
Barkhausen stability criterion
Encyclopedia
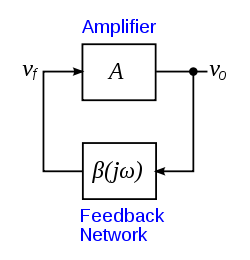
The Barkhausen stability criterion is a mathematical condition to determine when a linear
Linear
In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
electronic circuit
Electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
will oscillate. It was put forth in 1921 by German
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
physicist Heinrich Georg Barkhausen (1881-1956). It is widely used in the design of electronic oscillator
Electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a repetitive electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave. They are widely used in innumerable electronic devices...
s, and also in the design of general negative feedback
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when the output of a system acts to oppose changes to the input of the system, with the result that the changes are attenuated. If the overall feedback of the system is negative, then the system will tend to be stable.- Overview :...
circuits such as op amps, to prevent them from oscillating.
Limitations
Barkhausen's criterion applies to linear circuits with a feedback loop. Therefore it cannot be applied to one port negative resistanceNegative resistance
Negative resistance is a property of some electric circuits where an increase in the current entering a port results in a decreased voltage across the same port. This is in contrast to a simple ohmic resistor, which exhibits an increase in voltage under the same conditions. Negative resistors are...
active elements like tunnel diode
Tunnel diode
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode which is capable of very fast operation, well into the microwave frequency region, by using quantum mechanical effects....
oscillators.
Criterion
It states that if is the gain
is the gainGain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
of the amplifying element in the circuit and
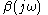 is the transfer function
is the transfer functionTransfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
of the feedback path, so
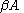 is the loop gain
is the loop gainLoop gain
Loop gain is an engineering term used to quantify the gain of a system controlled by feedback loops. As such, the concept of loop gain is useful in a variety of disciplines. Traditionally, most of those have been in the field of electronics, telecommunications, or control systems...
around the feedback loop of the circuit, the circuit will sustain steady-state oscillations only at frequencies for which:
- The loop gain is equal to unity in absolute magnitude, that is,
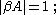
- There must be a positive feedback i.e., the phase shift around the loop is zero or an integer multiple of 2π:
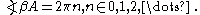
Barkhausen's criterion is a necessary condition for oscillation, not sufficient. This means there are some circuits which satisfy the criterion but do not oscillate. Unfortunately these can not be distinguished with the Nyquist stability criterion
Nyquist stability criterion
When designing a feedback control system, it is generally necessary to determine whether the closed-loop system will be stable. An example of a destabilizing feedback control system would be a car steering system that overcompensates -- if the car drifts in one direction, the control system...
. The Nyquist stability criterion in its general form only indicates instability but cannot provide any information if this instability will cause oscillations or not. Thus, there seems to be still no compact formulation of an oscillation criterion that is both necessary as well as
sufficient.

