
Blue Lias
Encyclopedia

England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
and parts of South Wales
South Wales
South Wales is an area of Wales bordered by England and the Bristol Channel to the east and south, and Mid Wales and West Wales to the north and west. The most densely populated region in the south-west of the United Kingdom, it is home to around 2.1 million people and includes the capital city of...
, part of the Lias Group
Lias Group
The Lias Group or Lias is a lithostratigraphic unit found in a large area of western Europe, including the British Isles, the North Sea, the low countries and the north of Germany...
. The Blue Lias consists of a sequence of limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
and shale
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals and tiny fragments of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite. The ratio of clay to other minerals is variable. Shale is characterized by breaks along thin laminae or parallel layering...
layers, laid down in latest Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
and early Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
times, between 195 and 200 million years ago. The Blue Lias is famous for its fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s, especially ammonite
Ammonite
Ammonite, as a zoological or paleontological term, refers to any member of the Ammonoidea an extinct subclass within the Molluscan class Cephalopoda which are more closely related to living coleoids Ammonite, as a zoological or paleontological term, refers to any member of the Ammonoidea an extinct...
s.
Its age corresponds to the Rhaetian
Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is in geochronology the latest age of the Triassic period or in chronostratigraphy the uppermost stage of the Triassic system. It lasted from 203.6 ± 1.5 to 199.6 ± 0.6 million years ago...
to lower Sinemurian
Sinemurian
In the geologic timescale, the Sinemurian is an age or stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic epoch or series. It spans the time between 196.5 ± 2 Ma and 189.6 ± 1.5 Ma...
stages of the geologic timescale, thus fully including the Hettangian
Hettangian
The Hettangian is the earliest age or lowest stage of the Jurassic period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 199.6 ± 0.6 Ma and 196.5 ± 1 Ma . The Hettangian follows the Rhaetian and is followed by the Sinemurian.In Europe stratigraphy the Hettangian is a part of the time span in...
stage. It is the lowest of the three divisions of the Lower Jurassic period and, as such, is also given the name Lower Lias. Stratigraphically
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy, a branch of geology, studies rock layers and layering . It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks....
it can be subdivided into three members: the Wilmcote Limestone, Saltford Shale and Rugby Limestone.
Lithology and facies
The Blue Lias comprises decimetre scale alternations of argillaceousClay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
and mudstone
Mudstone
Mudstone is a fine grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Grain size is up to 0.0625 mm with individual grains too small to be distinguished without a microscope. With increased pressure over time the platey clay minerals may become aligned, with the...
. These alternations are caused by short-term climatic variations during the Early Jurassic attributed to orbital forcing (Milankovitch cycles). These limestone-mudstone alternations pass up into a clay member formerly known as the Lower Lias Clay now the Charmouth Mudstone Formation. This lithology consists of monotonous mudstones weathering to clay at the surface. Sparse thin limestone and nodule bands are seen where the rocks are exposed. The deposition of a clay-rich mudstone member normally indicates deposition in a deeper marine environment.
Occurrence
The Blue Lias is a prevalent feature of the cliffs around Lyme RegisLyme Regis
Lyme Regis is a coastal town in West Dorset, England, situated 25 miles west of Dorchester and east of Exeter. The town lies in Lyme Bay, on the English Channel coast at the Dorset-Devon border...
and Charmouth
Charmouth
Charmouth is a village at the mouth of the River Char in West Dorset, England, with a population of 1,687 according to the 2001 census.-The village:...
, on the Jurassic Coast
Jurassic Coast
The Jurassic Coast is a World Heritage Site on the English Channel coast of southern England. The site stretches from Orcombe Point near Exmouth in East Devon to Old Harry Rocks near Swanage in East Dorset, a distance of ....
in Dorset
Dorset
Dorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974...
, where it exists in layers of limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
interspersed with softer clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
. It is also present in Somerset
Somerset
The ceremonial and non-metropolitan county of Somerset in South West England borders Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. It is partly bounded to the north and west by the Bristol Channel and the estuary of the...
, particularly around the Polden Hills
Polden Hills
The Polden Hills in Somerset, England are a long, low ridge, extending for , and separated from the Mendip Hills, to which they are nearly parallel, by a marshy tract, known as the Somerset Levels...
and Glastonbury
Glastonbury
Glastonbury is a small town in Somerset, England, situated at a dry point on the low lying Somerset Levels, south of Bristol. The town, which is in the Mendip district, had a population of 8,784 in the 2001 census...
, and it forms a broad plain across the East Midlands. It also appears near Whitby
Whitby
Whitby is a seaside town, port and civil parish in the Scarborough borough of North Yorkshire, England. Situated on the east coast of Yorkshire at the mouth of the River Esk, Whitby has a combined maritime, mineral and tourist heritage, and is home to the ruins of Whitby Abbey where Caedmon, the...
in Yorkshire
Yorkshire
Yorkshire is a historic county of northern England and the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its great size in comparison to other English counties, functions have been increasingly undertaken over time by its subdivisions, which have also been subject to periodic reform...
and Southam
Southam
Southam is a small market town in the Stratford-on-Avon district of Warwickshire, England. The 2001 census recorded a population of 6,509 in the town.The nearest sizeable town to Southam is Leamington Spa, located roughly 7 miles to the west...
in Warwickshire where a pub is named after it. There are outcrops along the coast of South Wales
South Wales
South Wales is an area of Wales bordered by England and the Bristol Channel to the east and south, and Mid Wales and West Wales to the north and west. The most densely populated region in the south-west of the United Kingdom, it is home to around 2.1 million people and includes the capital city of...
, notably that of the Vale of Glamorgan
Vale of Glamorgan
The Vale of Glamorgan is a county borough in Wales; an exceptionally rich agricultural area, it lies in the southern part of Glamorgan, South Wales...
. The type section of the Blue Lias is at Saltford
Saltford
Saltford is a large village and civil parish in the Bath and North East Somerset unitary authority, Somerset, England. It lies between the cities of Bristol and Bath....
near Bath.
Use in construction

Lime (mineral)
Lime is a general term for calcium-containing inorganic materials, in which carbonates, oxides and hydroxides predominate. Strictly speaking, lime is calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide. It is also the name for a single mineral of the CaO composition, occurring very rarely...
for making lime mortar
Lime mortar
Lime mortar is a type of mortar composed of lime and an aggregate such as sand, mixed with water. It is one of the oldest known types of mortar, dating back to the 4th century BC and widely used in Ancient Rome and Greece, when it largely replaced the clay and gypsum mortars common to Ancient...
. Because it is argillaceous, the lime is hydraulic
Hydraulic lime
Hydraulic lime is a variety of lime, a slaked lime used to make lime mortar. Hydraulicity is the ability of lime to set under water. Hydraulic lime is produced by heating calcining limestone that contains clay and other impurities. Calcium reacts in the kiln with the clay minerals to produce...
. Since the mid-nineteenth century, it has been used as a raw material for cement
Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world because it is a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco and most non-specialty grout...
, in South Wales
Aberthaw
Aberthaw is a village of the Vale of Glamorgan west of Barry on the coast of South Wales.The village is split into two halves - East Aberthaw and West Aberthaw, separated by the River Thaw. It is home to Aberthaw Cement Works and Aberthaw Power Station a coal power station plant that was linked to...
, Somerset, Warwickshire and Leicestershire. The cement plant quarry at Rugby, Warwickshire
Rugby, Warwickshire
Rugby is a market town in Warwickshire, England, located on the River Avon. The town has a population of 61,988 making it the second largest town in the county...
is probably the best exposure of the formation: more than 100 layers can be seen.
Occurrences of Blue Lias can be found in buildings local to its source as well as the local churches and cemeteries (where it is used in tombstones). A prime example of a 'Blue Lias' town would be Street
Street, Somerset
Street is a small village and civil parish in the county of Somerset, England. It is situated on a dry spot in the Somerset Levels, at the end of the Polden Hills, south-west of Glastonbury. The 2001 census records the village as having a population of 11,066...
, near Glastonbury
Glastonbury
Glastonbury is a small town in Somerset, England, situated at a dry point on the low lying Somerset Levels, south of Bristol. The town, which is in the Mendip district, had a population of 8,784 in the 2001 census...
. Other local examples of Blue Lias buildings can be found in the nearby towns of Somerton
Somerton
Somerton is a small town and civil parish in the South Somerset district of the English county of Somerset. It gave its name to the county of Somerset, was briefly, around the start of the 14th century, the county town, and around 900 AD was possibly the capital of Wessex...
& Ilchester
Ilchester
Ilchester is a village and civil parish, situated on the River Yeo or Ivel, five miles north of Yeovil, in the English county of Somerset. The parish, which includes the village of Sock Dennis and the old parish of Northover, has a population of 2,021...
.
It is still popular in more modern-day surroundings where it is still used in the construction of new housing developments and extensions for existing buildings in conservation areas. Blue Lias is mainly used in flooring, walling and paving slabs - both coursed and layered. It is evident too in the making of flagstones
Flagstones
Flagstones is a late Neolithic interrupted ditch enclosure in the English county of Dorset. The enclosure is formed by a ring of pits dug into the chalk bedrock, with 'causeways' between the pits. Half of the enclosure was discovered beneath the site of the demolished Flagstones House in advance...
and cobbles.
There are only three quarries in the country quarrying Blue Lias at present. Ham & Doulting Stone Co Ltd operate one of these, Tout Quarry near Somerton
Somerton
Somerton is a small town and civil parish in the South Somerset district of the English county of Somerset. It gave its name to the county of Somerset, was briefly, around the start of the 14th century, the county town, and around 900 AD was possibly the capital of Wessex...
.
Paleofauna
The rock is rich in fossilFossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
remains from the Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
period. The blue-grey colour is provided by its iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
content, enclosed to a large extent in pyrites.
Dinosaurs
| Dinosaur Dinosaur Dinosaurs are a diverse group of animals of the clade and superorder Dinosauria. They were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates for over 160 million years, from the late Triassic period until the end of the Cretaceous , when the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event led to the extinction of... s of the Blue Lias |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Notes | Images | |
Infraorder:
|
Warwickshire Warwickshire is a landlocked non-metropolitan county in the West Midlands region of England. The county town is Warwick, although the largest town is Nuneaton. The county is famous for being the birthplace of William Shakespeare... , England. |
|
   |
|
Genus:
|
Leicestershire Leicestershire is a landlocked county in the English Midlands. It takes its name from the heavily populated City of Leicester, traditionally its administrative centre, although the City of Leicester unitary authority is today administered separately from the rest of Leicestershire... , England. |
|||
|
Genus:
|
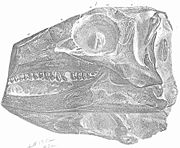
Dorset Dorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974... , England. |
"Nearly complete skull with associated postcrania, articulated postcranial skeleton, partial skull and associated postcrania, juvenile and adult." |
||
Suborder:
|
County Antrim County Antrim is one of six counties that form Northern Ireland, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of 2,844 km², with a population of approximately 616,000... , Northern Ireland. Dorset Dorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974... , England. |
|
||
|
Suborder:
|
County Antrim County Antrim is one of six counties that form Northern Ireland, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of 2,844 km², with a population of approximately 616,000... , Northern Ireland. |
|||
Pterosaurs
| Pterosaur Pterosaur Pterosaurs were flying reptiles of the clade or order Pterosauria. They existed from the late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous Period . Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight... s of the Blue Lias |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Notes | Images | |
Genus:
|
Lyme Regis Lyme Regis is a coastal town in West Dorset, England, situated 25 miles west of Dorchester and east of Exeter. The town lies in Lyme Bay, on the English Channel coast at the Dorset-Devon border... in Dorset, England. |
 |
||

