Bayer designation
Encyclopedia
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek letter
, followed by the genitive
form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars.
Most of the brighter stars were assigned their first systematic names by the German
astronomer
Johann Bayer
in 1603, in his star atlas Uranometria
(named after Urania
, the Greek Muse
of Astronomy
, along with Uranus
, the Greek god of the sky and heavens). Bayer assigned a lower-case Greek letter, such as alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ), etc., to each star he catalogued, combined with the Latin name of the star’s parent constellation in genitive
(possessive) form. (See List of constellations for the genitive forms.) For example, Aldebaran
is designated α Tauri , which means "Alpha of the Bull
". (The letters of the Greek alphabet were used in antiquity as numerals
, so Bayer's scheme might be regarded as a numbering system.)
A single constellation may contain fifty or more stars, but the Greek alphabet has only twenty-four letters; when these ran out, Bayer began using lower-case Latin letters: hence s Carinae
(s of the Keel
) and d Centauri
(d of the Centaur
). Within constellations having an extremely large number of stars, Bayer eventually advanced to upper-case Latin letters, as in G Scorpii
(G of the Scorpion) and N Velorum
(N of the Sails
). The last letter used by Bayer was Q.
Bayer did not always follow this rule; he sometimes assigned letters to stars according to their location within a constellation (for example: the northern, southern, eastern, or western part of a constellation), according to the order in they rise in the east, according to historical or mythological information on specific stars within a constellation, or according to his own random choosing. Usually the stars were roughly ordered from the head to the feet (or tail) of the figure (as in the Big Dipper
).
Of the 88 modern constellations, there are at least 30 in which "Alpha" is not the brightest star, and four of those lack an alpha star altogether. (Constellations with no alpha include Vela
and Puppis
, both formerly part of Argo Navis
whose alpha is Canopus
in Carina
.)
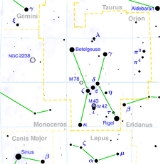
Orion
provides a good example of Bayer's method. (The lower the magnitude, the brighter the star; additionally, there is a precise definition: a "2nd-magnitude" star ranks between 1.51 and 2.50, inclusive.) Bayer first designated the two 1st-magnitude stars, Betelgeuse and Rigel, as Alpha and Beta, with Betelgeuse (the shoulder) coming ahead of Rigel (the foot), even though the latter is usually the brighter. (Betelgeuse, a variable star, can at its maximum very occasionally be brighter than Rigel.)
He then repeated the procedure for the stars of the 2nd magnitude. As is evident from the map and chart, he again followed a "top-down" ("north-south") route.
and Pollux
of Gemini
. Although Pollux is brighter than Castor, the latter was assigned alpha because it rises in the east ahead of the former. Bayer may also have assigned the stars Castor and Pollux in terms of historical or mythological knowledge. Both historically and mythologically, Castor's name is almost always mentioned first (Castor and Pollux) whenever the twins are mentioned, and that may have compelled him to assign alpha (α) to Castor and beta (β) to Pollux.
Although the brightest star in Draco is Eltanin (Gamma Draconis), Thuban
was assigned alpha (α) by Bayer because Thuban, in history, was once the north pole star
, 4,000 years ago. Almost every star with a history of being the North Star, including Vega
, Alderamin and Polaris
, were designated as the alpha (α) of their parent constellations by Bayer.
Sometimes, indeed, there's no apparent order, as exemplified by the stars in Libra
and Sagittarius
, where Bayer assigned designations to stars at random.
/γ Aur
, and α And
/δ Peg
. When the International Astronomical Union
(IAU) outlined the official 88 constellations with definite boundaries in 1930, it declared that stars and other celestial objects can be assigned to only one constellation. Consequently, the redundant Bayer designations for those two stars were scrapped, and now only Beta Tauri and Alpha Andromedae are used. Another star, σ Lib
, was formerly known as γ Sco, though it is well inside Libra
. A few stars still do not lie (according to the modern constellation boundaries) within the constellation for which they are named. Nonetheless, these designations have proved useful and are widely used today.
) and P Cygni
. Uppercase Latin Bayer designations never went beyond Q; names such as R Leporis
and W Ursae Majoris
are variable star designation
s, not Bayer designations.
A further complication is the use of numeric superscripts to distinguish between stars with the same Bayer letter. Usually these are double star
s (mostly optical doubles rather than true binary star
s), but there are some exceptions such as the chain of stars π1, π2, π3
, π4
, π5 and π6 Orionis
.
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
, followed by the genitive
Genitive case
In grammar, genitive is the grammatical case that marks a noun as modifying another noun...
form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars.
Most of the brighter stars were assigned their first systematic names by the German
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer was a German lawyer and uranographer . He was born in Rain, Bavaria, in 1572. He began his study of philosophy in Ingolstadt in 1592, and moved later to Augsburg to begin work as a lawyer. He grew interested in astronomy during his time in Augsburg...
in 1603, in his star atlas Uranometria
Uranometria
Uranometria is the short title of a star atlas produced by Johann Bayer.It was published in Augsburg, Germany, in 1603 by Christophorus Mangus under the full title Uranometria : omnium asterismorum continens schemata, nova methodo delineata, aereis laminis expressa. This translates to...
(named after Urania
Urania
Urania was, in Greek mythology, the muse of astronomy. Some accounts list her as the mother of the musician Linus. She is usually depicted with a globe in her left hand. She is able to foretell the future by the arrangement of the stars...
, the Greek Muse
Muse
The Muses in Greek mythology, poetry, and literature, are the goddesses who inspire the creation of literature and the arts. They were considered the source of the knowledge, related orally for centuries in the ancient culture, that was contained in poetic lyrics and myths...
of Astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, along with Uranus
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
, the Greek god of the sky and heavens). Bayer assigned a lower-case Greek letter, such as alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ), etc., to each star he catalogued, combined with the Latin name of the star’s parent constellation in genitive
Genitive case
In grammar, genitive is the grammatical case that marks a noun as modifying another noun...
(possessive) form. (See List of constellations for the genitive forms.) For example, Aldebaran
Aldebaran
Aldebaran is a red giant star located about 65 light years away in the zodiac constellation of Taurus. With an average apparent magnitude of 0.87 it is the brightest star in the constellation and is one of the brightest stars in the nighttime sky...
is designated α Tauri , which means "Alpha of the Bull
Taurus (constellation)
Taurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is a Latin word meaning 'bull', and its astrological symbol is a stylized bull's head:...
". (The letters of the Greek alphabet were used in antiquity as numerals
Greek numerals
Greek numerals are a system of representing numbers using letters of the Greek alphabet. They are also known by the names Ionian numerals, Milesian numerals , Alexandrian numerals, or alphabetic numerals...
, so Bayer's scheme might be regarded as a numbering system.)
A single constellation may contain fifty or more stars, but the Greek alphabet has only twenty-four letters; when these ran out, Bayer began using lower-case Latin letters: hence s Carinae
HD 90853
HD 90853, also called s Carinae , is a star in the constellation Carina.s Carinae is a yellow-white F-type bright giant with an apparent magnitude of +3.81. It is approximately 1040 light years from Earth....
(s of the Keel
Carina (constellation)
Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was formerly part of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until that constellation was divided in three.-Stars:...
) and d Centauri
D Centauri
D Centauri is a double star in the constellation Centaurus. The system has a combined apparent magnitude of +5.31 and is approximately 566 light years from Earth....
(d of the Centaur
Centaurus
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:...
). Within constellations having an extremely large number of stars, Bayer eventually advanced to upper-case Latin letters, as in G Scorpii
G Scorpii
G Scorpii is a star in the constellation Scorpius. It is an orange K-type giant with an apparent magnitude of +3.19. It is approximately 126 light years from Earth.Just 8.5 arcminutes to the east is the globular cluster NGC 6441....
(G of the Scorpion) and N Velorum
HD 82668
N Velorum is a 3rd-magunitude star on the border between the constellations Carina and Vela. It is an orange K-type giant. It is approximately 250 light years from the Earth.The star should not be confused with n Velorum....
(N of the Sails
Vela (constellation)
Vela is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the sails of a ship, and it was originally part of a larger constellation, the ship Argo Navis, which was later divided into three parts, the others being Carina and Puppis.-Stars:...
). The last letter used by Bayer was Q.
Is Alpha always the brightest star?
For the most part, Bayer assigned Greek and Latin letters to stars in rough order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest, within a particular constellation. Since in a majority of constellations the brightest star is designated Alpha (α), many people wrongly assume that Bayer meant to put the stars exclusively in order of their brightness, but in his day there was no way to measure stellar brightness precisely. Traditionally, the stars were assigned to one of six magnitude classes, and Bayer's catalog lists all the first-magnitude stars, followed by all the second-magnitude stars, and so on. Within each magnitude class, Bayer made no attempt to arrange stars by relative brightness.Bayer did not always follow this rule; he sometimes assigned letters to stars according to their location within a constellation (for example: the northern, southern, eastern, or western part of a constellation), according to the order in they rise in the east, according to historical or mythological information on specific stars within a constellation, or according to his own random choosing. Usually the stars were roughly ordered from the head to the feet (or tail) of the figure (as in the Big Dipper
Big Dipper
The Plough, also known as the Big Dipper or the Saptarishi , is an asterism of seven stars that has been recognized as a distinct grouping in many cultures from time immemorial...
).
Of the 88 modern constellations, there are at least 30 in which "Alpha" is not the brightest star, and four of those lack an alpha star altogether. (Constellations with no alpha include Vela
Vela (constellation)
Vela is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the sails of a ship, and it was originally part of a larger constellation, the ship Argo Navis, which was later divided into three parts, the others being Carina and Puppis.-Stars:...
and Puppis
Puppis
Puppis is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is the Latin word for the poop deck of a ship, and Puppis represents the deck of the ship and its deckhouses...
, both formerly part of Argo Navis
Argo Navis
Argo Navis was a large constellation in the southern sky that has since been divided into three constellations. It represented the Argo, the ship used by Jason and the Argonauts in Greek mythology...
whose alpha is Canopus
Canopus
Canopus |Alpha]] Carinae) is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina and Argo Navis, and the second brightest star in the night-time sky, after Sirius. Canopus's visual magnitude is −0.72, and it has an absolute magnitude of −5.53.Canopus is a supergiant of spectral...
in Carina
Carina (constellation)
Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was formerly part of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until that constellation was divided in three.-Stars:...
.)
Bayer designations in Orion
| Bayer Designation |
Apparent Magnitude |
Proper Name |
|---|---|---|
| α Ori | 0.45 | Betelgeuse Betelgeuse Betelgeuse, also known by its Bayer designation Alpha Orionis , is the eighth brightest star in the night sky and second brightest star in the constellation of Orion, outshining its neighbour Rigel only rarely... |
| β Ori | 0.18 | Rigel Rigel Rigel is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the sixth brightest star in the sky, with visual magnitude 0.18... |
| γ Ori | 1.64 | Bellatrix |
| δ Ori | 2.23 | Mintaka |
| ε Ori | 1.69 | Alnilam |
| ζ Ori | 1.70 | Alnitak |
Orion
Orion (constellation)
Orion, often referred to as The Hunter, is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous, and most recognizable constellations in the night sky...
provides a good example of Bayer's method. (The lower the magnitude, the brighter the star; additionally, there is a precise definition: a "2nd-magnitude" star ranks between 1.51 and 2.50, inclusive.) Bayer first designated the two 1st-magnitude stars, Betelgeuse and Rigel, as Alpha and Beta, with Betelgeuse (the shoulder) coming ahead of Rigel (the foot), even though the latter is usually the brighter. (Betelgeuse, a variable star, can at its maximum very occasionally be brighter than Rigel.)
He then repeated the procedure for the stars of the 2nd magnitude. As is evident from the map and chart, he again followed a "top-down" ("north-south") route.
Various Bayer designation arrangements
This "First to Rise in the East" method is done in a number of other instances, even for CastorCastor (star)
Castor is the second brightest star in the constellation Gemini and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. Although it has the Bayer designation "alpha", it is actually fainter than Beta Geminorum...
and Pollux
Pollux (star)
Pollux is an orange giant star approximately 34 light-years from the Earth in the constellation of Gemini . Pollux is the brightest star in the constellation, brighter than Castor...
of Gemini
Gemini (constellation)
Gemini is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It was one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. Its name is Latin for "twins", and it is associated with the twins Castor and Pollux in Greek mythology...
. Although Pollux is brighter than Castor, the latter was assigned alpha because it rises in the east ahead of the former. Bayer may also have assigned the stars Castor and Pollux in terms of historical or mythological knowledge. Both historically and mythologically, Castor's name is almost always mentioned first (Castor and Pollux) whenever the twins are mentioned, and that may have compelled him to assign alpha (α) to Castor and beta (β) to Pollux.
Although the brightest star in Draco is Eltanin (Gamma Draconis), Thuban
Thuban
Thuban also known by its Bayer designation Alpha Draconis is a star in the constellation of Draco. A relatively inconspicuous star in the night sky of the Northern Hemisphere, it is historically significant as having been the north pole star in ancient times...
was assigned alpha (α) by Bayer because Thuban, in history, was once the north pole star
Pole star
The term "Pole Star" usually refers to Polaris, which is the current northern pole star, also known as the North Star.In general, however, a pole star is a visible star, especially a prominent one, that is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation; that is, a star whose apparent...
, 4,000 years ago. Almost every star with a history of being the North Star, including Vega
Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the constellation Lyra, the fifth brightest star in the night sky and the second brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus...
, Alderamin and Polaris
Polaris
Polaris |Alpha]] Ursae Minoris, commonly North Star or Pole Star, also Lodestar) is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor. It is very close to the north celestial pole, making it the current northern pole star....
, were designated as the alpha (α) of their parent constellations by Bayer.
Sometimes, indeed, there's no apparent order, as exemplified by the stars in Libra
Libra (constellation)
Libra is a constellation of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for weighing scales, and its symbol is . It is fairly faint, with no first magnitude stars, and lies between Virgo to the west and Scorpius to the east.-Notable features:]...
and Sagittarius
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow...
, where Bayer assigned designations to stars at random.
Revised Bayer designations
Some stars were "border stars", falling on the boundaries between two constellations, and Bayer would assign them a Greek letter from each constellation. The two most prominent examples are β TauBeta Tauri
Beta Tauri is the second brightest star in the constellation Taurus, with an apparent magnitude of 1.68. Because it is on the boundary of Taurus and Auriga, it also has the redundant Bayer designation Gamma Aurigae , which today is rarely used...
/γ Aur
Auriga (constellation)
Auriga is a constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'charioteer' and its stars form a shape that has been associated with the pointed helmet of a charioteer. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains among the 88 modern...
, and α And
Alpha Andromedae
Alpha Andromedae , which has the traditional names Alpheratz and Sirrah , is the brightest star in the constellation of Andromeda. Located immediately northeast of the constellation of Pegasus, it is the northeastern star of the Great Square of Pegasus...
/δ Peg
Pegasus (constellation)
Pegasus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:...
. When the International Astronomical Union
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
(IAU) outlined the official 88 constellations with definite boundaries in 1930, it declared that stars and other celestial objects can be assigned to only one constellation. Consequently, the redundant Bayer designations for those two stars were scrapped, and now only Beta Tauri and Alpha Andromedae are used. Another star, σ Lib
Sigma Librae
Sigma Librae is a star in the constellation Libra. It has the traditional names Brachium , Cornu , and Zubenalgubi ....
, was formerly known as γ Sco, though it is well inside Libra
Libra (constellation)
Libra is a constellation of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for weighing scales, and its symbol is . It is fairly faint, with no first magnitude stars, and lies between Virgo to the west and Scorpius to the east.-Notable features:]...
. A few stars still do not lie (according to the modern constellation boundaries) within the constellation for which they are named. Nonetheless, these designations have proved useful and are widely used today.
Bayer designation styles
There are two common ways in which Bayer designations can be written. The designation can be written out in full, as in Alpha Canis Majoris or Beta Persei, or a lowercase Greek letter can be used together with the standard 3-letter abbreviation of the constellation, as in α CMa or β Per. Or the two can be combined (α Canis Majoris). Earlier 4-letter abbreviations (such as α CMaj) are rarely used today.Other Bayer designations
The Latin-letter extended designations are rarely used, but there are some exceptions such as h Persei (which is actually a star clusterStar cluster
Star clusters or star clouds are groups of stars. Two types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters, more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally contain less than...
) and P Cygni
P Cygni
P Cygni is a variable star in the constellation Cygnus. The designation "P" was originally assigned by Johann Bayer in Uranometria as a nova....
. Uppercase Latin Bayer designations never went beyond Q; names such as R Leporis
R Leporis
R Leporis , sometimes called Hind's Crimson Star, is a well-known variable star in the constellation Lepus, near its border with Eridanus. It is designated "R" in the chart to the right....
and W Ursae Majoris
W Ursae Majoris
W Ursae Majoris is a variable star in the constellation Ursa Major. It is an eclipsing contact binary whose two component stars share a common outer layer, and is the prototype of a class of contact binary variables known as W Ursae Majoris variables...
are variable star designation
Variable star designation
Variable stars are named using a variation on the Bayer designation format of an identifying label combined with the Latin genitive of the name of the constellation in which the star lies...
s, not Bayer designations.
A further complication is the use of numeric superscripts to distinguish between stars with the same Bayer letter. Usually these are double star
Double star
In observational astronomy, a double star is a pair of stars that appear close to each other in the sky as seen from Earth when viewed through an optical telescope. This can happen either because the pair forms a binary star, i.e...
s (mostly optical doubles rather than true binary star
Binary star
A binary star is a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass. The brighter star is called the primary and the other is its companion star, comes, or secondary...
s), but there are some exceptions such as the chain of stars π1, π2, π3
Pi3 Orionis
Pi3 Orionis , formally designated Tabit, is a white F-type dwarf star approximately 26 light-years away in the constellation of Orion. It is thought that the star may, in fact, be a binary star system. Though no extrasolar planets have been observed around Pi3 Orionis, the star is considered a...
, π4
Pi4 Orionis
Pi4 Orionis is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation Orion. It is about 1,300 light years away and is one of the most luminous stars known. It is one of a series of stars that share the Bayer designation Pi Orionis....
, π5 and π6 Orionis
Pi Orionis
Pi Orionis is a group of fairly widely scattered stars in the constellation Orion that constitute Orion's shield.They form an exception to the general rule that stars that share the same Bayer designation are close together: π1 is nearly 9° north of π6 .* π1 Ori * π2 Ori * π3 Ori...
.
See also
Bayer objects- Flamsteed designationFlamsteed designationFlamsteed designations for stars are similar to Bayer designations, except that they use numbers instead of Greek letters. Each star is assigned a number and the Latin genitive of the constellation it lies in...
- Gould designationGould designationGould designations for stars are similar to Flamsteed designations in the way that they number stars within a constellation in increasing order of right ascension. Each star is assigned an integer , followed by " G. " , and then the Latin genitive of the constellation it lies in...
- List of constellations
- Star catalogueStar catalogueA star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some...
- Star designationStar designationDesignations of stars are done by the International Astronomical Union . Many of the star names in use today were inherited from the time before the IAU existed. Other names, mainly for variable stars , are being added all the time.Approximately 10,000 stars are visible to the naked eye...
- Table of stars with Bayer designationsTable of stars with Bayer designationsThis table lists those stars/objects which have Greek-letter Bayer designations.Only those stars which have individual articles are shown in the table. The name given is that of the article if it does not reflect the Bayer designation...
- Variable star designationVariable star designationVariable stars are named using a variation on the Bayer designation format of an identifying label combined with the Latin genitive of the name of the constellation in which the star lies...

