
Boxing the compass
Encyclopedia

Compass
A compass is a navigational instrument that shows directions in a frame of reference that is stationary relative to the surface of the earth. The frame of reference defines the four cardinal directions – north, south, east, and west. Intermediate directions are also defined...
in clockwise order. Such names are formed by the initials of the cardinal direction
Cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions or cardinal points are the directions of north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials: N, E, S, W. East and west are at right angles to north and south, with east being in the direction of rotation and west being directly opposite. Intermediate...
s and their intermediate ordinal directions, and are very handy to refer to a heading
Heading
Heading can refer to:*Heading , a process which incorporates the extruding and upsetting processes*Headline, text at the top of a newspaper article*The direction a person or vehicle is facing, usually similar to its course...
(or course
Course (navigation)
In navigation, a vehicle's course is the angle that the intended path of the vehicle makes with a fixed reference object . Typically course is measured in degrees from 0° clockwise to 360° in compass convention . Course is customarily expressed in three digits, using preliminary zeros if needed,...
or azimuth) in a general or colloquial
Colloquialism
A colloquialism is a word or phrase that is common in everyday, unconstrained conversation rather than in formal speech, academic writing, or paralinguistics. Dictionaries often display colloquial words and phrases with the abbreviation colloq. as an identifier...
fashion, without having to resort to computing or recalling degrees. For most applications, the minor points have been superseded by degrees measured clockwise from North.
Compass points
| # | Compass point | Abbr. | Traditional wind point | Lowest | Middle | Highest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | North | N | Tramontana Tramontana Tramontana or Tramontane can refer to:*Tramontane, a northern wind *the Pole Star*Tramontane, a science fiction novel by Emil Petaja... |
0.00° | 5.62° | |
| 2 | North by east | NbE | Qto Tramontana verso Greco | 5.63° | 11.25° | 16.87° |
| 3 | North-northeast | NNE | Greco-Tramontana | 16.88° | 22.50° | 28.12° |
| 4 | Northeast by north | NEbN | Qto Greco verso Tramontana | 28.13° | 33.75° | 39.37° |
| 5 | Northeast | NE | Greco Gregale The Gregale is a Mediterranean wind that can occur during times when a low pressure area moves through the area to the south of Malta and causes a strong, cool, northeasterly wind to affect the island... |
39.38° | 45.00° | 50.62° |
| 6 | Northeast by east | NEbE | Qto Greco verso Levante | 50.63° | 56.25° | 61.87° |
| 7 | East-northeast | ENE | Greco-Levante | 61.88° | 67.50° | 73.12° |
| 8 | East by north | EbN | Qto Levante verso Greco | 73.13° | 78.75° | 84.37° |
| 9 | East | E | Levante Levant (wind) The levant is an easterly wind that blows in the western Mediterranean Sea and southern France, an example of mountain-gap wind. In Roussillon it is called "llevant" and in Corsica "levante"... |
84.38° | 90.00° | 95.62° |
| 10 | East by south | EbS | Qto Levante verso Scirocco | 95.63° | 101.25° | 106.87° |
| 11 | East-southeast | ESE | Levante-Scirocco | 106.88° | 112.50° | 118.12° |
| 12 | Southeast by east | SEbE | Qto Scirocco verso Levante | 118.13° | 123.75° | 129.37° |
| 13 | Southeast | SE | Scirocco Sirocco Sirocco, scirocco, , jugo or, rarely, siroc is a Mediterranean wind that comes from the Sahara and reaches hurricane speeds in North Africa and Southern Europe. It is known in North Africa by the Arabic word qibli or ghibli Sirocco, scirocco, , jugo or, rarely, siroc is a Mediterranean wind... |
129.38° | 135.00° | 140.62° |
| 14 | Southeast by south | SEbS | Qto Scirocco verso Ostro | 140.63° | 146.25° | 151.87° |
| 15 | South-southeast | SSE | Ostro-Scirocco | 151.88° | 157.50° | 163.12° |
| 16 | South by east | SbE | Qto Ostro verso Scirocco | 163.13° | 168.75° | 174.37° |
| 17 | South | S | Ostro Ostro Ostro is the traditional Italian name of a southerly wind in the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Adriatic. Its name is derived from the Latin name Auster, which also meant a southerly wind and is part of the etymology of Australia... |
174.38° | 180.00° | 185.62° |
| 18 | South by west | SbW | Qto Ostro verso Libeccio | 185.63° | 191.25° | 196.87° |
| 19 | South-southwest | SSW | Ostro-Libeccio | 196.88° | 202.50° | 208.12° |
| 20 | Southwest by south | SWbS | Qto Libeccio verso Ostro | 208.13° | 213.75° | 219.37° |
| 21 | Southwest | SW | Libeccio Libeccio The libeccio is the westerly or south-westerly wind which predominates in northern Corsica all year round; it frequently raises high seas and may give violent westerly squalls. In summer it is most persistent, but in winter it alternates with the Tramontane... |
219.38° | 225.00° | 230.62° |
| 22 | Southwest by west | SWbW | Qto Libeccio verso Ponente | 230.63° | 236.25° | 241.87° |
| 23 | West-southwest | WSW | Ponente-Libeccio | 241.88° | 247.50° | 253.12° |
| 24 | West by south | WbS | Qto Ponente verso Libeccio | 253.13° | 258.75° | 264.37° |
| 25 | West | W | Ponente | 264.38° | 270.00° | 275.62° |
| 26 | West by north | WbN | Qto Ponente verso Maestro | 275.63° | 281.25° | 286.87° |
| 27 | West-northwest | WNW | Maestro-Ponente | 286.88° | 292.50° | 298.12° |
| 28 | Northwest by west | NWbW | Qto Maestro verso Ponente | 298.13° | 303.75° | 309.37° |
| 29 | Northwest | NW | Maestro Mistral (wind) The mistral is a strong, cold and usually dry regional wind in France, coming from the north or northwest, which accelerates when it passes through the valleys of the Rhone and the Durance Rivers to the coast of the Mediterranean around the Camargue region. It affects the northeast of the plain... |
309.38° | 315.00° | 320.62° |
| 30 | Northwest by north | NWbN | Qto Maestro verso Tramontana | 320.63° | 326.25° | 331.87° |
| 31 | North-northwest | NNW | Maestro-Tramontana | 331.88° | 337.50° | 343.12° |
| 32 | North by west | NbW | Qto Tramontana verso Maestro | 343.13° | 348.75° | 354.37° |
| 1 | North | N | Tramontana Tramontane Tramontane is a classical name for a northern wind. The exact form of the name and precise direction varies from country to country. The word came to English from Italian tramontana, which developed from Latin trānsmontānus , "beyond the mountains/across the mountains", referring to the alps in... |
354.38° | 360.00° |
A simple algorithm can be used to convert a heading (range: 0° to 360°) to an approximate compass point:
- Divide the heading in degrees by 11.25 (360°/32) to get to the case of 32 named points (range: 0 to 32).
- Add 1.5 to center the named points in their respective sectors on the circle (range: 1.5 to 33.5).
- If the result is 33 or more, subtract 32Modular arithmeticIn mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" after they reach a certain value—the modulus....
to keep within the 32-point set (range: 1 to 32.999...). - Now look up the integer part of the result in the table above.
For example:
A heading of 75°, divided by 11.25 gives 6.67, added to 1.5 gives 8.17, truncated
Truncation
In mathematics and computer science, truncation is the term for limiting the number of digits right of the decimal point, by discarding the least significant ones.For example, consider the real numbersThe result would be:- Truncation and floor function :...
to give 8. 8 in the table above corresponds to east by north.
Compass point names

- The cardinal direction
Cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions or cardinal points are the directions of north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials: N, E, S, W. East and west are at right angles to north and south, with east being in the direction of rotation and west being directly opposite. Intermediate...
s are North (N), East (E), South (S), West (W), at 90° angles on the compass rose.
- The ordinal directions are Northeast (NE), Southeast (SE), Southwest (SW) and Northwest (NW), formed by bisecting the angle of the cardinal winds. The name is merely a combination of the cardinals it bisects.
- The eight principal winds (or main winds) are the cardinals and ordinals considered thogether, that is N, NE, E, SE, S, SW, W, NW. Each principal wind is 45° from its neighbor. The principal winds form the basic eight-wind compass rose.
- The eight half-winds are the points obtained by bisecting the angles between the principal winds. The half-winds are North-northeast (NNE), East-northeast (ENE), East-southeast (ESE), South-southeast (SSE), South-southwest (SSW), West-southwest (WSW), West-northwest (WNW) and North-northwest (NNW). Notice that the name is constructed simply by combining the names of the principal winds to either side, with the cardinal wind coming first, the ordinal wind second. The eight principal winds and the eight half-winds together yield a 16-wind compass rose, with each compass point at a 22° angle from the next.
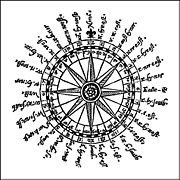
The eight principal winds, eight half-winds and sixteen quarter winds together yield a 32-wind compass rose, with each compass direction point at 11° angle from the next.
The name of a quarter-wind is typically "X by Y", where X and Y are principal winds (never half-winds). As a mnemonic device, it is useful to think of "X by Y" as a shortcut for the phrase "one quarter wind from X towards Y", where a "quarter" is 11°, X is the nearest principal wind, and Y the next (more distant) principal wind. So "Northeast by east" means "one quarter from NE towards E", "Southwest by south" means "one quarter from SW towards S". There is, however, an important exception to this rule: namely, that if the first name is a cardinal wind (N, E, S, W), then a quarter wind away from it is expressed as being towards the next cardinal wind (rather than the next principal wind). So one quarter away from North towards the direction of Northwest is expressed as "North by west", and not "North by northwest". (Thus the title of the famous Alfred Hitchcock
Alfred Hitchcock
Sir Alfred Joseph Hitchcock, KBE was a British film director and producer. He pioneered many techniques in the suspense and psychological thriller genres. After a successful career in British cinema in both silent films and early talkies, Hitchcock moved to Hollywood...
1959 movie, North by Northwest
North by Northwest
North by Northwest is a 1959 American thriller film directed by Alfred Hitchcock, starring Cary Grant, Eva Marie Saint and James Mason, and featuring Leo G. Carroll and Martin Landau...
, is actually not a direction point on the 32-wind compass.)
Traditional names
The traditional compass roseCompass rose
A compass rose, sometimes called a windrose, is a figure on a compass, map, nautical chart or monument used to display the orientation of the cardinal directions — North, East, South and West - and their intermediate points. It is also the term for the graduated markings found on the traditional...
of eight winds (and its 16-wind and 32-wind derivatives) was invented by seafarers in the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
during the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
(the ancient Greco-Roman 12 Classical compass winds
Classical compass winds
thumb|250px|The [[Tower of the Winds]] in [[Athens]]Classical compass winds refers to the naming and association of winds in Mediterranean classical antiquity with the points of geographic direction and orientation...
have little to do with them). The traditional mariner's wind names were expressed in Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
- or, more precisely, the Italianate Mediterranean lingua franca
Mediterranean Lingua Franca
The Mediterranean Lingua Franca or Sabir was a pidgin language used as a lingua franca in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th century.-History:...
common among sailors in the 13th and 14th C., that was principally composed of Genoese (Ligurian
Ligurian language (Romance)
Ligurian is a Gallo-Romance language spoken in Liguria in Northern Italy, parts of the Mediterranean coastal zone of France, Monaco and in the villages of Carloforte and Calasetta in Sardinia. Genoese , spoken in Genoa, the capital of Liguria, is its most important dialect...
), mixed with Venetian
Venetian language
Venetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken as a native language by over two million people, mostly in the Veneto region of Italy, where of five million inhabitants almost all can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto, in Trentino, Friuli, Venezia...
, Sicilian
Sicilian language
Sicilian is a Romance language. Its dialects make up the Extreme-Southern Italian language group, which are spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands; in southern and central Calabria ; in the southern parts of Apulia, the Salento ; and Campania, on the Italian mainland, where it is...
, Provençal, Catalan
Catalan language
Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island...
, Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
and Arabic terms from around the Mediterranean basin.
This Italianate patois was used to designate the names of the principal winds on the compass rose
Compass rose
A compass rose, sometimes called a windrose, is a figure on a compass, map, nautical chart or monument used to display the orientation of the cardinal directions — North, East, South and West - and their intermediate points. It is also the term for the graduated markings found on the traditional...
found in mariner compass
Compass
A compass is a navigational instrument that shows directions in a frame of reference that is stationary relative to the surface of the earth. The frame of reference defines the four cardinal directions – north, south, east, and west. Intermediate directions are also defined...
es and portolan chart
Portolan chart
Portolan charts are navigational maps based on realistic descriptions of harbours and coasts. They were first made in the 14th century in Italy, Portugal and Spain...
s of the 14th and 15th C. The "traditional" names of the eight principal winds are:
- (N) - Tramontana
- (NW) - Greco (or BoraBora (wind)Bora or Bura is a northern to north-eastern katabatic wind in the Adriatic, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro, Italy, Greece, Slovenia, and Turkey....
in some Venetian sources) - (E) - Levante (sometimes Oriente)
- (SE) - Scirocco (or Exaloc in Catalan)
- (S) - Ostro (or Mezzogiorno in Venetian)
- (SW) - Libeccio (or Garbino, Eissalot in Provençal)
- (W) - Ponente (or Zephyrus in Greek)
- (NW) - Maestro (or Mistral in Provençal)
Local spelling variations are far more numerous than listed, e.g. Tramutana, Gregale, Grecho, Sirocco, Xaloc, Lebeg, Libezo, Leveche, Mezzodi, Migjorn, Magistro, Mestre, etc. Traditional compass roses will typically have the initials T, G, L, S, O, L, P, and M on the main points. Portolan chart
Portolan chart
Portolan charts are navigational maps based on realistic descriptions of harbours and coasts. They were first made in the 14th century in Italy, Portugal and Spain...
s also color-coded the compass winds: black for the eight principal winds, green for the eight half-winds and red for the sixteen quarter-winds.
In the English compass, all wind names are constructed on the basis of the cardinal four names (N, E, S, W). In the traditional compass, one needs to memorize eight basic names - one for each of the eight principal winds. While there are more names to memorize, the payoff is that the name construction rules for the 32-wind compass are more straightforward. The half-winds are just a combination of the two principal winds it bisects, with the shortest name usually coming first (e.g. NNE is "Greco-Tramontana", ENE is "Greco-Levante", SSE is "Ostro-Scirocco", etc.). The quarter winds are phrased "Quarto di X verso Y" (one quarter from X towards Y) or "X al Y" (X to Y) or "X per Y" (X by Y). There are no irregularities to trip over: the nearest principal wind always comes first, the more distant one second, e.g. North-by-east is "Quarto di Tramontana verso Greco", Northeast-by-north "Quarto di Greco verso Tramontana". The names are perfectly symmetric.
See also
- Bearing (navigation)Bearing (navigation)In marine navigation, a bearing is the direction one object is from another object, usually, the direction of an object from one's own vessel. In aircraft navigation, a bearing is the actual compass direction of the forward course of the aircraft...
- Cardinal directionCardinal directionThe four cardinal directions or cardinal points are the directions of north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials: N, E, S, W. East and west are at right angles to north and south, with east being in the direction of rotation and west being directly opposite. Intermediate...
- Compass roseCompass roseA compass rose, sometimes called a windrose, is a figure on a compass, map, nautical chart or monument used to display the orientation of the cardinal directions — North, East, South and West - and their intermediate points. It is also the term for the graduated markings found on the traditional...
- Course (navigation)Course (navigation)In navigation, a vehicle's course is the angle that the intended path of the vehicle makes with a fixed reference object . Typically course is measured in degrees from 0° clockwise to 360° in compass convention . Course is customarily expressed in three digits, using preliminary zeros if needed,...
- HeadingHeadingHeading can refer to:*Heading , a process which incorporates the extruding and upsetting processes*Headline, text at the top of a newspaper article*The direction a person or vehicle is facing, usually similar to its course...
(disambiguation)
- NavigationNavigationNavigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
- Classical compass windsClassical compass windsthumb|250px|The [[Tower of the Winds]] in [[Athens]]Classical compass winds refers to the naming and association of winds in Mediterranean classical antiquity with the points of geographic direction and orientation...
- Ordinal direction
- Wind roseWind roseA wind rose is a graphic tool used by meteorologists to give a succinct view of how wind speed and direction are typically distributed at a particular location. Historically, wind roses were predecessors of the compass rose , as there was no differentiation between a cardinal direction and the wind...
- South by SouthwestSouth by SouthwestSouth by Southwest is an Austin, Texas based company dedicated to planning conferences, trade shows, festivals and other events. Their current roster of annual events include: SXSW Music, SXSW Film, SXSW Interactive, SXSWedu, and SXSWeco and take place every spring in Austin, Texas, United States...
External links
- Wind Rose (Archived) – discusses the origins of the names for compass directions.

