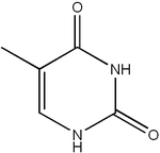
Thymine
Encyclopedia
Thymine is one of the four nucleobase
s in the nucleic acid
of DNA
that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine
, guanine
, and cytosine
. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine
nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at the 5th carbon. In RNA
, thymine is replaced with uracil
in most cases. In DNA, thymine (T) binds to adenine
(A) via two hydrogen bonds, thus stabilizing the nucleic acid structures.
Thymine combined with deoxyribose
creates the nucleoside
deoxythymidine, which is synonymous with the term thymidine
. Thymidine can be phosphorylated with one, two, or three phosphoric acid groups, creating, respectively, TMP, TDP, or TTP (thymidine mono-, di-, or triphosphate).
One of the common mutations of DNA involves two adjacent thymines or cytosine, which, in presence of ultraviolet light
, may form thymine dimers, causing "kinks" in the DNA molecule that inhibit normal function.
Thymine could also be a target for actions of 5-fluorouracil
(5-FU) in cancer
treatment. 5-FU can be a metabolic analog of thymine (in DNA synthesis) or uracil (in RNA synthesis). Substitution of this analog inhibits DNA synthesis
in actively dividing cells.
Thymine bases are frequently oxidized to hydantoins over time after the death of an organism.
Nucleobase
Nucleobases are a group of nitrogen-based molecules that are required to form nucleotides, the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nucleobases provide the molecular structure necessary for the hydrogen bonding of complementary DNA and RNA strands, and are key components in the formation of stable...
s in the nucleic acid
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biological molecules essential for life, and include DNA and RNA . Together with proteins, nucleic acids make up the most important macromolecules; each is found in abundance in all living things, where they function in encoding, transmitting and expressing genetic information...
of DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide , and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA...
, guanine
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
, and cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound similar to benzene and pyridine, containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 of the six-member ring...
nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at the 5th carbon. In RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
, thymine is replaced with uracil
Uracil
Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. The others are adenine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine.Uracil is a common and...
in most cases. In DNA, thymine (T) binds to adenine
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide , and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA...
(A) via two hydrogen bonds, thus stabilizing the nucleic acid structures.
Thymine combined with deoxyribose
Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, more, precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H---3-H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom...
creates the nucleoside
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage...
deoxythymidine, which is synonymous with the term thymidine
Thymidine
Thymidine is a chemical compound, more precisely a pyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine in double-stranded DNA...
. Thymidine can be phosphorylated with one, two, or three phosphoric acid groups, creating, respectively, TMP, TDP, or TTP (thymidine mono-, di-, or triphosphate).
One of the common mutations of DNA involves two adjacent thymines or cytosine, which, in presence of ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
, may form thymine dimers, causing "kinks" in the DNA molecule that inhibit normal function.
Thymine could also be a target for actions of 5-fluorouracil
Fluorouracil
Fluorouracil is a drug that is a pyrimidine analog which is used in the treatment of cancer. It is a suicide inhibitor and works through irreversible inhibition of thymidylate synthase. It belongs to the family of drugs called antimetabolites...
(5-FU) in cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
treatment. 5-FU can be a metabolic analog of thymine (in DNA synthesis) or uracil (in RNA synthesis). Substitution of this analog inhibits DNA synthesis
DNA synthesis
DNA synthesis commonly refers to:*DNA replication - DNA biosynthesis *Polymerase chain reaction - enzymatic DNA synthesis *Oligonucleotide synthesis - chemical synthesis of nucleic acids...
in actively dividing cells.
Thymine bases are frequently oxidized to hydantoins over time after the death of an organism.

