
Rayleigh length
Encyclopedia
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
and especially laser science
Laser science
Laser science or laser physics is a branch of optics that describes the theory and practice of lasers.Laser science is principally concerned with quantum electronics, laser construction, optical cavity design, the physics of producing a population inversion in laser media, and the temporal...
, the Rayleigh length or Rayleigh range is the distance along the propagation direction of a beam
Light beam
A light beam or beam of light is a narrow projection of light energy radiating from a source into a beam. Sunlight is a natural example of a light beam when filtered through various mediums...
from the waist to the place where the area of the cross section
Cross section (geometry)
In geometry, a cross-section is the intersection of a figure in 2-dimensional space with a line, or of a body in 3-dimensional space with a plane, etc...
is doubled. A related parameter is the confocal parameter, b, which is twice the Rayleigh length. The Rayleigh length is particularly important when beams are modeled as Gaussian beam
Gaussian beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is a beam of electromagnetic radiation whose transverse electric field and intensity distributions are well approximated by Gaussian functions. Many lasers emit beams that approximate a Gaussian profile, in which case the laser is said to be operating on the fundamental...
s.
Explanation
For a Gaussian beam propagating in free space along the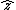 axis, the Rayleigh length is given by
axis, the Rayleigh length is given by 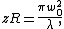
where
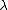 is the wavelength
is the wavelengthWavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
and
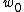 is the beam waist, the radial size of the beam at its narrowest point.
is the beam waist, the radial size of the beam at its narrowest point.The radius of the beam at a distance
 from the waist is
from the waist is 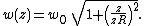
The minimum value of
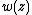 occurs at
occurs at 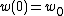 , by definition. At distance
, by definition. At distance  from the beam waist, the beam radius is increased by a factor
from the beam waist, the beam radius is increased by a factor 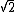 and the cross sectional area by 2.
and the cross sectional area by 2.Related quantities
The total angular spread of a Gaussian beam in radianRadian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
s is related to the Rayleigh length by
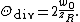
The diameter
Beam diameter
The beam diameter or beam width of an electromagnetic beam is the diameter along any specified line that is perpendicular to the beam axis and intersects it. Since beams typically do not have sharp edges, the diameter can be defined in many different ways. Five definitions of the beam width are in...
of the beam at its waist (focus spot size) is given by
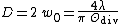 .
.See also
- Beam divergenceBeam divergenceThe beam divergence of an electromagnetic beam is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter or radius with distance from the optical aperture or antenna aperture from which the electromagnetic beam emerges. The term is relevant only in the "far field", away from any focus of the beam...
- Beam parameter productBeam parameter productIn laser science, the beam parameter product is the product of a laser beam's divergence angle and the radius of the beam at its narrowest point . The BPP quantifies the quality of a laser beam, and how well it can be focused to a small spot.A Gaussian beam has the lowest possible BPP,...
- Gaussian function
- Electromagnetic wave equationElectromagnetic wave equationThe electromagnetic wave equation is a second-order partial differential equation that describes the propagation of electromagnetic waves through a medium or in a vacuum...
- John Strutt, 3rd Baron RayleighJohn Strutt, 3rd Baron RayleighJohn William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh, OM was an English physicist who, with William Ramsay, discovered the element argon, an achievement for which he earned the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1904...
- Robert Strutt, 4th Baron Rayleigh
- Depth of fieldDepth of fieldIn optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image...

