
Bragg Peak
Encyclopedia
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
during its travel through matter. For proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s, α-rays
Alpha particle
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name...
, and other ion rays, the peak occurs immediately before the particles come to rest. This is called Bragg peak, for William Henry Bragg
William Henry Bragg
Sir William Henry Bragg OM, KBE, PRS was a British physicist, chemist, mathematician and active sportsman who uniquely shared a Nobel Prize with his son William Lawrence Bragg - the 1915 Nobel Prize in Physics...
who discovered it in 1903.
When a fast charged particle
Charged particle
In physics, a charged particle is a particle with an electric charge. It may be either a subatomic particle or an ion. A collection of charged particles, or even a gas containing a proportion of charged particles, is called a plasma, which is called the fourth state of matter because its...
moves through matter, it ionizes atoms of the material and deposits a dose
Absorbed dose
Absorbed dose is a measure of the energy deposited in a medium by ionizing radiation per unit mass...
along its path. A peak occurs because the interaction cross section
Cross section (physics)
A cross section is the effective area which governs the probability of some scattering or absorption event. Together with particle density and path length, it can be used to predict the total scattering probability via the Beer-Lambert law....
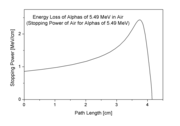
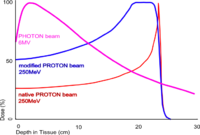
increases as the charged particle's energy decreases. In the upper figure, it is the peak for alpha particles of 5.49 MeV moving through air. In the lower figure, it is the narrow peak of the "native" proton beam curve which is produced by a particle accelerator
Particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and to contain them in well-defined beams. An ordinary CRT television set is a simple form of accelerator. There are two basic types: electrostatic and oscillating field accelerators.In...
of 250 MeV
Electronvolt
In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt...
. The figure also shows the absorption of a beam of energetic photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s (X rays) which is entirely different in nature; the curve is mainly exponential
Exponential function
In mathematics, the exponential function is the function ex, where e is the number such that the function ex is its own derivative. The exponential function is used to model a relationship in which a constant change in the independent variable gives the same proportional change In mathematics,...
.
The phenomenon is exploited in particle therapy
Particle therapy
Particle therapy is a form of external beam radiotherapy using beams of energetic protons, neutrons, or positive ions for cancer treatment. The most common type of particle therapy as of 2009 is proton therapy. Although a photon, used in x-ray or gamma ray therapy, can also be considered a...
of cancer, to concentrate the effect of light ion beam
Ion beam
An ion beam is a type of charged particle beam consisting of ions. Ion beams have many uses in electronics manufacturing and other industries. A variety of ion beam sources exist, some derived from the mercury vapor thrusters developed by NASA in the 1960s.-Ion beam etching or sputtering:One type...
s on the tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
being treated while minimizing the effect on the surrounding healthy tissue. The blue curve in the figure ("modified proton beam
Proton beam
Proton beams, a type of ion beams, are the result of proton particle acceleration by means of a cyclotron or a synchrotron and can be used e.g. in Proton Beam Therapy for cancer treatment or for proton beam writing in lithography....
") shows how the originally monoenergetic proton beam with the sharp peak is widened by increasing the range of energies, so that a larger tumor volume can be treated. This can be achieved by using variable thickness attenuators like spinning wedges.

