
Belarusians
Encyclopedia
Belarusians; are an East Slavic
ethnic group
who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian language spoken by the Ruthenian
ethnic group that ruled (together with ancestors of today's Lithuanians
) the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
. However, after the creation of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, many of the Old Belarusian-speaking Ruthenian nobles
would be absorbed by the Polish szlachta in the West and, later, the Russian nobility
in the East, leaving only a small rural-dwelling population to be the propagators of a distinct non-literary Belarusian language
up until its revival.
There are over 8 million people who associate themselves with the Belarusian nationality today.
.
Noticeable numbers have emigrated to the United States, Brazil and Canada in the early 20th century. During Soviet times, many Belarusians were deported or migrated
to various regions of the USSR, including Siberia
, Kazakhstan and Ukraine.
Since the breakup of the USSR several hundred thousand have emigrated to the European Union, United States, Canada and Russia.
.
Genetical studies show that genetically Belarusians have close genetical similarities with Poles, Russians and Ukrainians, which belong to the same group. A study of the Y chromosome in East Slavs groups shows that there is no significant variation in the Y chromosome between Belarusians, Poles, central-southern Russians and Ukrainians, and it is overlapped by their vast similarities, thus revealing an overwhelmingly shared patrilineal ancestry.
A genetic portrait of modern Belarusians documents A separation of subpopulations along the south-north line, which is demonstrated particularly in distribution of Y chromosomal lineages R1b, I1a and I1b, N3 and G-chromosomes, has been noted; east-west gradient is insignificant.
ns (though not to be confused with the political group of White Russians that opposed the Bolshevik
s during the Russian Civil War
) and similar forms. Belarusians trace their name back to the people of Rus'.
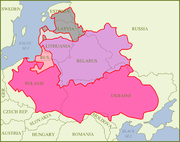
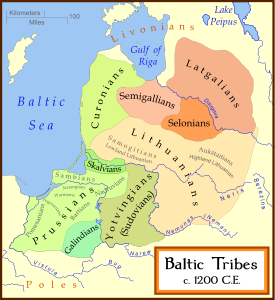 The Belarusian people trace their distinct culture to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and earlier Kievan Rus and the Principality of Polatsk. Most Belarusians are descendants of the East Slav tribes Dregovichs
The Belarusian people trace their distinct culture to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and earlier Kievan Rus and the Principality of Polatsk. Most Belarusians are descendants of the East Slav tribes Dregovichs
, Krivich
s and Radimichs, as well as of a Baltic tribe
of Jotvingians who lived in the west and north-west of today's Belarus.
In 13th-18th centuries Belarusians were mostly known under the name of Ruthenians
which refers to the Eastern part of state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (Litva, Vialikaja Litva) of which the White Ruthenian, Black Ruthenia
n and Polesia
n lands were part of since the 13th-14th centuries and where Ruthenian language
which developed in Old Belarusian language
gradually became the dominant written language in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, that replaced Latin. Casimir's Code of 1468 and all three editions of Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1529, 1566, and 1588) were written in Old Belarusian language. Eventually it was replaced by Polish.
On the grounds of the dominance of Ruthenian language (which later evolved into modern Belarusian and Ukrainian Language
s) culture in the Eastern parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, some modern Belarusian scholars and people in Belarus count that Grand Duchy of Lithuania
was mostly Belarusian state when it existed.
Between 1791 and 1917 much of Belarus, with its Christian and Jewish populations, was acquired by the Russian Empire
in a series of military conquests and diplomatic manoeuvres, and was part of a region known as the Pale of Settlement
.
After World War I Belarusians revived their own statehood, with varying degrees of independence - first as the short-lived Belarusian National Republic
under German occupation, then as the Byelorussian SSR
from 1919 until 1991, which merged with other republics to become a constituent member of the Soviet Union
in 1922). Belarus gained full independence with the dissolution of the Soviet Union
in 1991.

East Slavs
The East Slavs are Slavic peoples speaking East Slavic languages. Formerly the main population of the medieval state of Kievan Rus, by the seventeenth century they evolved into the Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian peoples.-Sources:...
ethnic group
Ethnic group
An ethnic group is a group of people whose members identify with each other, through a common heritage, often consisting of a common language, a common culture and/or an ideology that stresses common ancestry or endogamy...
who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian language spoken by the Ruthenian
Ruthenian
Ruthenian may refer to:*Ruthenia, a name applied to various parts of Eastern Europe*Ruthenians, a historic ethnic group*Ruthenian Catholic Church, the sui iuris particular church united to the Bishop of Rome and the Roman Catholic Church...
ethnic group that ruled (together with ancestors of today's Lithuanians
Lithuanians
Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language...
) the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
. However, after the creation of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, many of the Old Belarusian-speaking Ruthenian nobles
Ruthenian nobility
Ruthenian nobility can refer to:* Boyars* Ukrainian nobility * Belarusian nobility See also: Ruthenia, Ruthenians...
would be absorbed by the Polish szlachta in the West and, later, the Russian nobility
Russian nobility
The Russian nobility arose in the 14th century and essentially governed Russia until the October Revolution of 1917.The Russian word for nobility, Dvoryanstvo , derives from the Russian word dvor , meaning the Court of a prince or duke and later, of the tsar. A nobleman is called dvoryanin...
in the East, leaving only a small rural-dwelling population to be the propagators of a distinct non-literary Belarusian language
Belarusian language
The Belarusian language , sometimes referred to as White Russian or White Ruthenian, is the language of the Belarusian people...
up until its revival.
There are over 8 million people who associate themselves with the Belarusian nationality today.
Location
Belarusians also form minorities in neighboring Poland (especially in the Białystok Voivodeship), Russia and Lithuania. At the beginning of 20th century Belarusians constituted a majority in the regions around SmolenskSmolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River. Situated west-southwest of Moscow, this walled city was destroyed several times throughout its long history since it was on the invasion routes of both Napoleon and Hitler. Today, Smolensk...
.
Noticeable numbers have emigrated to the United States, Brazil and Canada in the early 20th century. During Soviet times, many Belarusians were deported or migrated
Population transfer in the Soviet Union
Population transfer in the Soviet Union may be classified into the following broad categories: deportations of "anti-Soviet" categories of population, often classified as "enemies of workers," deportations of entire nationalities, labor force transfer, and organized migrations in opposite...
to various regions of the USSR, including Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
, Kazakhstan and Ukraine.
Since the breakup of the USSR several hundred thousand have emigrated to the European Union, United States, Canada and Russia.
Languages
The most spoken language in Belarus is Russian, principally spoken by 72% of the population, while the other official language, Belarusian, is only used by 11,9% in every day life. Statistical data shows that Belarusian is fluently communicated, read and written by 29,4%, while 52,5% of the population can communicate and read in Belarusian. Belarusian is a language of the Eastern Slavic groupEast Slavic languages
The East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of Slavic languages, currently spoken in Eastern Europe. It is the group with the largest numbers of speakers, far out-numbering the Western and Southern Slavic groups. Current East Slavic languages are Belarusian, Russian,...
.
Genetics
Belarusians show the characteristic R1a genes of the male ancestorship at 51%, similar to other East slav groups. Such large frequencies of R1a have been found only in East Europe and India.Genetical studies show that genetically Belarusians have close genetical similarities with Poles, Russians and Ukrainians, which belong to the same group. A study of the Y chromosome in East Slavs groups shows that there is no significant variation in the Y chromosome between Belarusians, Poles, central-southern Russians and Ukrainians, and it is overlapped by their vast similarities, thus revealing an overwhelmingly shared patrilineal ancestry.
A genetic portrait of modern Belarusians documents A separation of subpopulations along the south-north line, which is demonstrated particularly in distribution of Y chromosomal lineages R1b, I1a and I1b, N3 and G-chromosomes, has been noted; east-west gradient is insignificant.
Name
The name Belarus can be literally translated as White Ruthenia that is a historical region in the east of modern Republic of Belarus, known in Latin as Ruthenia Alba. This name was in use in the West for some time in history, together with White Ruthenes, White RussiaWhite Russia
White Russia or White Ruthenia is a name that has historically been applied to a part of the wider region of Ruthenia or Rus', most often to that which roughly corresponds to the eastern part of present-day Belarus including the cities of Polatsk, Vitsyebsk and Mahiliou. In English, the use of the...
ns (though not to be confused with the political group of White Russians that opposed the Bolshevik
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, originally also Bolshevists , derived from bol'shinstvo, "majority") were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party which split apart from the Menshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903....
s during the Russian Civil War
Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire after the Russian provisional government collapsed to the Soviets, under the domination of the Bolshevik party. Soviet forces first assumed power in Petrograd The Russian Civil War (1917–1923) was a...
) and similar forms. Belarusians trace their name back to the people of Rus'.

History

Dregovichs
The Dregoviches were one of the tribal unions of Early East Slavs, and inhabited the territories down the stream of the Pripyat River and northern parts of the right bank of the Dnieper river...
, Krivich
Krivich
The Krivichi was one of the tribal unions of Early East Slavs between the 6th and the 12th centuries. They migrated to the mostly Finnic areas in the upper reaches of the Volga, Dnieper, Western Dvina, areas south of the lower reaches of river Velikaya and parts of the Neman basin.-Etymology:Many...
s and Radimichs, as well as of a Baltic tribe
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
of Jotvingians who lived in the west and north-west of today's Belarus.
In 13th-18th centuries Belarusians were mostly known under the name of Ruthenians
Ruthenians
The name Ruthenian |Rus']]) is a culturally loaded term and has different meanings according to the context in which it is used. Initially, it was the ethnonym used for the East Slavic peoples who lived in Rus'. Later it was used predominantly for Ukrainians...
which refers to the Eastern part of state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (Litva, Vialikaja Litva) of which the White Ruthenian, Black Ruthenia
Black Ruthenia
Black Ruthenia, Black Rus or Black Russia are variant conventional terms used for a region around Navahrudak , in the western part of contemporary Belarus on the upper reaches of the Neman River for the time period between the 13th and 14th centuries...
n and Polesia
Polesia
Polesia is one of the largest European swampy areas, located in the south-western part of the Eastern-European Lowland, mainly within Belarus and Ukraine but also partly within Poland and Russia...
n lands were part of since the 13th-14th centuries and where Ruthenian language
Ruthenian language
Ruthenian, or Old Ruthenian , is a term used for the varieties of Eastern Slavonic spoken in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later in the East Slavic territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth....
which developed in Old Belarusian language
Old Belarusian language
Old Belarusian was a historic East Slavic language, written and spoken at least in the 14th–17th century, and reported spoken as late as the very beginning of the 19th century, in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later in the East Slavic territories of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, probably...
gradually became the dominant written language in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, that replaced Latin. Casimir's Code of 1468 and all three editions of Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1529, 1566, and 1588) were written in Old Belarusian language. Eventually it was replaced by Polish.
On the grounds of the dominance of Ruthenian language (which later evolved into modern Belarusian and Ukrainian Language
Ukrainian language
Ukrainian is a language of the East Slavic subgroup of the Slavic languages. It is the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet....
s) culture in the Eastern parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, some modern Belarusian scholars and people in Belarus count that Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
was mostly Belarusian state when it existed.
Between 1791 and 1917 much of Belarus, with its Christian and Jewish populations, was acquired by the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
in a series of military conquests and diplomatic manoeuvres, and was part of a region known as the Pale of Settlement
Pale of Settlement
The Pale of Settlement was the term given to a region of Imperial Russia, in which permanent residency by Jews was allowed, and beyond which Jewish permanent residency was generally prohibited...
.
After World War I Belarusians revived their own statehood, with varying degrees of independence - first as the short-lived Belarusian National Republic
Belarusian National Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic was a self-declared independent Belarusian state, which declared independence in 1918. It is also called the Belarusian Democratic Republic or the Belarusian National Republic, in order to distinguish it from Communist People's Republics...
under German occupation, then as the Byelorussian SSR
Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic was one of fifteen constituent republics of the Soviet Union. It was one of the four original founding members of the Soviet Union in 1922, together with the Ukrainian SSR, the Transcaucasian SFSR and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic...
from 1919 until 1991, which merged with other republics to become a constituent member of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
in 1922). Belarus gained full independence with the dissolution of the Soviet Union
History of the Soviet Union (1985-1991)
The history of the Soviet Union from 1982 through 1991, spans the period from Leonid Brezhnev's death and funeral until the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Due to the years of Soviet military buildup at the expense of domestic development, economic growth stagnated...
in 1991.

See also
- Demographics of BelarusDemographics of BelarusThe Demographics of Belarus is about the demographic features of the population of Belarus, including population growth, population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population...
- DregovichsDregovichsThe Dregoviches were one of the tribal unions of Early East Slavs, and inhabited the territories down the stream of the Pripyat River and northern parts of the right bank of the Dnieper river...
- History of BelarusHistory of BelarusThis article describes the history of Belarus. The Belarusian ethnos is traced at least as far in time as other East Slavs.After an initial period of independent feudal consolidation, Belarusian lands were incorporated into the Kingdom of Lithuania, Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and later in the...
- List of Belarusians (ethnic group)
- Litvins
- RadimichsRadimichsThe Radimichs , were a tribe of West Slavs of the last few centuries of the 1st millennium, which inhabited upper east parts of the Dnieper down the Sozh River and its tributaries...
External links
- Ethnographic Map (New York, 1953)
- CIA World Fact Book 2005
- "ЧТО ТАКОЕ БЫТЬ БЕЛОРУСОМ?", ("What does it mean to be a Belarusian? ") a 2009 survey

