
Beam parameter product
Encyclopedia
In laser science
, the beam parameter product (BPP) is the product of a laser
beam's divergence
angle (half-angle) and the radius
of the beam at its narrowest point (the beam waist). The BPP quantifies the quality of a laser beam, and how well it can be focused to a small spot.
A Gaussian beam
has the lowest possible BPP,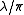 , where
, where 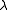 is the wavelength
is the wavelength
of the light. The ratio of the BPP of an actual beam to that of an ideal Gaussian beam at the same wavelength is denoted M² ("M squared
"). This parameter is a wavelength-independent measure of beam quality.
There are several ways to define the width of a beam. When measuring the beam parameter product and M², one uses the D4σ or "second moment" width of the beam to determine both the radius of the beam's waist and the divergence in the far field. Other definitions of beam quality have been used in the past, but the one using second moment widths is most commonly accepted.
The quality of a beam is important for many applications. In fiber-optic communications beams with an M2 close to 1 are required for coupling to single-mode optical fiber
. Laser machine shops care a lot about the M2 parameter of their lasers because the beams will focus to an area that is M2 times larger than that of a Gaussian beam with the same wavelength and D4σ waist width; in other words, the fluence
scales as 1/M2. The general rule of thumb is that M2 increases as the laser power increases. It is difficult to obtain excellent beam quality and high average power (100 W to kWs) due to thermal lensing in the laser gain medium.
of high optical quality and known focal length
. To properly obtain the BPP and M² the following steps must be followed:
In principle, one could use a single measurement at the waist to obtain the waist diameter, a single measurement in the far field to obtain the divergence, and then use these to calculate the BPP. The procedure above gives a more accurate result in practice, however.
Laser science
Laser science or laser physics is a branch of optics that describes the theory and practice of lasers.Laser science is principally concerned with quantum electronics, laser construction, optical cavity design, the physics of producing a population inversion in laser media, and the temporal...
, the beam parameter product (BPP) is the product of a laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
beam's divergence
Beam divergence
The beam divergence of an electromagnetic beam is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter or radius with distance from the optical aperture or antenna aperture from which the electromagnetic beam emerges. The term is relevant only in the "far field", away from any focus of the beam...
angle (half-angle) and the radius
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
of the beam at its narrowest point (the beam waist). The BPP quantifies the quality of a laser beam, and how well it can be focused to a small spot.
A Gaussian beam
Gaussian beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is a beam of electromagnetic radiation whose transverse electric field and intensity distributions are well approximated by Gaussian functions. Many lasers emit beams that approximate a Gaussian profile, in which case the laser is said to be operating on the fundamental...
has the lowest possible BPP,
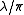 , where
, where 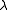 is the wavelength
is the wavelengthWavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of the light. The ratio of the BPP of an actual beam to that of an ideal Gaussian beam at the same wavelength is denoted M² ("M squared
M squared
In laser science, the parameter M² is the ratio of the beam parameter product of an actual beam to that of an ideal Gaussian beam at the same wavelength. It is often referred to as the beam quality factor, since its value can be used to quantify the degree of variation the actual beam is from such...
"). This parameter is a wavelength-independent measure of beam quality.
There are several ways to define the width of a beam. When measuring the beam parameter product and M², one uses the D4σ or "second moment" width of the beam to determine both the radius of the beam's waist and the divergence in the far field. Other definitions of beam quality have been used in the past, but the one using second moment widths is most commonly accepted.
The quality of a beam is important for many applications. In fiber-optic communications beams with an M2 close to 1 are required for coupling to single-mode optical fiber
Single-mode optical fiber
In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber is an optical fiber designed to carry only a single ray of light . Modes are the possible solutions of the Helmholtz equation for waves, which is obtained by combining Maxwell's equations and the boundary conditions...
. Laser machine shops care a lot about the M2 parameter of their lasers because the beams will focus to an area that is M2 times larger than that of a Gaussian beam with the same wavelength and D4σ waist width; in other words, the fluence
Fluence
In physics, fluence is the flux integrated over time. For particles, it is defined as the total number of particles that intersect a unit area in a specific time interval of interest, and has units of m–2...
scales as 1/M2. The general rule of thumb is that M2 increases as the laser power increases. It is difficult to obtain excellent beam quality and high average power (100 W to kWs) due to thermal lensing in the laser gain medium.
Measurement of the BPP
The BPP can be easily measured by placing an array detector or scanning-slit profiler at multiple positions within the beam after focussing it with a lensLens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
of high optical quality and known focal length
Focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
. To properly obtain the BPP and M² the following steps must be followed:
- Measure the D4σ widths at 5 axial positions near the beam waist (the location where the beam is narrowest).
- Measure the D4σ widths at 5 axial positions at least one Rayleigh lengthRayleigh lengthIn optics and especially laser science, the Rayleigh length or Rayleigh range is the distance along the propagation direction of a beam from the waist to the place where the area of the cross section is doubled. A related parameter is the confocal parameter, b, which is twice the Rayleigh length...
away from the waist. - Fit the 10 measured data points to
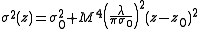 , where
, where 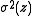 is the second moment of the distribution in the x or y direction (see section on D4σ beam width), and
is the second moment of the distribution in the x or y direction (see section on D4σ beam width), and 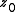 is the location of the beam waist with second moment width of
is the location of the beam waist with second moment width of 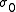 . Fitting the 10 data points yields M2,
. Fitting the 10 data points yields M2, 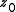 , and
, and 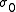 . Siegman showed that all beam profiles — Gaussian, flat topTophat beamIn optics, a tophat beam is a laser beam with a near-uniform fluence within a circular disk. It is typically formed by diffractive optical elements from a Gaussian beam. Tophat beams are often used in industry, for example for laser drilling of holes in printed circuit boards...
. Siegman showed that all beam profiles — Gaussian, flat topTophat beamIn optics, a tophat beam is a laser beam with a near-uniform fluence within a circular disk. It is typically formed by diffractive optical elements from a Gaussian beam. Tophat beams are often used in industry, for example for laser drilling of holes in printed circuit boards...
, TEMxy, or any shape — must follow the equation above provided that the beam radius uses the D4σ definition of the beam width. Using other definitions of beam width does not work.
In principle, one could use a single measurement at the waist to obtain the waist diameter, a single measurement in the far field to obtain the divergence, and then use these to calculate the BPP. The procedure above gives a more accurate result in practice, however.

