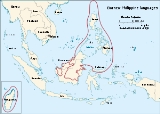
Borneo-Philippines languages
Encyclopedia
The Borneo–Philippines languages are a paraphyletic group of the Austronesian languages
which includes the languages of the Philippines
, Borneo
, the northern peninsula of Sulawesi
and Madagascar
.
In this classification, the previously posited clade of Western Malayo-Polynesian, also known as Hesperonesian, has been broken up into "outer" (Borneo–Philippines) and "inner" (Sunda–Sulawesi) clades and Western Malayo-Polynesian is considered a geographic term . These are both remnant groups: the Borneo–Philippine languages are those Malayo-Polynesian languages which are not included in Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian
and the Sunda–Sulawesi languages are those Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian languages which are not included in Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian. Indeed, a 2008 analysis of the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database supported at a 98% confidence level that the Bornean languages
, regardless of whether they themselves are a valid unit, form an exclusive unit with Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian, whereas Sama–Bajaw is more closely related to the Philippine languages.
Austronesian languages
The Austronesian languages are a language family widely dispersed throughout the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific, with a few members spoken on continental Asia that are spoken by about 386 million people. It is on par with Indo-European, Niger-Congo, Afroasiatic and Uralic as one of the...
which includes the languages of the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
, the northern peninsula of Sulawesi
Sulawesi
Sulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
and Madagascar
Madagascar
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean off the southeastern coast of Africa...
.
In this classification, the previously posited clade of Western Malayo-Polynesian, also known as Hesperonesian, has been broken up into "outer" (Borneo–Philippines) and "inner" (Sunda–Sulawesi) clades and Western Malayo-Polynesian is considered a geographic term . These are both remnant groups: the Borneo–Philippine languages are those Malayo-Polynesian languages which are not included in Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian
Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian languages are a branch of the Austronesian family, proposed by Wouk & Ross , that are thought to have dispersed from a possible homeland in Sulawesi. They are called nuclear because they are the conceptual core of the Malayo-Polynesian family, including both Malay and...
and the Sunda–Sulawesi languages are those Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian languages which are not included in Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian. Indeed, a 2008 analysis of the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database supported at a 98% confidence level that the Bornean languages
Bornean languages
The Bornean languages are the Austronesian language families indigenous to the island of Borneo, with the exclusion of Ibanic and other Malayic languages....
, regardless of whether they themselves are a valid unit, form an exclusive unit with Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian, whereas Sama–Bajaw is more closely related to the Philippine languages.

