
Block stacking problem
Encyclopedia
In statics
, the block-stacking problem (also the book-stacking problem, or a number of other similar terms) is the following puzzle:
The single-wide problem involves having only one block at any given level. In the ideal case of perfectly rectangular blocks, the solution to the single-wide problem is that the maximum overhang is given by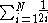 times the width of a block. This sum is one half of the harmonic series
times the width of a block. This sum is one half of the harmonic series
. The maximal overhang tends to
infinity
as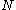 increases, meaning that it is possible to achieve any arbitrarily large overhang, with sufficient blocks.
increases, meaning that it is possible to achieve any arbitrarily large overhang, with sufficient blocks.
Multiwide stacks using counterbalancing
can give larger overhangs than a single width stack. Even for three blocks, stacking two counterbalanced blocks on top of another block can give overhang close to 1, while the overhang in the simple ideal case is at most 11/12. As showed, asymptotically, the maximum overhang that can be achieved by multiwide stacks is proportional to the cube root of the number of blocks, in contrast to the single-wide case in which the overhang is proportional to the logarithm of the number of blocks.
Paterson et al. provide a long list of references on this problem going back to mechanics
texts from the middle of the 19th century.
discusses this problem, shows that it is robust to nonidealizations such as rounded block corners and finite precision of block placing, and introduces several variants including nonzero friction
forces between adjacent blocks.
Statics
Statics is the branch of mechanics concerned with the analysis of loads on physical systems in static equilibrium, that is, in a state where the relative positions of subsystems do not vary over time, or where components and structures are at a constant velocity...
, the block-stacking problem (also the book-stacking problem, or a number of other similar terms) is the following puzzle:
Placerigid
StiffnessStiffness is the resistance of an elastic body to deformation by an applied force along a given degree of freedom when a set of loading points and boundary conditions are prescribed on the elastic body.-Calculations:...
rectangular blocks in a stable stack on a table edge in such a way as to maximize the overhang.
The single-wide problem involves having only one block at any given level. In the ideal case of perfectly rectangular blocks, the solution to the single-wide problem is that the maximum overhang is given by
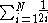 times the width of a block. This sum is one half of the harmonic series
times the width of a block. This sum is one half of the harmonic seriesHarmonic series (mathematics)
In mathematics, the harmonic series is the divergent infinite series:Its name derives from the concept of overtones, or harmonics in music: the wavelengths of the overtones of a vibrating string are 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, etc., of the string's fundamental wavelength...
. The maximal overhang tends to
Limit (mathematics)
In mathematics, the concept of a "limit" is used to describe the value that a function or sequence "approaches" as the input or index approaches some value. The concept of limit allows mathematicians to define a new point from a Cauchy sequence of previously defined points within a complete metric...
infinity
Infinity
Infinity is a concept in many fields, most predominantly mathematics and physics, that refers to a quantity without bound or end. People have developed various ideas throughout history about the nature of infinity...
as
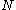 increases, meaning that it is possible to achieve any arbitrarily large overhang, with sufficient blocks.
increases, meaning that it is possible to achieve any arbitrarily large overhang, with sufficient blocks.Multiwide stacks using counterbalancing
Counterweight
A counterweight is an equivalent counterbalancing weight that balances a load.-Uses:A counterweight is often used in traction lifts , cranes and funfair rides...
can give larger overhangs than a single width stack. Even for three blocks, stacking two counterbalanced blocks on top of another block can give overhang close to 1, while the overhang in the simple ideal case is at most 11/12. As showed, asymptotically, the maximum overhang that can be achieved by multiwide stacks is proportional to the cube root of the number of blocks, in contrast to the single-wide case in which the overhang is proportional to the logarithm of the number of blocks.
Paterson et al. provide a long list of references on this problem going back to mechanics
Mechanics
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment....
texts from the middle of the 19th century.
discusses this problem, shows that it is robust to nonidealizations such as rounded block corners and finite precision of block placing, and introduces several variants including nonzero friction
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
forces between adjacent blocks.

