
Bopomofo
Encyclopedia
Zhuyin fuhao often abbreviated as zhuyin and colloquially called bopomofo, was introduced in the 1910s as the first official phonetic system for transcribing Chinese
, especially Mandarin
.
Consisting of 37 characters and four tone
marks, it transcribes all possible sounds in Mandarin.
Although phased out in Mainland China
in the 1950s, this system is still widely used as an educational tool and Chinese computer input method in Taiwan
.
in mainland China. In official documents, it is occasionally called the "Mandarin Phonetic Symbols I" , abbreviated as the "MPS I" .
In English translations, the system is often called either Chu-yin or the Mandarin Phonetic Symbols. A romanized version of bopomofo, released in 1984, is called MPS II.
, led by Woo Tsin-hang
from 1912 to 1913, created a system called Guóyīn Zìmǔ "National Pronunciation Letters") or Zhùyīn Zìmǔ ( or "Sound-annotating Letters") which is based on Zhang Binglin
's shorthands.
A draft was released on July 11, 1913, by the Republic of China National Ministry of Education, but it was not officially proclaimed until November 23, 1928. zhùyīn zìmǔ was renamed zhùyīn fúhào in April 1930.
The symbols were initially called Zhùyīn Zìmǔ ("Phonetic Alphabet"); later they were also called Guóyīn Zìmǔ ("National Phonetic Alphabet"). The fear that they might be considered an alphabetic system of writing independent of characters led to their being renamed Zhùyīn Fúhào ("Phonetic Symbols") in 1930.
After 1949, bopomofo was superseded in mainland China by the pinyin
system promulgated by the People's Republic of China
, but its use is retained in Taiwan
.
In grade one, Chinese characters in textbooks are often annotated with bopomofo as students take ten weeks to learn them.
In teaching Mandarin, Taiwan institutions and some overseas communities still use bopomofo as a learning tool.
Besides transcribing Chinese, bopomofo is also used as the primary writing system for a few aboriginal languages of Taiwan
, such as Atayal
, Seediq
, Paiwan
, or Tao
. It is sometimes used to annotate Taiwanese Hokkien, a widely spoken Chinese language in Taiwan, however pe̍h-ōe-jī romanization is more common in use.
, and mainly taken from "regularized
" forms of ancient Chinese characters, the modern readings of which contain the sound that each letter represents.
The zhuyin characters are represented in typographic fonts
as if drawn with an ink brush (as in Regular Script
). They are encoded in Unicode in the bopomofo block, in the range U+3105 ... U+312D.
The tone marks used in Bopomofo for the second, third, and fourth tones are the same as the ones used in Hanyu Pinyin. In Bopomofo, no marker is used for the first tone and a dot denotes the neutral tone, whereas in Pinyin, a dash (¯) represents the first tone and no marker is used for the neutral tone.
Bopomofo, when used in conjunction with Chinese characters, are typically placed to the right of the Chinese character vertically or to the top of the Chinese character in a horizontal print (see Ruby character
).
Below is an example for the word "bottle" :
are based on the same Mandarin pronunciations, hence there is a 1-to-1 correspondence between the two systems. In the table below, the 'bopomofo' and 'pinyin' columns show equivalency.
A comparison between pinyin
and bopomofo for Standard Chinese
can also be done by comparing the transcription of various syllables at Comparison of Chinese Phonetic Systems.
Another comparison table

.
Three letters formerly used in non-standard dialects of Mandarin are now also used to write other Chinese languages. Some bopomofo fonts do not contain these letters; see External links for PDF
pictures.
In addition, diacritics were used to create new letters for Min-nan and Hakka.
 Bopomofo can be used as an input method
Bopomofo can be used as an input method
for Chinese characters. It is one of the few input methods that can be found on most modern personal computers without the user having to download or install any additional software. It is also one of the few input methods that can be used for inputting Chinese characters on certain cell phones.

Standard in October, 1991 with the release of version 1.0.
The Unicode block for Bopomofo is U+3100 ... U+312F:
Extended Bopomofo was added to the Unicode Standard in September, 1999 with the release of version 3.0.
The Unicode block for Extended Bopomofo is U+31A0 ... U+31BF:
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
, especially Mandarin
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese, or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
.
Consisting of 37 characters and four tone
Tone (linguistics)
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or inflect words. All verbal languages use pitch to express emotional and other paralinguistic information, and to convey emphasis, contrast, and other such features in what is called...
marks, it transcribes all possible sounds in Mandarin.
Although phased out in Mainland China
Mainland China
Mainland China, the Chinese mainland or simply the mainland, is a geopolitical term that refers to the area under the jurisdiction of the People's Republic of China . According to the Taipei-based Mainland Affairs Council, the term excludes the PRC Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and...
in the 1950s, this system is still widely used as an educational tool and Chinese computer input method in Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
.
Name
Zhuyin is often called bopomofo whose name is derived from the first four letters of the system and occasionally used to refer to pinyinPinyin
Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into...
in mainland China. In official documents, it is occasionally called the "Mandarin Phonetic Symbols I" , abbreviated as the "MPS I" .
In English translations, the system is often called either Chu-yin or the Mandarin Phonetic Symbols. A romanized version of bopomofo, released in 1984, is called MPS II.
History
The Commission on the Unification of PronunciationCommission on the Unification of Pronunciation
The Commission on the Unification of Pronunciation was established in the Republic of China from 1912 to 1913 to select ancillary phonetic symbols for Mandarin, and set the standard Guoyu pronunciation of basic Chinese characters.- History :It was decided in a draft on August 7, 1912, a month...
, led by Woo Tsin-hang
Woo Tsin-hang
Woo Tsin-hang , born Wu Tiao , with the courtesy name Chih-hui , was a Chinese linguist and philosopher who was the chairman of the 1912–13 Commission on the Unification of Pronunciation that created Zhuyin and standardized Guoyu pronunciation.Woo Tsin-hang was born in Wujin ,...
from 1912 to 1913, created a system called Guóyīn Zìmǔ "National Pronunciation Letters") or Zhùyīn Zìmǔ ( or "Sound-annotating Letters") which is based on Zhang Binglin
Zhang Binglin
Zhang Binglin was a Chinese philologist, textual critic and anti-Manchu revolutionary.His philological works include Wen Shi , the first systematic work of Chinese etymology...
's shorthands.
A draft was released on July 11, 1913, by the Republic of China National Ministry of Education, but it was not officially proclaimed until November 23, 1928. zhùyīn zìmǔ was renamed zhùyīn fúhào in April 1930.
The symbols were initially called Zhùyīn Zìmǔ ("Phonetic Alphabet"); later they were also called Guóyīn Zìmǔ ("National Phonetic Alphabet"). The fear that they might be considered an alphabetic system of writing independent of characters led to their being renamed Zhùyīn Fúhào ("Phonetic Symbols") in 1930.
After 1949, bopomofo was superseded in mainland China by the pinyin
Pinyin
Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into...
system promulgated by the People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, but its use is retained in Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
.
Modern use
Bopomofo remains the predominant phonetic system in teaching reading and writing in elementary school in Taiwan. It is also one of the most popular ways to enter Chinese characters into computers and look up characters in a dictionary in Taiwan.In grade one, Chinese characters in textbooks are often annotated with bopomofo as students take ten weeks to learn them.
In teaching Mandarin, Taiwan institutions and some overseas communities still use bopomofo as a learning tool.
Besides transcribing Chinese, bopomofo is also used as the primary writing system for a few aboriginal languages of Taiwan
Formosan languages
The Formosan languages are the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Taiwanese aborigines currently comprise about 2% of the island's population. However, far fewer can still speak their ancestral language, after centuries of language shift...
, such as Atayal
Atayal language
The Atayal language is spoken by the Atayal people of Taiwan. Squliq and C’uli’ are two major dialects...
, Seediq
Seediq language
Seediq is an Atayalic language spoken in the mountains of Northern Taiwan by the Seediq and Truku people. There are 4,750 speakers out of a total of 25,000 ethnic members .-Subdivisions:Seediq consists of three main dialects...
, Paiwan
Paiwan language
Paiwan is a native language of Taiwan, spoken by the Paiwan people, one tribe of the Taiwanese aborigines. Paiwan is a Formosan language of the Austronesian language family...
, or Tao
Tao people
The Tao , originally recognized as Yami , are a Taiwanese aboriginal people, native to tiny outlying Orchid Island in Taiwan. The Tao are an Austronesian people linguistically and culturally closer to the Ivatan people of the Batanes islands in the Philippines than to other aboriginal peoples on...
. It is sometimes used to annotate Taiwanese Hokkien, a widely spoken Chinese language in Taiwan, however pe̍h-ōe-jī romanization is more common in use.
Etymology
The zhuyin letters were created by Zhang BinglinZhang Binglin
Zhang Binglin was a Chinese philologist, textual critic and anti-Manchu revolutionary.His philological works include Wen Shi , the first systematic work of Chinese etymology...
, and mainly taken from "regularized
Regular script
Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 , 楷体 and 正書 , is the newest of the Chinese script styles Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 (zhēnshū), 楷体 (kǎitǐ) and 正書 (zhèngshū), is the newest of the Chinese script styles Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 (zhēnshū), 楷体 (kǎitǐ) and 正書 (zhèngshū), is...
" forms of ancient Chinese characters, the modern readings of which contain the sound that each letter represents.
| Zhuyin | | Pinyin | |Origin |
|---|---|---|
| b | From , the ancient form and current top portion of bāo | |
| p | From , the combining form of pū | |
| m | From , the archaic character and current radical mì | |
| f | From fāng | |
| d | From the archaic form of dāo. Compare the bamboo form  . . |
|
| t | From the upside-down seen at the top of | |
| n | From  /, ancient form of nǎi /, ancient form of nǎi |
|
| l | From the archaic form of lì | |
| g | From the obsolete character guì/kuài" 'river' | |
| k | From the archaic character kǎo | |
| h | From the archaic character and current radical hàn | |
| j | From the archaic character jiū | |
| q | From the archaic character quǎn, graphic root of the character chuān (modern ) | |
| x | From , an ancient form of xià. | |
| zh | From 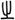 /, archaic form of zhī. /, archaic form of zhī. |
|
| ch | From the character and radical chì | |
| sh | From the character shī | |
| r | Modified from the seal script form of rì | |
| z | From the archaic character and current radical jié, dialectically zié | |
| c | Variant of qī, dialectically ciī. Compare semi-cursive form  and seal-script and seal-script 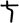 . . |
|
| s | From the archaic character sī, which was later replaced by its compound sī. | |
| i, y | From yī | |
| u, w | From , ancient form of wǔ. | |
| ü, yu | From the ancient character qū, which remains as a radical | |
| a | From yā | |
| o | From the obsolete character hē, inhalation, the reverse of kǎo, which is preserved as a phonetic in the compound kě. | |
| e | Derived from its allophone in Standard Chinese, o | |
| ê | From yě. Compare the Warring States bamboo form 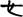 |
|
| ai | From hài, bronze form of . | |
| ei | From yí, an obsolete character meaning yí "to move". | |
| ao | From yāo | |
| ou | From yòu | |
| an | From the obsolete character hàn "to bloom", preserved as a phonetic in the compound fàn | |
| en | From yǐn | |
| ang | From wāng | |
| eng | From , an obsolete form of gōng | |
| er | From , the bottom portion of ér used as a cursive form | |
(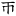 , and inverted ) Perhaps , in addition to . It is the minimal vowel of , , , , , , that is spelled "ih" in Tongyong Pinyin and Wade-Giles and "i" in pinyin. , and inverted ) Perhaps , in addition to . It is the minimal vowel of , , , , , , that is spelled "ih" in Tongyong Pinyin and Wade-Giles and "i" in pinyin. |
The zhuyin characters are represented in typographic fonts
Typeface
In typography, a typeface is the artistic representation or interpretation of characters; it is the way the type looks. Each type is designed and there are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly....
as if drawn with an ink brush (as in Regular Script
Regular script
Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 , 楷体 and 正書 , is the newest of the Chinese script styles Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 (zhēnshū), 楷体 (kǎitǐ) and 正書 (zhèngshū), is the newest of the Chinese script styles Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 (zhēnshū), 楷体 (kǎitǐ) and 正書 (zhèngshū), is...
). They are encoded in Unicode in the bopomofo block, in the range U+3105 ... U+312D.
Stroke order
Bopomofo is written in the same stroke order rule as Chinese characters. Note that ㄖ is written with three strokes, unlike the character from which it is derived (日, Hanyu Pinyin: rì), which has four strokes.Tonal marks
| Tone Tone number A tone number is a numeral used in a notational system for marking the tones of a language. The number is usually placed after the romanized syllable. Notice that a number may have very different meanings in different contexts since the systems may have developed independently.Other means of... |
bopomofo | Pinyin |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| short | none |
The tone marks used in Bopomofo for the second, third, and fourth tones are the same as the ones used in Hanyu Pinyin. In Bopomofo, no marker is used for the first tone and a dot denotes the neutral tone, whereas in Pinyin, a dash (¯) represents the first tone and no marker is used for the neutral tone.
Alignment
Unlike bopomofo, Hanyu Pinyin does not align well with the hanzi characters in books whose texts are printed vertically, making bopomofo better suited for annotating the pronunciation of vertically oriented Chinese text.Bopomofo, when used in conjunction with Chinese characters, are typically placed to the right of the Chinese character vertically or to the top of the Chinese character in a horizontal print (see Ruby character
Ruby character
are small, annotative glosses that can be placed above or to the right of a Chinese character when writing languages with logographic characters such as Chinese or Japanese to show the pronunciation...
).
Below is an example for the word "bottle" :
| EWLINE |
or | EWLINE |
Comparison
Bopomofo and pinyinPinyin
Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into...
are based on the same Mandarin pronunciations, hence there is a 1-to-1 correspondence between the two systems. In the table below, the 'bopomofo' and 'pinyin' columns show equivalency.
- 【】represents the form used in combination with other letters.
A comparison between pinyin
Pinyin
Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into...
and bopomofo for Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese, or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
can also be done by comparing the transcription of various syllables at Comparison of Chinese Phonetic Systems.
| Initials | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bopomofo | Hanyu Pinyin | Tongyong Pinyin | Wade-Giles | Example (Bopomofo, Pinyin) |
| ㄅ | b | b | p | 八 (ㄅㄚ, bā) |
| ㄆ | p | p | p' | 杷 (ㄆㄚˊ, pá) |
| ㄇ | m | m | m | 馬 (ㄇㄚˇ, mǎ) |
| ㄈ | f | f | f | 法 (ㄈㄚˇ, fǎ) |
| ㄉ | d | d | t | 地 (ㄉㄧˋ, dì) |
| ㄊ | t | t | t' | 提 (ㄊㄧˊ, tí) |
| ㄋ | n | n | n | 你 (ㄋㄧˇ, nǐ) |
| ㄌ | l | l | l | 利 (ㄌㄧˋ, lì) |
| ㄍ | g | g | k | 告 (ㄍㄠˋ, gào) |
| ㄎ | k | k | k' | 考 (ㄎㄠˇ, kǎo) |
| ㄏ | h | h | h | 好 (ㄏㄠˇ, hǎo) |
| ㄐ | j | j | ch | 叫 (ㄐㄧㄠˋ, jiào) |
| ㄑ | q | c | ch' | 巧 (ㄑㄧㄠˇ, qiǎo) |
| ㄒ | x | s | hs | 小 (ㄒㄧㄠˇ, xiǎo) |
| ㄓ | zhi 【zh】 | jhih 【jh】 | chih 【ch】 | 主 (ㄓㄨˇ, zhǔ) |
| ㄔ | chi 【ch】 | chih 【ch】 | ch'ih 【ch'】 | 出 (ㄔㄨ, chū) |
| ㄕ | shi 【sh】 | shih 【sh】 | shih 【sh】 | 束 (ㄕㄨˋ, shù) |
| ㄖ | ri 【r】 | rih 【r】 | jih 【j】 | 入 (ㄖㄨˋ, rù) |
| ㄗ | zi 【z】 | zih 【z】 | tzû 【ts】 | 在 (ㄗㄞˋ, zài) |
| ㄘ | ci 【c】 | cih 【c】 | tz'û 【ts'】 | 才 (ㄘㄞˊ, cái) |
| ㄙ | si 【s】 | sih 【s】 | ssû 【s】 | 塞 (ㄙㄞ, sāi) |
| Finals | ||||
| Bopomofo | Hanyu Pinyin | Tongyong Pinyin | Wade-Giles | Example(Bopomofo, Hanyu) |
| ㄚ | a | a | a | 大 (ㄉㄚˋ, dà) |
| ㄛ | o | o | o | 多 (ㄉㄨㄛ, duō) |
| ㄜ | e | e | e | 得 (ㄉㄜˊ, dé) |
| ㄝ | ê | e | eh | 爹 (ㄉㄧㄝ, diē) |
| ㄞ | ai | ai | ai | 晒 (ㄕㄞˋ, shài) |
| ㄟ | ei | ei | ei | 誰 (ㄕㄟˊ, shéi) |
| ㄠ | ao | ao | ao | 少 (ㄕㄠˇ, shǎo) |
| ㄡ | ou | ou | ou | 收 (ㄕㄡ, shōu) |
| ㄢ | an | an | an | 山 (ㄕㄢ, shān) |
| ㄣ | en | en | en | 申 (ㄕㄣ, shēn) |
| ㄤ | ang | ang | ang | 上 (ㄕㄤˋ, shàng) |
| ㄥ | eng | eng | eng | 生 (ㄕㄥ, shēng) |
| ㄦ | er | er | erh | 而 (ㄦˊ, ér) |
| ㄧ | yi 【i】 | yi 【i】 | yi 【i】 | 逆 (ㄋㄧˋ, nì) |
| ㄧㄣ | yin 【in】 | yin 【in】 | yin 【in】 | 音 (ㄧㄣ, yīn) |
| ㄧㄥ | ying 【ing】 | ying 【ing】 | ying 【ing】 | 英 (ㄧㄥ, yīng) |
| ㄨ | wu 【u】 | wu 【u】 | wu 【u】 | 努 (ㄋㄨˇ, nǔ) |
| ㄨㄣ | wen 【un】 | wun 【un】 | wen 【un】 | 文 (ㄨㄣˊ, wén) |
| ㄨㄥ | weng 【ong】 | wong 【ong】 | ng 【ung】 | 翁 (ㄨㄥ, wēng) |
| ㄩ | yu 【u, ü】 | yu 【u, yu】 | yü 【ü】 | 女 (ㄋㄩˇ, nǚ) |
| ㄩㄣ | yun 【un】 | yun 【un, yun】 | yün 【ün】 | 韻 (ㄩㄣˋ, yūn) |
| ㄩㄥ | yong 【iong】 | yong | yung 【iung】 | 永 (ㄩㄥˇ, yǒng) |
Another comparison table

Other languages
Zhuyin is used to write several varieties of Chinese, as well as some Formosan languagesFormosan languages
The Formosan languages are the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Taiwanese aborigines currently comprise about 2% of the island's population. However, far fewer can still speak their ancestral language, after centuries of language shift...
.
Three letters formerly used in non-standard dialects of Mandarin are now also used to write other Chinese languages. Some bopomofo fonts do not contain these letters; see External links for PDF
Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
pictures.
| Char | Pinyin |
|---|---|
| ㄪ | v |
| ㄫ | ng |
| ㄬ | ny |
In addition, diacritics were used to create new letters for Min-nan and Hakka.
| Char | Pinyin | Char | Pinyin | Char | Pinyin | Char | Pinyin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ㆠ( ) ) |
bb* | ㆦ(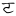 ) ) |
oo ɔ | ㆬ(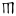 ) ) |
syllabic m | ㆲ( ) ) |
ong | |||
ㆡ(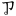 ) ) |
zz* | ㆧ(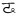 ) ) |
onn [õ] | ㆭ(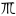 ) ) |
syllabic ng | ㆳ(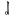 ) ) |
innn | |||
ㆢ(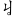 ) ) |
jj* | ㆨ( ) ) |
ir ɨ | ㆮ(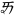 ) ) |
ainn [aĩ] | ㆴ(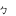 ) ) |
Final p | |||
ㆣ( ) ) |
gg* | ㆩ( ) ) |
ann [ã] | ㆯ( ) ) |
aunn [aũ] | ㆵ(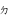 ) ) |
Final t | |||
ㆤ(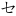 ) ) |
ee [e] | ㆪ() | inn [ĩ] | ㆰ( ) ) |
am | ㆶ(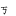 ) ) |
Final k | |||
ㆥ(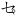 ) ) |
enn [ẽ] | ㆫ(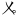 ) ) |
unn [ũ] | ㆱ( ) ) |
om | ㆷ(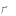 ) ) |
Final h ʔ |
| Char | Tone Value | Unicode |
|---|---|---|
| ˪ (└) | Chao number "11", depicts 低平"low, level tone" (陰去聲 "upper departing") in Taiwanese Minnan | U+02EA |
| ˫ (├) | Chao number "33", depicts 平"mid, level tone" (陽去聲 "lower departing") in Taiwanese Minnan | U+02EB |
Input method

Input method
An input method is an operating system component or program that allows any data, such as keyboard strokes or mouse movements, to be received as input. In this way users can enter characters and symbols not found on their input devices...
for Chinese characters. It is one of the few input methods that can be found on most modern personal computers without the user having to download or install any additional software. It is also one of the few input methods that can be used for inputting Chinese characters on certain cell phones.

Unicode
Bopomofo was added to the UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
Standard in October, 1991 with the release of version 1.0.
The Unicode block for Bopomofo is U+3100 ... U+312F:
Extended Bopomofo was added to the Unicode Standard in September, 1999 with the release of version 3.0.
The Unicode block for Extended Bopomofo is U+31A0 ... U+31BF:
See also
- FuriganaFuriganais a Japanese reading aid, consisting of smaller kana, or syllabic characters, printed next to a kanji or other character to indicate its pronunciation. In horizontal text, yokogaki, they are placed above the line of text, while in vertical text, tategaki, they are placed to the right of the line...
- Zhuyin tableZhuyin tableThis bopomofo table is a complete listing of all Zhuyin/Bopomofo syllables used in Standard Chinese. Each syllable in a cell is composed of an initial and a final . An empty cell indicates that the corresponding syllable does not exist in Standard Chinese.Finals are grouped into subsets ㄚ, ㄧ, ㄨ...
- Chinese languageChinese languageThe Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
- Mandarin Chinese
- Standard ChineseStandard ChineseStandard Chinese, or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
- PinyinPinyinPinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into...
- Chinese input methods for computersChinese input methods for computersHundreds of Chinese input methods are available for entry of Chinese characters into computers, but most keyboard-based methods rely on either pinyin phonetic readings or root shapes in Chinese characters...
- Ruby characterRuby characterare small, annotative glosses that can be placed above or to the right of a Chinese character when writing languages with logographic characters such as Chinese or Japanese to show the pronunciation...
- Taiwanese Hokkien
- Written HokkienWritten HokkienHokkien, a Min Nan variety of Chinese spoken in Southeastern China, Taiwan and Southeast Asia, does not have a standardized writing system, in comparison with the well-developed written forms of Cantonese and Mandarin. Since there is no official standardizing body for Hokkien, there are a wide...
- FanqieFanqièIn Chinese phonology, fanqie is a method to indicate the pronunciation of a character by using two other characters.-The Origin:...
External links
- UnicodeUnicodeUnicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
reference glyphs for and - Bopomofo annotations – adds inline and pop-up annotations with bopomofo pronunciation and English definitions to Chinese text or web pages.
- Mandarin Dictionary – needs Chinese font for Big5Big5Big-5 or Big5 is a character encoding method used in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau for Traditional Chinese characters.Mainland China, which uses Simplified Chinese Characters, uses the GB instead.- Organization :...
encoding - Chinese Phonetic Conversion Tool – converts between Pinyin, Zhuyin and other phonetic systems
- Chinese Romanization Converter – converts between Hanyu Pinyin, Wade-Giles, Gwoyeu Romatzyh and other known or (un-)common Romanization systems
- Bopomofo -> Wade-Giles -> Pinyin -> Word List
- NPA->IPA National Phonetic Alphabet (bopomofo) spellings of words transliterated into the International Phonetic Alphabet. The vowel values have been verified against the official IPA site. See IPA help preview, SIL International website. See IPA help preview, SIL International website. (Accessed 23-12-2010).
- Bopomofo to Pinyin converter and reverse
- bopomofo syllable chart, with Hanyu Pinyin equivalents
- Pinyin Annotator – adds bopomofo (bopomofo) or pinyin on top of any Chinese text, prompts alternative pronunciations to homonyms, has the option of exporting into OpenOffice Writer for further editing
- 《請利用螢幕上的小鍵盤輸入注音符號》 – online keyboard for bopomofo which can turn it into Chinese characters
- Online Zhuyin-Bopomofo Input Method Editor 免费在线中文输入法,使用注音

