
Bidirectional Associative Memory
Encyclopedia
Bidirectional associative memory (BAM) is a type of recurrent neural network
. BAM was introduced by Bart Kosko
in 1988. There are two types of associative memory, auto-associative and hetero-associative. BAM is hetero-associative, meaning given a pattern it can return another pattern which is potentially of a different size. It is similar to the Hopfield network in that they are both forms of associative memory
. However, Hopfield nets return patterns of the same size.
s one we shall call X and Y. Layer X and Y are fully connected with each other. Once the weights have been established, input into layer X presents the pattern in layer Y, and vice versa.
These are then transformed into the bipolar forms:
From there, we calculate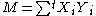 where
where 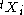 denotes the transpose.
denotes the transpose.
So,
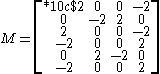
To find the reverse association, multiply this by the transpose of M.
Recurrent neural network
A recurrent neural network is a class of neural network where connections between units form a directed cycle. This creates an internal state of the network which allows it to exhibit dynamic temporal behavior. Unlike feedforward neural networks, RNNs can use their internal memory to process...
. BAM was introduced by Bart Kosko
Bart Kosko
Bart Andrew Kosko is a writer and professor of electrical engineering and law at the University of Southern California...
in 1988. There are two types of associative memory, auto-associative and hetero-associative. BAM is hetero-associative, meaning given a pattern it can return another pattern which is potentially of a different size. It is similar to the Hopfield network in that they are both forms of associative memory
Associative memory
Associative memory may refer to:* A type of memory closely associated with neural networks.* A recent technology that involves creating a memory of multiple databases, both structured and unstructured data, and making associations in a manner that is similar to the human brain's memory functions.**...
. However, Hopfield nets return patterns of the same size.
Topology
It contains two layers of neuronNeuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s one we shall call X and Y. Layer X and Y are fully connected with each other. Once the weights have been established, input into layer X presents the pattern in layer Y, and vice versa.
Learning
Imagine we wish to store two associations, A1:B1 and A2:B2.- A1 = (1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0), B1 = (1, 1, 0, 0)
- A2 = (1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0), B2 = (1, 0, 1, 0)
These are then transformed into the bipolar forms:
- X1 = (1, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1), Y1 = (1, 1, -1, -1)
- X2 = (1, 1, 1, -1, -1, -1), Y2 = (1, -1, 1, -1)
From there, we calculate
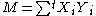 where
where 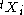 denotes the transpose.
denotes the transpose.So,
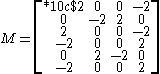
Recall
To retrieve the association A1, we multiply it by M to get (4, 2, -2, -4), which, when run through a threshold, yields (1, 1, 0, 0), which is B1.To find the reverse association, multiply this by the transpose of M.

