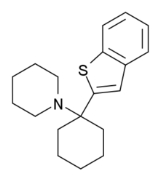
Benocyclidine
Encyclopedia
Benocyclidine or benzothiophenylcyclohexylpiperidine (BTCP), is a psychoactive drug
and research chemical of the arylcyclohexylamine
and piperidine
chemical classes. It act
s a potent
and selective
dopamine reuptake inhibitor
(DRI) and a stimulant
. Unlike related compound
s like phencyclidine
and ketamine
, benocyclidine is a pure DRI with negligible affinity for the NMDA receptor
, and it therefore lacks any anticonvulsant
, anesthetic, hallucinogenic, or dissociative
effects. It has been used to label the dopamine transporter
.
BCP was also used to try and find a common pharmacophore
for DRI type stimulants.
Psychoactive drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, or psychotropic is a chemical substance that crosses the blood–brain barrier and acts primarily upon the central nervous system where it affects brain function, resulting in changes in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, and behavior...
and research chemical of the arylcyclohexylamine
Arylcyclohexylamine
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.- History :...
and piperidine
Piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula 5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene units and one nitrogen atom...
chemical classes. It act
Drug action
The action of drugs on the human body is called pharmacodynamics, and what the body does with the drug is called pharmacokinetics. The drugs that enter the human tend to stimulate certain receptors, ion channels, act on enzymes or transporter proteins...
s a potent
Potency (pharmacology)
In the field of pharmacology, potency is a measure of drug activity expressed in terms of the amount required to produce an effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug evokes a larger response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency evokes a small response at low concentrations...
and selective
Functional Selectivity
Functional selectivity is the ligand-dependent selectivity for certain signal transduction pathways in one and the same receptor. This can be present when a receptor has several possible signal transduction pathways...
dopamine reuptake inhibitor
Dopamine reuptake inhibitor
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor is a type of drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter...
(DRI) and a stimulant
Stimulant
Stimulants are psychoactive drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both. Examples of these kinds of effects may include enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion, among others...
. Unlike related compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
s like phencyclidine
Phencyclidine
Phencyclidine , commonly initialized as PCP and known colloquially as angel dust, is a recreational dissociative drug...
and ketamine
Ketamine
Ketamine is a drug used in human and veterinary medicine. Its hydrochloride salt is sold as Ketanest, Ketaset, and Ketalar. Pharmacologically, ketamine is classified as an NMDA receptor antagonist...
, benocyclidine is a pure DRI with negligible affinity for the NMDA receptor
NMDA receptor
The NMDA receptor , a glutamate receptor, is the predominant molecular device for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function....
, and it therefore lacks any anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
, anesthetic, hallucinogenic, or dissociative
Dissociative drug
Dissociatives are a class of psychoactive drugs which are said to reduce or block signals to the conscious mind from other parts of the brain...
effects. It has been used to label the dopamine transporter
Dopamine transporter
The dopamine transporter is a membrane-spanning protein that pumps the neurotransmitter dopamine out of the synapse back into cytosol, from which other transporters sequester DA and NE into vesicles for later storage and release...
.
BCP was also used to try and find a common pharmacophore
Pharmacophore
thumb|right|300px|An example of a pharmacophore model.A pharmacophore is an abstract description of molecular features which are necessary for molecular recognition of a ligand by a biological macromolecule....
for DRI type stimulants.

