
Bond order potential
Encyclopedia
Bond order potential is a class of empirical (analytical) potentials used, e.g., in molecular dynamics
and molecular
statics simulations. Examples include the Tersoff
potential, the Brenner potential, the Finnis-Sinclair potentials
and the second-moment tight-binding potentials.
They have the advantage over conventional molecular mechanics
force fields
in that they can, with the same parameters, describe several different bonding states of an atom
, and thus to some extent may be able to describe chemical reaction
s correctly. The potentials were developed partly independently of each other, but share the common idea that the strength of a chemical bond depends on the bonding environment, including the number of bonds and possibly also angles
and bond length
. It is based on the Linus Pauling
bond order
concept
,
and can be written in the form
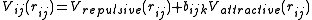
This means that the potential is written as a simple pair potential depending on the distance between two atoms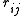 , but the strength
, but the strength
of this bond is modified by the environment of the atom i via the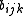 term. Alternatively, the energy
term. Alternatively, the energy
can be written in the form
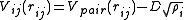
where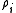 is the electron density
is the electron density
at the location of atom i. These two forms for the energy can be shown to be equivalent.
A more detailed summary of how the bond order concept can be motivated by the second-moment approximation of tight binding and both of these functional forms derived from it can be found in
The original bond order potential concept has been developed further to include distinct bond orders for sigma bonds and pi bonds in the so called BOP potentials.
.
Extending the analytical expression for the bond order of the sigma bonds to include fourth moments of the exact tight binding bond order reveals contributions from both sigma- and pi- bond integrals between neighboring atoms. These pi-bond contributions to the sigma bond order are responsible to stabilize the asymmetric before the symmetric (2x1) dimerized reconstruction of the Si(100) surface.
Also the ReaxFF
potential can be considered a bond order potential, although the motivation of its bond order terms is different from that described here.
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
and molecular
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
statics simulations. Examples include the Tersoff
Jerry Tersoff
Jerry Tersoff is a Research Staff Member at the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center. His work spans diverse topics in the theoretical understanding of surfaces, interfaces, electronic materials, epitaxial growth, and nanoscale devices...
potential, the Brenner potential, the Finnis-Sinclair potentials
and the second-moment tight-binding potentials.
They have the advantage over conventional molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses Newtonian mechanics to model molecular systems. The potential energy of all systems in molecular mechanics is calculated using force fields...
force fields
Force field (chemistry)
In the context of molecular modeling, a force field refers to the form and parameters of mathematical functions used to describe the potential energy of a system of particles . Force field functions and parameter sets are derived from both experimental work and high-level quantum mechanical...
in that they can, with the same parameters, describe several different bonding states of an atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
, and thus to some extent may be able to describe chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
s correctly. The potentials were developed partly independently of each other, but share the common idea that the strength of a chemical bond depends on the bonding environment, including the number of bonds and possibly also angles
Molecular geometry
Molecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It determines several properties of a substance including its reactivity, polarity, phase of matter, color, magnetism, and biological activity.- Molecular geometry determination...
and bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
. It is based on the Linus Pauling
Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling was an American chemist, biochemist, peace activist, author, and educator. He was one of the most influential chemists in history and ranks among the most important scientists of the 20th century...
bond order
Bond order
Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. For example, in diatomic nitrogen N≡N the bond order is 3, while in acetylene H−C≡C−H the bond order between the two carbon atoms is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order gives an indication to the stability of a bond....
concept
,
and can be written in the form
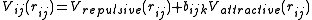
This means that the potential is written as a simple pair potential depending on the distance between two atoms
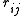 , but the strength
, but the strengthBond strength
In chemistry, bond strength is measured between two atoms joined in a chemical bond. It is the degree to which each atom linked to another atom contributes to the valency of this other atom...
of this bond is modified by the environment of the atom i via the
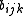 term. Alternatively, the energy
term. Alternatively, the energyEnergy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
can be written in the form
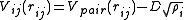
where
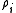 is the electron density
is the electron densityElectron density
Electron density is the measure of the probability of an electron being present at a specific location.In molecules, regions of electron density are usually found around the atom, and its bonds...
at the location of atom i. These two forms for the energy can be shown to be equivalent.
A more detailed summary of how the bond order concept can be motivated by the second-moment approximation of tight binding and both of these functional forms derived from it can be found in
The original bond order potential concept has been developed further to include distinct bond orders for sigma bonds and pi bonds in the so called BOP potentials.
.
Extending the analytical expression for the bond order of the sigma bonds to include fourth moments of the exact tight binding bond order reveals contributions from both sigma- and pi- bond integrals between neighboring atoms. These pi-bond contributions to the sigma bond order are responsible to stabilize the asymmetric before the symmetric (2x1) dimerized reconstruction of the Si(100) surface.
Also the ReaxFF
ReaxFF
ReaxFF is a force field developed by Adri van Duin, William A. Goddard, III and co-workers at the California Institute of Technology for use e.g. in molecular dynamics simulations...
potential can be considered a bond order potential, although the motivation of its bond order terms is different from that described here.

