
Bipolaron
Encyclopedia
Bipolarons in physics
In physicsPhysics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, a bipolaron is a bound pair of two polaron
Polaron
A polaron is a quasiparticle composed of a charge and its accompanying polarization field. A slow moving electron in a dielectric crystal, interacting with lattice ions through long-range forces will permanently be surrounded by a region of lattice polarization and deformation caused by the moving...
s. An electron in a material may cause a distortion in the underlying lattice. The combination of electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
and distortion (which may also be understood as a cloud of phonon
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, such as solids and some liquids...
s) is known as a polaron
Polaron
A polaron is a quasiparticle composed of a charge and its accompanying polarization field. A slow moving electron in a dielectric crystal, interacting with lattice ions through long-range forces will permanently be surrounded by a region of lattice polarization and deformation caused by the moving...
(in part because the interaction between electron and lattice
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
is via a polarization). When two polaron
Polaron
A polaron is a quasiparticle composed of a charge and its accompanying polarization field. A slow moving electron in a dielectric crystal, interacting with lattice ions through long-range forces will permanently be surrounded by a region of lattice polarization and deformation caused by the moving...
s are close together, they can lower their energy by sharing the same distortions, which leads to an effective attraction between the polaron
Polaron
A polaron is a quasiparticle composed of a charge and its accompanying polarization field. A slow moving electron in a dielectric crystal, interacting with lattice ions through long-range forces will permanently be surrounded by a region of lattice polarization and deformation caused by the moving...
s. If the interaction is sufficiently large, then that attraction leads to a bound bipolaron. For strong attraction, bipolarons may be small. Small bipolarons have integer spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
and thus share some of the properties of boson
Boson
In particle physics, bosons are subatomic particles that obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Several bosons can occupy the same quantum state. The word boson derives from the name of Satyendra Nath Bose....
s. If many bipolarons form without coming too close, they might be able to form a Bose-Einstein condensate. This has led to a suggestion that bipolarons could be a possible mechanism for high temperature superconductivity
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance occurring in certain materials below a characteristic temperature. It was discovered by Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum...
. For example, they can lead to a very direct interpretation of the isotope effect
Isotope effect
Isotope effect can refer to:* Kinetic isotope effect* Magnetic isotope effect* Superconductive transition temperature varying by isotope atomic weight; See BCS theory#Successes of the BCS theory...
.
Bipolarons in organic chemistry
In organic chemistryOrganic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
a bipolaron is a molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
or part of a macromolecular chain containing two positive charge
Charge (physics)
In physics, a charge may refer to one of many different quantities, such as the electric charge in electromagnetism or the color charge in quantum chromodynamics. Charges are associated with conserved quantum numbers.-Formal definition:...
s in a conjugated system
Conjugated system
In chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in compounds with alternating single and multiple bonds, which in general may lower the overall energy of the molecule and increase stability. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the...
. The charges can be located in the centre of the chain or at its termini. Bipolarons and polaron
Polaron
A polaron is a quasiparticle composed of a charge and its accompanying polarization field. A slow moving electron in a dielectric crystal, interacting with lattice ions through long-range forces will permanently be surrounded by a region of lattice polarization and deformation caused by the moving...
s are encountered in doped conducting polymers such as polythiophene
Polythiophene
Polythiophenes result from the polymerization of thiophenes, a sulfur heterocycle, that can become conducting when electrons are added or removed from the conjugated π-orbitals via doping....
.
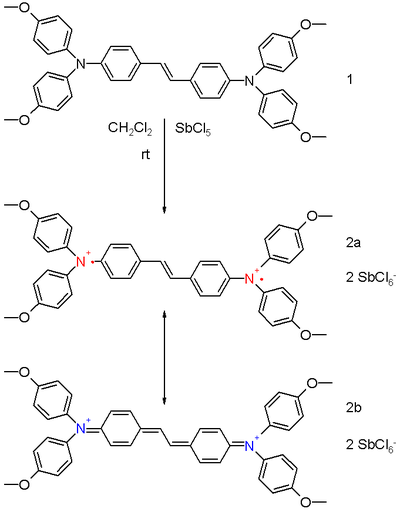
It is possible to synthesize and isolate bipolaron model compounds for X-ray diffraction studies. The diamagnetic bis(triaryl)amine dication 2 in scheme 1 is prepared from the neutral precursor 1 in dichloromethane
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane is an organic compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a moderately sweet aroma is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is miscible with many organic solvents...
by reaction with 4 equivalents of antimony pentachloride
Antimony pentachloride
Antimony pentachloride is a the chemical compound with the formula SbCl5. It is a colourless oil, but typical samples are yellowish due to impurities...
. Two resonance structures exist for the dication. Structure 2a is a (singlet) diradical and 2b is the closed shell quinoid. The experimental bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
s for the central vinylidene group in 2 are 141 pm and 137 pm compared to 144 pm and 134 pm for the precursor 1 implying some contribution from the quinoid structure.
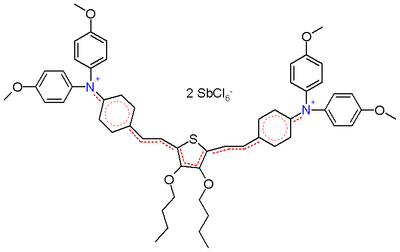
Thiophene
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a flat five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. Related to thiophene are benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene, containing the thiophene ring fused with one and two benzene...
unit is added to the core in the structure depicted in scheme 2, these bond lengths are identical (around 138 pm) making it a true hybrid.
See also
- High temperature superconductivity
- PolaronPolaronA polaron is a quasiparticle composed of a charge and its accompanying polarization field. A slow moving electron in a dielectric crystal, interacting with lattice ions through long-range forces will permanently be surrounded by a region of lattice polarization and deformation caused by the moving...
- Bose-Einstein condensate
- PhononPhononIn physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, such as solids and some liquids...
- ElectronElectronThe electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
- Quinonoid zwitterionQuinonoid zwitterionA Quinonoid zwitterion is a special type of zwitterion based on quinone related chemical compounds. The benzene derivate 1,3-dihydroxy-4,6-diaminobenzene is easily oxidized by air in water or methanol to the quinonoid. This compound was first prepared in 1883 and the quinonoid structure first...
s

