altered through a chemical change in the base makeup. To date, such changes have been observed in tRNA, rRNA, mRNA and microRNA molecules of eukaryotes but not prokaryotes...
) is read as a G, and 5-methyl-cytosine (created from cytosine by DNA methylation
DNA methylation
DNA methylation is a biochemical process that is important for normal development in higher organisms. It involves the addition of a methyl group to the 5 position of the cytosine pyrimidine ring or the number 6 nitrogen of the adenine purine ring...
) is read as a C. With current technology, it is difficult to sequence small amounts of DNA, as the signal is too weak to measure. This is overcome by polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
(PCR) amplification.
Digital representation

In silico
In silico is an expression used to mean "performed on computer or via computer simulation." The phrase was coined in 1989 as an analogy to the Latin phrases in vivo and in vitro which are commonly used in biology and refer to experiments done in living organisms and outside of living organisms,...
in digital format. Digital genetic sequences may be stored in sequence database
Sequence database
In the field of bioinformatics, a sequence database is a large collection of computerized nucleic acid sequences, protein sequences, or other sequences stored on a computer...
s, be analyzed (see Sequence analysis below), be digitally altered and/or be used as templates for creating new actual DNA using artificial gene synthesis.
Sequence analysis
Digital genetic sequences may be analyzed using the tools of bioinformaticsBioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
to attempt to determine its function.
Genetic testing
The DNA in an organism's genomeGenome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
can be analyzed to diagnose
Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis refers both to the process of attempting to determine or identify a possible disease or disorder , and to the opinion reached by this process...
vulnerabilities to inherited disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
s, and can also be used to determine a child's paternity (genetic father) or a person's ancestry. Normally, every person carries two variations of every gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
, one inherited from their mother, the other inherited from their father. The human genome
Human genome
The human genome is the genome of Homo sapiens, which is stored on 23 chromosome pairs plus the small mitochondrial DNA. 22 of the 23 chromosomes are autosomal chromosome pairs, while the remaining pair is sex-determining...
is believed to contain around 20,000 - 25,000 genes. In addition to studying chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
s to the level of individual genes, genetic testing in a broader sense includes biochemical tests for the possible presence of genetic diseases, or mutant forms of genes associated with increased risk of developing genetic disorders.
Genetic testing identifies changes in chromosomes, genes, or proteins. Usually, testing is used to find changes that are associated with inherited disorders. The results of a genetic test can confirm or rule out a suspected genetic condition or help determine a person's chance of developing or passing on a genetic disorder. Several hundred genetic tests are currently in use, and more are being developed.
Sequence alignment
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNADNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
, RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
, or protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
to identify regions of similarity that may be due to functional, structural
Structural biology
Structural biology is a branch of molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics concerned with the molecular structure of biological macromolecules, especially proteins and nucleic acids, how they acquire the structures they have, and how alterations in their structures affect their function...
, or evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
ary relationships between the sequences. If two sequences in an alignment share a common ancestor, mismatches can be interpreted as point mutation
Point mutation
A point mutation, or single base substitution, is a type of mutation that causes the replacement of a single base nucleotide with another nucleotide of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. Often the term point mutation also includes insertions or deletions of a single base pair...
s and gaps as insertion or deletion mutations (indel
Indel
Indel is a molecular biology term that has different definitions in different fields:*In evolutionary studies, indel is used to mean an insertion or a deletion and indels simply refers to the mutation class that includes both insertions, deletions, and the combination thereof, including insertion...
s) introduced in one or both lineages in the time since they diverged from one another. In sequence alignments of proteins, the degree of similarity between amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s occupying a particular position in the sequence can be interpreted as a rough measure of how conserved a particular region or sequence motif
Sequence motif
In genetics, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and has, or is conjectured to have, a biological significance...
is among lineages. The absence of substitutions, or the presence of only very conservative substitutions (that is, the substitution of amino acids whose side chain
Side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called "main chain" or backbone. The placeholder R is often used as a generic placeholder for alkyl group side chains in chemical structure diagrams. To indicate other non-carbon...
s have similar biochemical properties) in a particular region of the sequence, suggest that this region has structural or functional importance. Although DNA and RNA nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
bases are more similar to each other than are amino acids, the conservation of base pairs can indicate a similar functional or structural role.
Computational phylogenetics
Computational phylogenetics
Computational phylogenetics is the application of computational algorithms, methods and programs to phylogenetic analyses. The goal is to assemble a phylogenetic tree representing a hypothesis about the evolutionary ancestry of a set of genes, species, or other taxa...
makes extensive use of sequence alignments in the construction and interpretation of phylogenetic tree
Phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical and/or genetic characteristics...
s, which are used to classify the evolutionary relationships between homologous genes represented in the genomes of divergent species. The degree to which sequences in a query set differ is qualitatively related to the sequences' evolutionary distance from one another. Roughly speaking, high sequence identity suggests that the sequences in question have a comparatively young most recent common ancestor
Most recent common ancestor
In genetics, the most recent common ancestor of any set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all organisms in the group are directly descended...
, while low identity suggests that the divergence is more ancient. This approximation, which reflects the "molecular clock
Molecular clock
The molecular clock is a technique in molecular evolution that uses fossil constraints and rates of molecular change to deduce the time in geologic history when two species or other taxa diverged. It is used to estimate the time of occurrence of events called speciation or radiation...
" hypothesis that a roughly constant rate of evolutionary change can be used to extrapolate the elapsed time since two genes first diverged (that is, the coalescence time), assumes that the effects of mutation and selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
are constant across sequence lineages. Therefore it does not account for possible difference among organisms or species in the rates of DNA repair
DNA repair
DNA repair refers to a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1...
or the possible functional conservation of specific regions in a sequence. (In the case of nucleotide sequences, the molecular clock hypothesis in its most basic form also discounts the difference in acceptance rates between silent mutation
Silent mutation
Silent mutations are DNA mutations that do not result in a change to the amino acid sequence of a protein. They may occur in a non-coding region , or they may occur within an exon in a manner that does not alter the final amino acid sequence...
s that do not alter the meaning of a given codon and other mutations that result in a different amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
being incorporated into the protein.) More statistically accurate methods allow the evolutionary rate on each branch of the phylogenetic tree to vary, thus producing better estimates of coalescence times for genes.
Sequence motifs
Frequently the primary structure encodes motifs that are of functional importance. Some examples of sequence motifs are: the C/Dand H/ACA boxes
of snoRNA
SnoRNA
Small nucleolar RNAs are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs...
s, Sm binding site
LSm
In biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins...
found in spliceosomal RNAs such as U1
U1 spliceosomal RNA
U1 spliceosomal RNA is the small nuclear RNA component of U1 snRNP , an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs...
, U2
U2 spliceosomal RNA
U2 spliceosomal RNA is a small nuclear RNA component of the spliceosome . Complementary binding between U2 snRNA and the branchpoint sequence of the intron results in the bulging out of an unpaired adenosine, on the BPS, which initiates a nucleophilic attack at the intronic 5' splice...
, U4
U4 spliceosomal RNA
The U4 small nuclear Ribo-Nucleic Acid is a non-coding RNA component of the major or U2-dependent spliceosome – a eukaryotic molecular machine involved in the splicing of pre-messenger RNA...
, U5
U5 spliceosomal RNA
U5 RNA is a non-coding RNA that is a component of both types of known spliceosome. The precise function of this molecule is unknown, though it is known that the 5' loop is required for splice site selection and p220 binding, and that both the 3' stem-loop and the Sm site are important for Sm...
, U6
U6 spliceosomal RNA
U6 snRNA is the non-coding small nuclear RNA component of U6 snRNP , an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs...
, U12
U12 minor spliceosomal RNA
U12 minor spliceosomal RNA is formed from U12 small nuclear , together with U4atac/U6atac, U5, and U11 snRNAs and associated proteins, forms a spliceosome that cleaves a divergent class of low-abundance pre-mRNA introns. Although the U12 sequence is very divergent from that of U2, the two are...
and U3
Small nucleolar RNA U3
U3 snoRNA is a non-coding RNA found predominantly in the nucleolus.U3 has C/D box motifs that technically make it a member of the box C/D class of snoRNAs; however, unlike other C/D box snoRNAs, it has not been shown to direct 2'-O-methylation of other RNAs.Rather, U3 is thought to guide...
, the Shine-Dalgarno sequence
Shine-Dalgarno sequence
The Shine-Dalgarno sequence , proposed by Australian scientists John Shine and Lynn Dalgarno , is a ribosomal binding site in the mRNA, generally located 8 basepairs upstream of the start codon AUG. The Shine-Dalgarno sequence exists only in prokaryotes. The six-base consensus sequence is AGGAGG;...
,
the Kozak consensus sequence
Kozak consensus sequence
The Kozak consensus sequence, Kozak consensus or Kozak sequence, is a sequence which occurs on eukaryotic mRNA and has the consensus gccRccAUGG, where R is a purine three bases upstream of the start codon , which is followed by another 'G'. The Kozak consensus sequence plays a major role in the...
and the RNA polymerase III terminator
RNA polymerase III
RNA polymerase III transcribes DNA to synthesize ribosomal 5S rRNA, tRNA and other small RNAs. The genes transcribed by RNA Pol III fall in the category of "housekeeping" genes whose expression is required in all cell types and most environmental conditions...
.

