
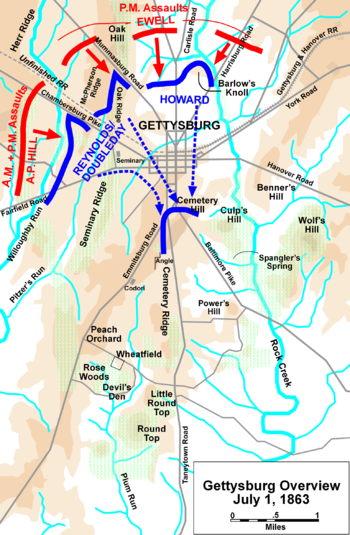
Battle of Gettysburg, First Day
Encyclopedia
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
took place on July 1, 1863, and began as an engagement between isolated units of the Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
under Confederate
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
General Robert E. Lee
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War....
and the Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
under Union
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
Maj. Gen.
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
George G. Meade. It soon escalated into a major battle which culminated in the outnumbered and defeated Union forces retreating to the high ground south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania
Gettysburg, Pennsylvania
Gettysburg is a borough that is the county seat, part of the Gettysburg Battlefield, and the eponym for the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg. The town hosts visitors to the Gettysburg National Military Park and has 3 institutions of higher learning: Lutheran Theological Seminary, Gettysburg College, and...
.
The first-day battle proceeded in three phases as combatants continued to arrive at the battlefield. In the morning, two brigades of Confederate Maj. Gen. Henry Heth
Henry Heth
Henry "Harry" Heth was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general in the American Civil War. He is best remembered for inadvertently precipitating the Battle of Gettysburg, when he sent some of his troops of the Army of Northern Virginia to the small Pennsylvania village,...
's division (of Lt. Gen. A.P. Hill's Third Corps
Third Corps, Army of Northern Virginia
The Third Corps of the Army of Northern Virginia was a military organization within the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia during much of the American Civil War. The corps was formed in mid-1863 and served until Lee's surrender April 9, 1865, near the end of the war.-Formation:After the death of...
) were delayed by dismounted Union cavalrymen under Brig. Gen.
Brigadier general (United States)
A brigadier general in the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, is a one-star general officer, with the pay grade of O-7. Brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below major general. Brigadier general is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral in the other uniformed...
John Buford
John Buford
John Buford, Jr. was a Union cavalry officer during the American Civil War, with a prominent role at the start of the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early years:...
. As infantry reinforcements arrived under Maj. Gen. John F. Reynolds
John F. Reynolds
John Fulton Reynolds was a career United States Army officer and a general in the American Civil War. One of the Union Army's most respected senior commanders, he played a key role in committing the Army of the Potomac to the Battle of Gettysburg and was killed at the start of the battle.-Early...
of the Union I Corps, the Confederate assaults down the Chambersburg Pike were repulsed, although Gen. Reynolds was killed. By early afternoon, the Union XI Corps had arrived, and the Union position was in a semicircle from west to north of the town. The Confederate Second Corps
Second Corps, Army of Northern Virginia
The Second Corps of the Army of Northern Virginia was a military organization within the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia during much of the American Civil War. It was officially created and named following the Battle of Sharpsburg in 1862, but comprised units in a corps organization for quite...
under Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell
Richard S. Ewell
Richard Stoddert Ewell was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general during the American Civil War. He achieved fame as a senior commander under Stonewall Jackson and Robert E...
began a massive assault from the north, with Maj. Gen. Robert E. Rodes
Robert E. Rodes
Robert Emmett Rodes was a railroad civil engineer and a promising young Confederate general in the American Civil War, killed in battle in the Shenandoah Valley.-Education, antebellum career:...
's division attacking from Oak Hill and Maj. Gen. Jubal A. Early's division attacking across the open fields north of town. The Union lines generally held under extremely heavy pressure, although the salient at Barlow's Knoll was overrun.
The third phase of the battle came as Rodes renewed his assault from the north and Heth returned with his entire division from the west, accompanied by the division of Maj. Gen. W. Dorsey Pender
William Dorsey Pender
William Dorsey Pender was one of the youngest, and most promising, generals fighting for the Confederacy in the American Civil War. He was mortally wounded at the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early life:...
. Heavy fighting in Herbst's Woods (near the Lutheran Theological Seminary
Lutheran Theological Seminary at Gettysburg
The Lutheran Theological Seminary at Gettysburg is America's oldest Lutheran seminary and a site of 1863 Battle of Gettysburg military engagements.-History:...
) and on Oak Ridge finally caused the Union line to collapse. Some of the Federals conducted a fighting withdrawal through the town, suffering heavy casualties and losing many prisoners; others simply retreated. They took up good defensive positions on Cemetery Hill
Cemetery Hill
Cemetery Hill is a Gettysburg Battlefield landform which had 1863 military engagements each day of the July 1–3 Battle of Gettysburg. The northernmost part of the Army of the Potomac defensive "fish-hook" line, the hill is gently sloped and provided a site for American Civil War artillery...
and waited for additional attacks. Despite discretionary orders from Robert E. Lee to take the heights "if practicable," Richard Ewell chose not to attack. Historians have debated ever since how the battle might have ended differently if he had found it practicable to do so.
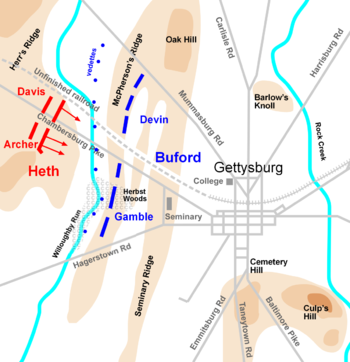
Defense by Buford's cavalry
Cavalry
Cavalry or horsemen were soldiers or warriors who fought mounted on horseback. Cavalry were historically the third oldest and the most mobile of the combat arms...
in the division
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or formation usually consisting of between 10,000 and 20,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades, and in turn several divisions typically make up a corps...
of Brig. Gen. John Buford
John Buford
John Buford, Jr. was a Union cavalry officer during the American Civil War, with a prominent role at the start of the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early years:...
were awaiting the approach of Confederate infantry
Infantry
Infantrymen are soldiers who are specifically trained for the role of fighting on foot to engage the enemy face to face and have historically borne the brunt of the casualties of combat in wars. As the oldest branch of combat arms, they are the backbone of armies...
forces from the direction of Cashtown, to the northwest. Confederate forces from the brigade of Brig. Gen. J. Johnston Pettigrew
J. Johnston Pettigrew
James Johnston Pettigrew was an author, lawyer, linguist, diplomat, and a Confederate general in the American Civil War...
had briefly clashed with Union forces the day before but believed they were Pennsylvania militia of little consequence, not the regular army cavalry that was screening the approach of the Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
.
General Buford realized the importance of the high ground directly to the south of Gettysburg. He knew that if the Confederates could gain control of the heights, Meade's army would have a hard time dislodging them. He decided to utilize three ridges west of Gettysburg: Herr Ridge, McPherson Ridge, and Seminary Ridge (proceeding west to east toward the town). These were appropriate terrain for a delaying action by his small division against superior Confederate infantry forces, meant to buy time awaiting the arrival of Union infantrymen who could occupy the strong defensive positions south of town, Cemetery Hill
Cemetery Hill
Cemetery Hill is a Gettysburg Battlefield landform which had 1863 military engagements each day of the July 1–3 Battle of Gettysburg. The northernmost part of the Army of the Potomac defensive "fish-hook" line, the hill is gently sloped and provided a site for American Civil War artillery...
, Cemetery Ridge
Cemetery Ridge
Cemetery Ridge is a geographic feature in Gettysburg National Military Park south of the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, that figured prominently in the Battle of Gettysburg, July 1 to July 3, 1863. It formed a primary defensive position for the Union Army during the battle, roughly the center of...
, and Culp's Hill
Culp's Hill
Culps Hill is a Battle of Gettysburg landform south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, with a heavily wooded summit of . The east slope is to Rock Creek , 160 feet lower in elevation, and the west slope is to a saddle with Stevens Knoll with a summit lower than the Culps Hill summit...
. Early that morning, Reynolds, who was commanding the Left Wing of the Army of the Potomac, ordered his corps to march to Buford's location, with the XI Corps (Maj. Gen. Oliver O. Howard
Oliver O. Howard
Oliver Otis Howard was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War...
) to follow closely behind.
Confederate Maj. Gen. Henry Heth
Henry Heth
Henry "Harry" Heth was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general in the American Civil War. He is best remembered for inadvertently precipitating the Battle of Gettysburg, when he sent some of his troops of the Army of Northern Virginia to the small Pennsylvania village,...
's division, from Lt. Gen. A.P. Hill's Third Corps, advanced towards Gettysburg. Heth deployed no cavalry and led, unconventionally, with the artillery battalion of Major William J. Pegram. Two infantry brigades followed, commanded by Brig. Gens. James J. Archer
James J. Archer
James Jay Archer was a lawyer and an officer in the United States Army during the Mexican-American War, and he later served as a general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War....
and Joseph R. Davis
Joseph R. Davis
Joseph Robert Davis was a Confederate general during the American Civil War and nephew of Confederate President Jefferson Davis. His troops played an important role in the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early life:...
, proceeding easterly in columns along the Chambersburg Pike. Three miles (5 km) west of town, about 7:30 a.m., Heth's two brigades met light resistance from cavalry vedette
Vedette
The French military term vedette , also spelled vidette, migrated into English and other languages to refer to a mounted sentry or outpost, who has the function of bringing information, giving signals or warnings of danger, etc., to a main body of troops...
s and deployed into line. Eventually, they reached dismounted troopers from Col. William Gamble
William Gamble (USA)
William Gamble was a civil engineer and a Union cavalry officer in the American Civil War.-Early life:...
's cavalry brigade. The first shot of the battle was claimed to be fired by Lieutenant
Lieutenant
A lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer in many nations' armed forces. Typically, the rank of lieutenant in naval usage, while still a junior officer rank, is senior to the army rank...
Marcellus E. Jones of the 8th Illinois Cavalry
8th Regiment Illinois Volunteer Cavalry
The 8th Regiment Illinois Volunteer Cavalry was a cavalry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The regiment served the duration of the war, and was the only cavalry regiment to serve the entire war in the Army of the Potomac...
, fired at an unidentified man on a gray horse over a half-mile away; the act was merely symbolic. Buford's 2,748 troopers would soon be faced with 7,600 Confederate infantrymen, deploying from columns into line of battle.
Gamble's men mounted determined resistance and delaying tactics from behind fence posts with rapid fire from their breech-loading carbine
Carbine
A carbine , from French carabine, is a longarm similar to but shorter than a rifle or musket. Many carbines are shortened versions of full rifles, firing the same ammunition at a lower velocity due to a shorter barrel length....
s. It is a modern myth that they were armed with multi-shot repeating carbines. Nevertheless, they were able to fire two or three times faster than a muzzle-loaded carbine or rifle. Also, the breech-loading design meant that Union troops did not have to stand to reload and could do so safely behind cover. This was a great advantage over the Confederates, who still had to stand to reload, thus providing an easier target. But this was so far a relatively bloodless affair. By 10:20 a.m., the Confederates had reached Herr Ridge and had pushed the Federal cavalrymen east to McPherson Ridge, when the vanguard of the I Corps finally arrived, the division of Maj. Gen. James S. Wadsworth
James S. Wadsworth
James Samuel Wadsworth was a philanthropist, politician, and a Union general in the American Civil War. He was killed in battle during the Battle of the Wilderness of 1864.-Early years:...
. The troops were led personally by Gen. Reynolds, who conferred briefly with Buford and hurried back to bring more men forward.
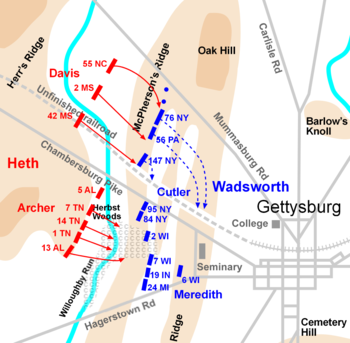
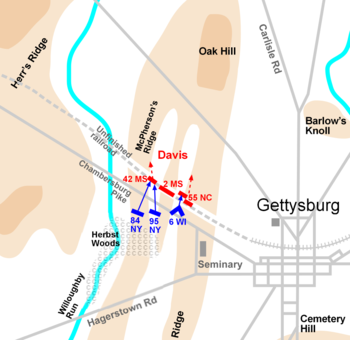
Davis versus Cutler
Lysander Cutler
Lysander Cutler was an American businessman, educator, politician, and a Union Army General during the American Civil War.-Early years:Cutler was born in Royalston, Massachusetts, the son of a farmer...
's Union brigade opposed Davis's brigade; two of Cutler's regiments were north of the Pike, two to the south. To the left of Cutler, Brig. Gen. Solomon Meredith
Solomon Meredith
Solomon Meredith was a prominent Indiana farmer, politician, and lawman who was a controversial Union Army general in the American Civil War...
's Iron Brigade
Iron Brigade
The Iron Brigade, also known as the Iron Brigade of the West or the Black Hat Brigade, was an infantry brigade in the Union Army of the Potomac during the American Civil War. Although it fought entirely in the Eastern Theater, it was composed of regiments from Western states...
opposed Archer.
General Reynolds directed both brigades into position and placed guns from the Maine battery of Capt. James A. Hall where Calef's had stood earlier. While the general rode his horse along the east end of Herbst Woods, shouting "Forward men! Forward for God's sake, and drive those fellows out of the woods," he fell from his horse, killed instantly by a bullet striking him behind the ear. (Some historians believe Reynolds was felled by a sharpshooter, but it is more likely that he was killed by random shot in a volley of rifle fire directed at the 2nd Wisconsin.) Maj. Gen. Abner Doubleday
Abner Doubleday
Abner Doubleday was a career United States Army officer and Union general in the American Civil War. He fired the first shot in defense of Fort Sumter, the opening battle of the war, and had a pivotal role in the early fighting at the Battle of Gettysburg. Gettysburg was his finest hour, but his...
assumed command of the I Corps.
On the right of the Union line, three regiments of Cutler's brigade were fired on by Davis's brigade before they could get into position on the ridge. Davis's line overlapped the right of Cutler's, making the Union position untenable, and Wadsworth ordered Cutler's regiments back to Seminary Ridge. The commander of the 147th New York, Lt. Col.
Lieutenant Colonel (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Air Force, and United States Marine Corps, a lieutenant colonel is a field grade military officer rank just above the rank of major and just below the rank of colonel. It is equivalent to the naval rank of commander in the other uniformed services.The pay...
Francis C. Miller, was shot before he could inform his troops of the withdrawal, and they remained to fight under heavy pressure until a second order came. In under 30 minutes, 45% of Gen. Cutler's 1,007 men became casualties, with the 147th losing 207 of its 380 officers and men. Some of Davis's victorious men turned toward the Union positions south of the railroad bed while others drove east toward Seminary Ridge. This defocused the Confederate effort north of the pike.
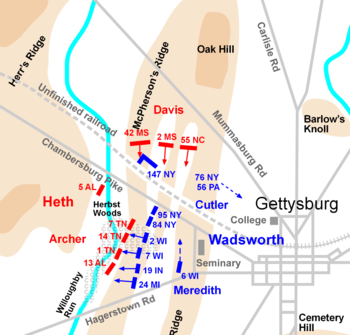
Archer versus Meredith
Hardee hat
The Hardee hat, also known as the Model 1858 Dress Hat and sometimes nicknamed the "Jeff Davis", was the regulation dress hat for enlisted men in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The Hardee hat was also worn by Confederate soldiers. However, most soldiers found the black felt hat to...
s worn by the men facing them through the woods: the famous Iron Brigade
Iron Brigade
The Iron Brigade, also known as the Iron Brigade of the West or the Black Hat Brigade, was an infantry brigade in the Union Army of the Potomac during the American Civil War. Although it fought entirely in the Eastern Theater, it was composed of regiments from Western states...
, formed from regiments in the Western states of Indiana, Michigan, and Wisconsin, had a reputation as fierce, tenacious fighters. As the Confederates crossed Willoughby Run and climbed the slope into Herbst Woods, they were enveloped on their right by the longer Union line, the reverse of the situation north of the pike.
Brig. Gen. Archer was captured in the fighting, the first general officer in Robert E. Lee's army to suffer that fate. Archer was most likely positioned around the 14th Tennessee when he was captured by Private
Private (rank)
A Private is a soldier of the lowest military rank .In modern military parlance, 'Private' is shortened to 'Pte' in the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth countries and to 'Pvt.' in the United States.Notably both Sir Fitzroy MacLean and Enoch Powell are examples of, rare, rapid career...
Patrick Moloney of Company G., 2nd Wisconsin, "a brave patriotic and fervent young Irishman." Archer resisted capture, but Moloney overpowered him. Moloney was killed later that day, but he received the Medal of Honor
Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor is the highest military decoration awarded by the United States government. It is bestowed by the President, in the name of Congress, upon members of the United States Armed Forces who distinguish themselves through "conspicuous gallantry and intrepidity at the risk of his or her...
for his exploit. When Archer was taken to the rear, he encountered his former Army colleague Gen. Doubleday, who greeted him good-naturedly, "Good morning, Archer! How are you? I am glad to see you!" Archer replied, "Well, I am not glad to see you by a damn sight!"
Railroad cut
Rufus R. Dawes
Rufus R. Dawes was a military officer in the United States Army during the American Civil War. He used the middle initial "R" but had no middle name. He was noted for his service in the famed Iron Brigade, particularly during the Battle of Gettysburg...
, north in the direction of Davis's disorganized brigade. The Wisconsin men paused at the fence along the pike and fired, which halted Davis's attack on Cutler's men and caused many of them to seek cover in the unfinished railroad cut. The 6th joined the 95th New York and the 84th New York
14th Regiment (New York State Militia)
The 14th Regiment New York State Militia was a volunteer militia regiment from the City of Brooklyn, New York. It is primarily known for its service in the American Civil War from April 1861 to May 1864, although it later served in the Spanish American War and World War I .In the Civil War, the...
(also known as the 14th Brooklyn), a "demi-brigade" commanded by Col. E.B. Fowler
Edward Brush Fowler
Edward Brush Fowler was an officer in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He is best known for his command of the 14th Brooklyn and a demi-brigade during the Battle of Gettysburg in July 1863....
, along the pike. The three regiments charged to the railroad cut, where Davis's men were seeking cover. The majority of the 600-foot (180 m) cut (shown on the map as the center cut of three) was too deep to be an effective firing position—as deep as 15 feet (4.5 m). Making the situation more difficult was the absence of their overall commander, General Davis, whose location was unknown.
The men of the three regiments nevertheless faced daunting fire as they charged toward the cut. The 6th Wisconsin's American flag went down at least three times during the charge. At one point Dawes took up the fallen flag before it was seized from him by a corporal of the color guard. As the Union line neared the Confederates, its flanks became folded back and it took on the appearance of an inverted V. When the Union men reached the railroad cut, vicious hand-to-hand and bayonet fighting broke out. They were able to pour enfilading fire from both ends of the cut, and many Confederates considered surrender. Colonel Dawes took the initiative by shouting "Where is the colonel of this regiment?" Major John Blair of the 2nd Mississippi stood up and responded, "Who are you?" Dawes replied, "I command this regiment. Surrender or I will fire." Dawes later described what happened next:
Despite this surrender, leaving Dawes standing awkwardly holding seven swords, the fighting continued for minutes more and numerous Confederates were able to escape back to Herr Ridge. The three Union regiments lost 390-440 of 1,184 engaged, but they had blunted Davis's attack, prevented them from striking the rear of the Iron Brigade, and so overwhelmed the Confederate brigade that it was unable to participate significantly in combat for the rest of the day. The Confederate losses were about 500 killed and wounded and over 200 prisoners out of 1,707 engaged.
Mid-day lull
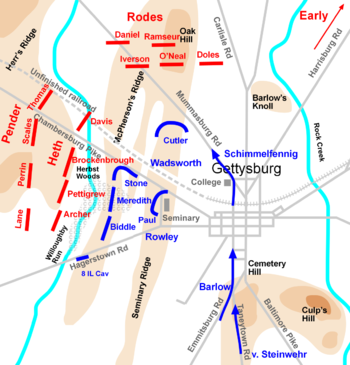
J. Johnston Pettigrew
James Johnston Pettigrew was an author, lawyer, linguist, diplomat, and a Confederate general in the American Civil War...
and Col. John M. Brockenbrough
John M. Brockenbrough
John Mercer Brockenbrough was a farmer and a Confederate colonel in the American Civil War.-Early life:Brockenbrough was born in Richmond County, Virginia, and graduated from the Virginia Military Institute in 1850....
, had arrived on the scene, as had the division (four brigades) of Maj. Gen. Dorsey Pender
William Dorsey Pender
William Dorsey Pender was one of the youngest, and most promising, generals fighting for the Confederacy in the American Civil War. He was mortally wounded at the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early life:...
, also from Hill's Corps. Hill's remaining division (Maj. Gen. Richard H. Anderson
Richard H. Anderson
Richard Heron Anderson was a career U.S. Army officer, fighting with distinction in the Mexican-American War. He also served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War, fighting in the Eastern Theater of the conflict and most notably during the 1864 Battle of Spotsylvania Court House...
) did not arrive until late in the day.
Considerably more Confederate forces were on the way, however. Two divisions of the Second Corps, commanded by Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell
Richard S. Ewell
Richard Stoddert Ewell was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general during the American Civil War. He achieved fame as a senior commander under Stonewall Jackson and Robert E...
, were approaching Gettysburg from the north, from the towns of Carlisle
Carlisle, Pennsylvania
Carlisle is a borough in and the county seat of Cumberland County, Pennsylvania, United States. The name is traditionally pronounced with emphasis on the second syllable. Carlisle is located within the Cumberland Valley, a highly productive agricultural region. As of the 2010 census, the borough...
and York
York, Pennsylvania
York, known as the White Rose City , is a city located in York County, Pennsylvania, United States which is in the South Central region of the state. The population within the city limits was 43,718 at the 2010 census, which was a 7.0% increase from the 2000 count of 40,862...
. The five brigades of Maj. Gen. Robert E. Rodes
Robert E. Rodes
Robert Emmett Rodes was a railroad civil engineer and a promising young Confederate general in the American Civil War, killed in battle in the Shenandoah Valley.-Education, antebellum career:...
marched down the Carlisle Road but left it before reaching town to advance down the wooded crest of Oak Ridge, where they could link up with the left flank of Hill's Corps. The four brigades under Maj. Gen. Jubal A. Early approached on the Harrisburg Road. Union cavalry outposts north of the town detected both movements. Ewell's remaining division (Maj. Gen. Edward "Allegheny" Johnson
Edward Johnson (general)
Edward Johnson , also known as Allegheny Johnson , was a United States Army officer and a Confederate general in the American Civil War.-Early life:...
) did not arrive until late in the day.
On the Union side, Doubleday reorganized his lines as more units of the I Corps arrived. First on hand was the Corps Artillery under Col. Charles S. Wainwright
Charles S. Wainwright
Charles Shiels Wainwright was a produce farmer in the state of New York and an artillery officer in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He played an important role in the defense of Cemetery Hill during the July 1863 Battle of Gettysburg, where his artillery helped repel a Confederate...
, followed by two brigades from Doubleday's division, now commanded by Brig. Gen. Thomas A. Rowley, which Doubleday placed on either end of his line. The XI Corps arrived from the south before noon, moving up the Taneytown and Emmitsburg Roads. Maj. Gen. Oliver O. Howard
Oliver O. Howard
Oliver Otis Howard was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War...
was surveying the area from the roof of the Fahnestock Brothers' dry-goods store downtown at about 11:30 when he heard that Reynolds had been killed and that he was now in command of all Union forces on the field. He recalled: "My heart was heavy and the situation was grave indeed, but surely I did not hesitate a moment. God helping us, we will stay here till the Army comes. I assumed the command of the field."
Howard immediately sent messengers to summon reinforcements from the III Corps (Maj. Gen. Daniel E. Sickles) and the XII Corps (Maj. Gen. Henry W. Slocum). Howard's first XI Corps division to arrive, under Maj. Gen. Carl Schurz
Carl Schurz
Carl Christian Schurz was a German revolutionary, American statesman and reformer, and Union Army General in the American Civil War. He was also an accomplished journalist, newspaper editor and orator, who in 1869 became the first German-born American elected to the United States Senate.His wife,...
, was sent north to take a position on Oak Ridge and link up with the right of the I Corps. (The division was commanded temporarily by Brig. Gen. Alexander Schimmelfennig
Alexander Schimmelfennig
Alexander Schimmelfennig was a German soldier and political revolutionary, and then an American Civil War general in the Union Army.-Early life and career:...
while Schurz filled in for Howard as XI Corps commander.) The division of Brig. Gen. Francis C. Barlow
Francis C. Barlow
Francis Channing Barlow was a lawyer, politician, and Union General during the American Civil War.-Early life and career:...
was placed on Schurz's right to support him. The third division to arrive, under Brig. Gen. Adolph von Steinwehr
Adolph von Steinwehr
Baron Adolph Wilhelm August Friedrich von Steinwehr was a German-Brunswick army officer who emigrated to the United States, became a geographer, cartographer, and author, and served as a Union general in the American Civil War.-Early life:Steinwehr was born in Blankenburg, in the Duchy of...
, was placed on Cemetery Hill along with two batteries of artillery to hold the hill as a rallying point if the Union troops could not hold their positions; this placement on the hill corresponded with orders sent earlier in the day to Howard by Reynolds just before he was killed.
However, Rodes beat Schurz to Oak Hill, so the XI Corps division was forced to take up positions in the broad plain north of the town, below and to the east of Oak Hill. They linked up with the I Corps reserve division of Brig. Gen. John C. Robinson
John C. Robinson
John Cleveland Robinson had a long and distinguished career in the United States Army, fighting in numerous wars and culminating his career as a Union Army brigadier general of volunteers and brevet major general of volunteers in the American Civil War. In 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated...
, whose two brigades had been sent forward by Doubleday when he heard about Ewell's arrival. Howard's defensive line was not a particularly strong one in the north. He was soon outnumbered (his XI Corps, still suffering the effects of their defeat at the Battle of Chancellorsville
Battle of Chancellorsville
The Battle of Chancellorsville was a major battle of the American Civil War, and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville Campaign. It was fought from April 30 to May 6, 1863, in Spotsylvania County, Virginia, near the village of Chancellorsville. Two related battles were fought nearby on...
, had only 8,700 effectives), and the terrain his men occupied in the north was poorly selected for defense. He held out some hope that reinforcements from Slocum's XII Corps would arrive up the Baltimore Pike in time to make a difference.
Afternoon
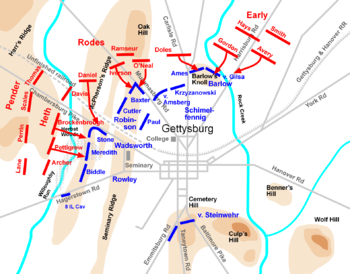
Rodes attacks from Oak Hill
Rodes initially sent three brigades south against Union troops that represented the right flank of the I Corps and the left flank of the XI Corps: from east to west, Brig. Gen. George P. DolesGeorge P. Doles
George Pierce Doles was a Georgia businessman and Confederate general during the American Civil War. His men played a key role on the first day of the Battle of Gettysburg in driving back the Union XI Corps.-Early life:...
, Col. Edward A. O'Neal, and Brig. Gen. Alfred Iverson
Alfred Iverson, Jr.
Alfred Iverson, Jr. was a lawyer, an officer in the Mexican-American War, a U.S. Army cavalry officer, and a Confederate general in the American Civil War. He served in the 1862–63 campaigns of the Army of Northern Virginia as a regimental and later brigade commander...
. Doles's Georgia brigade stood guarding the flank, awaiting the arrival of Early's division. Both O'Neal's and Iverson's attacks fared poorly against the six veteran regiments in the brigade of Brig. Gen. Henry Baxter
Henry Baxter
Henry Baxter was a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. At the Battle of Gettysburg, his brigade resisted a Confederate assault from parts of Maj. Gen. Robert E...
, manning a line in a shallow inverted V, facing north on the ridge behind the Mummasburg Road. O'Neal's men were sent forward without coordinating with Iverson on their flank and fell back under heavy fire from the I Corps troops.
Iverson failed to perform even a rudimentary reconnaissance and sent his men forward blindly while he stayed in the rear (as had O'Neal, minutes earlier). More of Baxter's men were concealed in woods behind a stone wall and rose to fire withering volleys from less than 100 yards (91.4 m) away, creating over 800 casualties among the 1,350 North Carolinians. Stories are told about groups of dead bodies lying in almost parade-ground formations, heels of their boots perfectly aligned. (The bodies were later buried on the scene, and this area is today known as "Iverson's Pits", source of many local tales of supernatural
Supernatural
The supernatural or is that which is not subject to the laws of nature, or more figuratively, that which is said to exist above and beyond nature...
phenomena.)
Baxter's brigade was worn down and out of ammunition. At 3:00 p.m. he withdrew his brigade, and Gen. Robinson replaced it with the brigade of Brig. Gen. Gabriel R. Paul. Rodes then committed his two reserve brigades: Brig. Gens. Junius Daniel
Junius Daniel
Junius Daniel was a planter and career military officer, serving in the United States Army, then in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War, as a brigadier general. His troops were instrumental in the Confederates' success at the first day of the Battle of Gettysburg...
and Dodson Ramseur
Stephen Dodson Ramseur
Stephen Dodson Ramseur was one of the youngest Confederate generals in the American Civil War. He was mortally wounded in battle at the Battle of Cedar Creek in the Shenandoah Valley.-Early life:...
. Ramseur attacked first, but Paul's brigade held its crucial position. Paul had a bullet go in one temple and out the other, blinding him permanently (he survived the wound and lived 20 more years after the battle). Before the end of the day, three other commanders of that brigade were wounded.
Daniel's North Carolina brigade then attempted to break the I Corps line to the southwest along the Chambersburg Pike. They ran into stiff resistance from Col. Roy Stone
Roy Stone
Roy Stone was a Union Army general during the American Civil War. He is most noted for his stubborn defense of the McPherson Farm during the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early life and family:...
's Pennsylvania "Bucktail Brigade" in the same area around the railroad cut as the morning's battle. Fierce fighting eventually ground to a standstill.
Heth renews his attack
Gen. Lee arrived on the battlefield at about 2:30 p.m., as Rodes's men were in mid-attack. Seeing that a major assault was underway, he lifted his restriction on a general engagement and gave permission to Hill to resume his attacks from the morning. First in line was Heth's division again, with two fresh brigades: Pettigrew's North Carolinians and Col. John M. BrockenbroughJohn M. Brockenbrough
John Mercer Brockenbrough was a farmer and a Confederate colonel in the American Civil War.-Early life:Brockenbrough was born in Richmond County, Virginia, and graduated from the Virginia Military Institute in 1850....
's Virginians.
Pettigrew's Brigade was deployed in a line that extended south beyond the ground defended by the Iron Brigade. Enveloping the left flank of the 19th Indiana, Pettigrew's North Carolinians, the largest brigade in the army, drove back the Iron Brigade in some of the fiercest fighting of the war. The Iron Brigade was pushed out of the woods, made three temporary stands in the open ground to the east, but then had to fall back toward the Lutheran Theological Seminary
Lutheran Theological Seminary at Gettysburg
The Lutheran Theological Seminary at Gettysburg is America's oldest Lutheran seminary and a site of 1863 Battle of Gettysburg military engagements.-History:...
. Gen. Meredith was downed with a head wound, made all the worse when his horse fell on him. To the left of the Iron Brigade was the brigade of Col. Chapman Biddle, defending open ground on McPherson Ridge, but they were outflanked and decimated. To the right, Stone's Bucktails, facing both west and north along the Chambersburg Pike, were attacked by both Brockenbrough and Daniel.
Casualties were severe that afternoon. The 26th North Carolina (the largest regiment of the army with 839 men) lost heavily, leaving the first day's fight with around 212 men. Their commander, Colonel Henry K. Burgwyn
Henry K. Burgwyn
Henry King Burgwyn, Jr. was a Confederate colonel in the American Civil War killed at the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early life:...
, was fatally wounded by a bullet through his chest. By the end of the three-day battle, they had about 152 men standing, the highest casualty percentage for one battle of any other regiment, North or South. One of the Union regiments, the 24th Michigan, lost 399 of 496. It had nine color bearers shot down, and its commander, Col. Henry A. Morrow, was wounded in the head and captured. The 151st Pennsylvania of Biddle's brigade lost 337 of 467.
The highest ranking casualty of this engagement was Gen. Heth, who was struck by a bullet in the head. He was apparently saved because he had stuffed wads of paper into a new hat, which was otherwise too large for his head. But there were two consequences to this glancing blow. Heth was unconscious for over 24 hours and had no further command involvement in the three-day battle. He was also unable to urge Pender's division to move forward and supplement his struggling assault. Pender was oddly passive during this phase of the battle; the typically more aggressive tendencies of a young general in Lee's army would have seen him move forward on his own accord. Hill shared the blame for failing to order him forward as well, but he claimed illness. History cannot know Pender's motivations; he was mortally wounded the next day and left no report.
Early attacks XI Corps
Carl Schurz of the XI Corps had a difficult defensive problem. He had only four brigades to cover the wide expanse of featureless farmland north of town. He deployed the division of Brig. Gen. Alexander Schimmelfennig on the left and Francis C. BarlowFrancis C. Barlow
Francis Channing Barlow was a lawyer, politician, and Union General during the American Civil War.-Early life and career:...
on the right. From the left, the brigades were Schimmelfennig's (under Col. George von Amsberg), Col. Włodzimierz Krzyżanowski, Brig. Gen. Adelbert Ames
Adelbert Ames
Adelbert Ames was an American sailor, soldier, and politician. He served with distinction as a Union Army general during the American Civil War. As a Radical Republican and a Carpetbagger, he was military governor, Senator and civilian governor in Reconstruction-era Mississippi...
, and Col. Leopold von Gilsa.
Making things more difficult, Barlow advanced much farther north than Schimmelfennig's division, occupying a 50-foot (15 m) elevation above Rock Creek named Blocher's Knoll (ever since the battle known as Barlow's Knoll). This turned out to be a serious misjudgment because it created a salient
Salients, re-entrants and pockets
A salient is a battlefield feature that projects into enemy territory. The salient is surrounded by the enemy on three sides, making the troops occupying the salient vulnerable. The enemy's line facing a salient is referred to as a re-entrant...
in the line that could be assaulted from multiple sides. Barlow's justification was that he wanted to prevent Doles's Brigade, of Rodes's division, from occupying it and using it as an artillery platform against him.
Richard Ewell's second division, under Jubal Early, swept down the Harrisburg Road, deployed in a battle line three brigades wide, almost a mile across (1,600 m) and almost half a mile (800 m) wider than the Union defensive line. Early started with a large-scale artillery bombardment. The Georgia brigade of Brig. Gen. John B. Gordon was then directed for a frontal attack against Barlow's Knoll, pinning down the defenders, while the brigades of Brig. Gen. Harry T. Hays
Harry T. Hays
Harry Thompson Hays was an American Army officer serving in the Mexican-American War and a general who served in the Confederate Army during the American Civil War....
and Col. Isaac E. Avery
Isaac E. Avery
Isaac Erwin Avery was a planter and an officer in the Confederate States Army. He died at the Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War...
swung around their exposed flank. At the same time the Georgians under Doles launched a synchronized assault with Gordon. The defenders of Barlow's Knoll targeted by Gordon were 900 men of von Gilsa's brigade; in May, two of his regiments had been the initial target of Stonewall Jackson
Stonewall Jackson
ຄຽשת״ׇׂׂׂׂ֣|birth_place= Clarksburg, Virginia |death_place=Guinea Station, Virginia|placeofburial=Stonewall Jackson Memorial CemeteryLexington, Virginia|placeofburial_label= Place of burial|image=...
's flanking attack
Flanking maneuver
In military tactics, a flanking maneuver, also called a flank attack, is an attack on the sides of an opposing force. If a flanking maneuver succeeds, the opposing force would be surrounded from two or more directions, which significantly reduces the maneuverability of the outflanked force and its...
at Chancellorsville. The men of the 54th and 68th New York held out as long as they could, but they were overwhelmed. Then the 153rd Pennsylvania succumbed. Barlow, attempting to rally his troops, was shot in the side and captured. Barlow's second brigade, under Ames, came under attack by Doles and Gordon. Both Union brigades conducted a disorderly retreat to the south.
On the left flank of the XI Corps, the attack focused on Gen. Schimmelfennig's division. They were subjected to a deadly artillery crossfire from Rodes's and Early's batteries, and as they deployed they were attacked by Doles's infantry. Early's troops were able to employ a flanking attack and roll up the division from the right, and they fell back in confusion toward the town. A desperate counterattack by the 157th New York from von Amsberg's brigade was surrounded on three sides, causing it to suffer 307 casualties (75%).
Gen. Howard, witnessing the disaster, sent forward an artillery battery and an infantry brigade from von Steinwehr's reserve force, under Col. Charles Coster. Coster's battle line just north of the town in a brickyard was overwhelmed by Hays and Avery. He did provide some valuable cover for the retreating soldiers, but at a high price: of Coster's 800 men, 313 were captured, as were two of the four guns from the battery.
The collapse of the XI Corps was completed by 4:00 p.m., after a fight of less than an hour. They suffered 3,200 casualties (1,400 of them prisoners), about half the number sent forward from Cemetery Hill. The losses in Gordon's and Doles's brigades were under 750.
Rodes and Pender break through
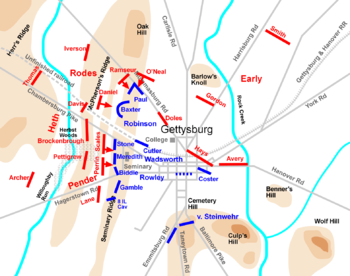
In the west, the Union troops had fallen back to the Seminary and built hasty breastworks running 600 yards (548.6 m) north-south before the western face of Schmucker Hall, bolstered by 20 guns of Wainwright's battalion. Dorsey Pender's division of Hill's Corps stepped through the exhausted lines of Heth's men at about 4:00 p.m. to finish off the I Corps survivors. The brigade of Brig. Gen. Alfred M. Scales attacked first, on the northern flank. His five regiments of 1,400 North Carolinians were virtually annihilated in one of the fiercest artillery barrages of the war, rivaling Pickett's Charge
Pickett's Charge
Pickett's Charge was an infantry assault ordered by Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee against Maj. Gen. George G. Meade's Union positions on Cemetery Ridge on July 3, 1863, the last day of the Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War. Its futility was predicted by the charge's commander,...
to come, but on a more concentrated scale. Twenty guns spaced only 5 yards (4.6 m) apart fired spherical case
Field artillery in the American Civil War
Field artillery in the American Civil War refers to the important artillery weapons, equipment, and practices used by the Artillery branch to support the infantry and cavalry forces in the field. It does not include siege artillery, use of artillery in fixed fortifications, or coastal or naval...
, explosive shells, canister
Canister shot
Canister shot is a kind of anti-personnel ammunition used in cannons. It was similar to the naval grapeshot, but fired smaller and more numerous balls, which did not have to punch through the wooden hull of a ship...
, and double canister rounds into the approaching brigade, which emerged from the fight with only 500 men standing and a single lieutenant in command. Scales wrote afterwards that he found "only a squad here and there marked the place where regiments had rested."
The attack continued in the southern-central area, where Col. Abner M. Perrin ordered his South Carolina brigade (four regiments of 1,500 men) to advance rapidly without pausing to fire. Perrin was prominently on horseback leading his men but miraculously was untouched. He directed his men to a weak point in the breastworks on the Union left, a 50 yards (45.7 m) gap between Biddle's left-hand regiment, the 121st Pennsylvania, and Gamble's cavalrymen, attempting to guard the flank. They broke through, enveloping the Union line and rolling it up to the north as Scales's men continued to pin down the right flank. By 4:30 p.m., the Union position was untenable, and the men could see the XI Corps retreating from the northern battle, pursued by masses of Confederates. Doubleday ordered a withdrawal east to Cemetery Hill.
On the southern flank, the North Carolina brigade of Brig. Gen. James H. Lane
James H. Lane (general)
James Henry Lane was a university professor and Confederate general in the American Civil War.He is considered to be the father of Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University and is the namesake of the University's oldest building, Lane Hall.-Early life:Lane was born in Mathews Court...
contributed little to the assault; he was kept busy by a clash with Union cavalry on the Hagerstown Road. Brig. Gen. Edward L. Thomas's Georgia Brigade was in reserve well to the rear, not summoned by Pender or Hill to assist or exploit the breakthrough.
Union retreat

Union troops retreated in different states of order. The brigades on Seminary Ridge were said to move deliberately and slowly, keeping in control, although Col. Wainwright's artillery was not informed of the order to retreat and found themselves alone. When Wainwright realized his situation, he ordered his gun crews to withdraw at a walk, not wishing to panic the infantry and start a rout. As pressure eventually increased, Wainwright ordered his 17 remaining guns to gallop down Chambersburg Street, three abreast. A.P. Hill failed to commit any of his reserves to the pursuit of the Seminary defenders, a great missed opportunity.
Near the railroad cut, Daniel's Brigade renewed their assault, and almost 500 Union soldiers surrendered and were taken prisoner. Paul's Brigade, under attack by Ramseur, became seriously isolated and Gen. Robinson ordered it to withdraw. He ordered the 16th Maine to hold its position "at any cost" as a rear guard against the enemy pursuit. The regiment, commanded by Col. Charles Tilden, returned to the stone wall on the Mummasburg Road, and their fierce fire gave sufficient time for the rest of the brigade to escape, which they did, in considerably more disarray than those from the Seminary. The 16th Maine started the day with 298 men, but at the end of this holding action there were only 35 survivors.
For the XI Corps, it was a sad reminder of their retreat at Chancellorsville in May. Under heavy pursuit by Hays and Avery, they clogged the streets of the town; no one in the corps had planned routes for this contingency. Hand-to-hand fighting broke out in various places. Parts of the corps conducted an organized fighting retreat, such as Coster's stand in the brickyard. The private citizens of Gettysburg panicked amidst the turmoil, and artillery shells bursting overhead and fleeing refugees added to the congestion. Some soldiers sought to avoid capture by hiding in basements and in fenced backyards. Gen. Alexander Schimmelfennig was one such person who climbed a fence and hid behind a woodpile in the kitchen garden of the Garlach family for the rest of the three-day battle. The only advantage that the XI Corps soldiers had was that they were familiar with the route to Cemetery Hill, having passed through that way in the morning; many in the I Corps, including senior officers, did not know where the cemetery was.
As the Union troops climbed Cemetery Hill, they encountered the determined Maj. Gen. Winfield Scott Hancock
Winfield Scott Hancock
Winfield Scott Hancock was a career U.S. Army officer and the Democratic nominee for President of the United States in 1880. He served with distinction in the Army for four decades, including service in the Mexican-American War and as a Union general in the American Civil War...
. At midday, Gen. Meade was nine miles (14 km) south of Gettysburg in Taneytown, Maryland
Taneytown, Maryland
Taneytown is a city in Carroll County, Maryland, United States. The population was 5,128 at the 2000 census. was founded in 1754. Of the town George Washington once wrote "Tan-nee town is but a small place with only the Street through wch. the road passes, built on...
, when he heard that Reynolds had been killed. He immediately dispatched Hancock, commander of the II Corps and his most trusted subordinate, to the scene with orders to take command of the field and to determine whether Gettysburg was an appropriate place for a major battle. (Meade's original plan had been to man a defensive line on Pipe Creek
Double Pipe Creek
Double Pipe Creek is a major tributary of the Monocacy River in Carroll County and Frederick County in Maryland, located several miles north and west of Westminster...
, a few miles south in Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
. But the serious battle underway was making that a difficult option.)
When Hancock arrived on Cemetery Hill, he met with Howard and they had a brief disagreement about Meade's command order. As the senior officer, Howard yielded only grudgingly to Hancock's direction. Although Hancock arrived after 4:00 p.m. and commanded no units on the field that day, he took control of the Union troops arriving on the hill and directed them to defensive positions with his "imperious and defiant" (and profane) persona. As to the choice of Gettysburg as the battlefield, Hancock told Howard "I think this the strongest position by nature upon which to fight a battle that I ever saw." When Howard agreed, Hancock concluded the discussion: "Very well, sir, I select this as the battle-field." Brig. Gen. Gouverneur K. Warren
Gouverneur K. Warren
Gouverneur Kemble Warren was a civil engineer and prominent general in the Union Army during the American Civil War...
, chief engineer of the Army of the Potomac, inspected the ground and concurred with Hancock.
Evening
Gen. Lee also understood the defensive potential to the Union army if they held the high ground of Cemetery Hill. He sent orders to Ewell to "carry the hill occupied by the enemy, if he found it practicable, but to avoid a general engagement until the arrival of the other divisions of the army." In the face of this discretionary, and possibly contradictory, order, Ewell chose not to attempt the assault. One reason posited was the battle fatigue of his men in the late afternoon, although "Allegheny" Johnson's division of Ewell's Corps was within an hour of arriving on the battlefield. Another was the difficulty of assaulting the hill through the narrow corridors afforded by the streets of Gettysburg immediately to the north. Ewell requested assistance from A.P. Hill, but that general felt his corps was too depleted from the day's battle and General Lee did not want to bring up Maj. Gen. Richard H. AndersonRichard H. Anderson
Richard Heron Anderson was a career U.S. Army officer, fighting with distinction in the Mexican-American War. He also served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War, fighting in the Eastern Theater of the conflict and most notably during the 1864 Battle of Spotsylvania Court House...
's division from the reserve. Ewell did consider taking Culp's Hill, which would have made the Union position on Cemetery Hill untenable. However, Jubal Early opposed the idea when it was reported that Union troops (probably Slocum's XII Corps) were approaching on the York Pike, and he sent the brigades of John B. Gordon and Brig. Gen. William "Extra Billy" Smith to block that perceived threat; Early urged waiting for Johnson's division to take the hill. After Johnson's division arrived via the Chambersburg Pike, it maneuvered toward the east of town in preparation to take the hill, but a small reconnaissance party sent in advance encountered a picket line of the 7th Indiana Infantry, which opened fire and captured a Confederate officer and soldier. The remainder of the Confederates fled and attempts to seize Culp's Hill on July 1 came to an end.
Lee's order has been criticized because it left too much discretion to Ewell. Numerous historians and proponents of the Lost Cause
Lost Cause of the Confederacy
The Lost Cause is the name commonly given to an American literary and intellectual movement that sought to reconcile the traditional white society of the U.S. South to the defeat of the Confederate States of America in the American Civil War of 1861–1865...
movement (most prominently Jubal Early, despite his own reluctance to support an attack at the time) have speculated how the more aggressive Stonewall Jackson
Stonewall Jackson
ຄຽשת״ׇׂׂׂׂ֣|birth_place= Clarksburg, Virginia |death_place=Guinea Station, Virginia|placeofburial=Stonewall Jackson Memorial CemeteryLexington, Virginia|placeofburial_label= Place of burial|image=...
would have acted on this order if he had lived to command this wing of Lee's army, and how differently the second day of battle would have proceeded with Confederate artillery on Cemetery Hill, commanding the length of Cemetery Ridge and the Federal lines of communications on the Baltimore Pike. Stephen W. Sears has suggested that Gen. Meade would have invoked his original plan for a defensive line on Pipe Creek and withdrawn the Army of the Potomac, although that movement would have been a dangerous operation under pressure from Lee.
Most of the rest of both armies arrived that evening or early the next morning. Johnson's division joined Ewell and Maj. Gen. Richard H. Anderson
Richard H. Anderson
Richard Heron Anderson was a career U.S. Army officer, fighting with distinction in the Mexican-American War. He also served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War, fighting in the Eastern Theater of the conflict and most notably during the 1864 Battle of Spotsylvania Court House...
's joined Hill. Two of the three divisions of the First Corps, commanded by Lt. Gen. James Longstreet
James Longstreet
James Longstreet was one of the foremost Confederate generals of the American Civil War and the principal subordinate to General Robert E. Lee, who called him his "Old War Horse." He served under Lee as a corps commander for many of the famous battles fought by the Army of Northern Virginia in the...
, arrived in the morning. Three cavalry brigades under Maj. Gen. J.E.B. Stuart
J.E.B. Stuart
James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart was a U.S. Army officer from Virginia and a Confederate States Army general during the American Civil War. He was known to his friends as "Jeb", from the initials of his given names. Stuart was a cavalry commander known for his mastery of reconnaissance and the use...
were still out of the area, on a wide-ranging raid to the northeast. Gen. Lee sorely felt the loss of the "eyes and ears of the Army"; Stuart's absence had contributed to the accidental start of the battle that morning and left Lee unsure about enemy dispositions through most of July 2. On the Union side, Meade arrived after midnight. The II Corps and III Corps took up positions on Cemetery Ridge, and the XII Corps and the V Corps were nearby to the east. Only the VI Corps was a significant distance from the battlefield, marching rapidly to join the Army of the Potomac.
The first day at Gettysburg—more significant than simply a prelude to the bloody second and third days—ranks as the 23rd biggest battle of the war by number of troops engaged. About one quarter of Meade's army (22,000 men) and one third of Lee's army (27,000) were engaged. Union casualties were almost 9,000, Confederate slightly more than 6,000.
Further reading
- Bearss, Edwin C. Receding Tide: Vicksburg and Gettysburg: The Campaigns That Changed the Civil War. Washington DC: National Geographic Society, 2010. ISBN 978-1-4262-0510-1.
- Catton, BruceBruce CattonCharles Bruce Catton was an American historian and journalist, best known for his books on the American Civil War. Known as a narrative historian, Catton specialized in popular histories that emphasized colorful characters and historical vignettes, in addition to the basic facts, dates, and analyses...
. Glory Road. Garden City, NY: Doubleday and Company, 1952. ISBN 0-385-04167-5. - Foote, ShelbyShelby FooteShelby Dade Foote, Jr. was an American historian and novelist who wrote The Civil War: A Narrative, a massive, three-volume history of the war. With geographic and cultural roots in the Mississippi Delta, Foote's life and writing paralleled the radical shift from the agrarian planter system of the...
. The Civil War: A NarrativeThe Civil War: A NarrativeThe Civil War: A Narrative is a three volume, 2,968-page, 1.2 million-word history of the American Civil War by Shelby Foote. Although previously known as a novelist, Foote is most famous for this non-fictional narrative history. While it touches on political and social themes, the main thrust of...
. Vol. 2, Fredericksburg to Meridian. New York: Random House, 1958. ISBN 0-394-49517-9. - Freeman, Douglas S.Douglas S. FreemanDouglas Southall Freeman was an American historian, biographer, newspaper editor, and author. He is best known for his multi-volume biographies of Robert E...
Lee's Lieutenants: A Study in Command. 3 vols. New York: Scribner, 1946. ISBN 0-684-85979-3. - Freeman, Douglas S. R. E. Lee, A Biography. 4 vols. New York: Scribner, 1934.
- Gottfried, Bradley M. The Maps of Gettysburg: An Atlas of the Gettysburg Campaign, June 3 – June 13, 1863. New York: Savas Beatie, 2007. ISBN 978-1-932714-30-2.
- Grimsley, Mark, and Brooks D. Simpson. Gettysburg: A Battlefield Guide. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 1999. ISBN 0-8032-7077-1.
- Hall, Jeffrey C. The Stand of the U.S. Army at Gettysburg. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2003. ISBN 0-253-34258-9.
- Laino, Philip, Gettysburg Campaign Atlas. 2nd ed. Dayton, OH: Gatehouse Press 2009. ISBN 978-1-934900-45-1.

