Particle therapy
Encyclopedia
Particle therapy is a form of external beam radiotherapy
using beams of energetic proton
s, neutron
s, or positive ion
s for cancer treatment. The most common type of particle therapy as of 2009 is proton therapy
. Although a photon
, used in x-ray
or gamma ray
therapy, can also be considered a particle, photon therapy is not considered here. Additionally, electron therapy
is generally put into its own category. Because of this, particle therapy is sometimes referred to, more correctly, as hadron
therapy (that is, therapy with particles that are made of quark
s).
Muon
therapy has occasionally been attempted; it is a rare type of particle therapy that does not belong to the previously mentioned categories.
of tissue cells, ultimately causing their death. Because of their reduced ability to repair damaged DNA, cancerous cells are particularly vulnerable to attack.
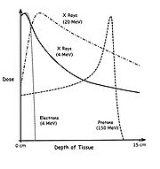
The figure shows how beams of electrons, X-rays or protons of different energies (expressed in MeV) penetrate human tissue. Electrons have a short range and are therefore only of interest close to the skin (see electron therapy
). Bremsstrahlung
X-rays penetrate more deeply, but the dose
absorbed by the tissue then shows the typical exponential decay with increasing thickness. For protons and heavier ions, on the other hand, the dose increases while the particle penetrates the tissue and loses energy
continuously. Hence the dose increases with increasing thickness up to the Bragg peak
that occurs near the end of the particle's range
. Beyond the Bragg peak, the dose drops to zero (for protons) or almost zero (for heavier ions).
The advantage of this energy deposition profile is that less energy is deposited into the healthy tissue surrounding the target tissue.
The ions are first accelerated by means of a cyclotron
or synchrotron
. The final energy of the emerging particle beam defines the depth of penetration, and hence, the location of the maximum energy deposition. Since it is easy to deflect the beam by means of electro-magnets in a transverse direction, it is possible to employ a raster scan
method, i.e., to scan the target area quickly like the electron beam scans a TV tube. If, in addition, the beam energy and hence, the depth of penetration is varied, an entire target volume can be covered in three dimensions, providing an irradiation exactly following the shape of the tumor. This is one of the great advantages compared to conventional x-ray therapy.
At the end of 2008, 28 treatment facilities were in operation worldwide, and over 70000 patients had been treated by means of pion
s, protons and heavier ions worldwide. Most of this therapy has been with protons..
ion
s. Compared to protons, carbon ions have an advantage: due to the higher density of ionisation at the end of their range, correlated damages of the DNA structure within one cell occur more often so that it becomes more difficult for the cancerous cell to repair
the damage. This increases the biological efficiency of the dose by a factor between 1.5 and 3.
Compared to protons, carbon ions have the disadvantage that beyond the Bragg peak, the dose does not decrease to zero, since nuclear reactions between the carbon ions and the atoms of the tissue lead to production of lighter ions which have a higher range. Therefore, some damage occurs also beyond the Bragg peak.
By the end of 2008, more than 5000 patients had been treated using carbon ions.
and the HIBMC at Hyogo. In Germany, treatment at the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung
(GSI) in Darmstadt
, which is primarily a physics laboratory, has been discontinued in 2008, but the new HIT in Heidelberg
, which is a dedicated facility, started in November 2009. The CNAO in Pavia, Italy is going to open in 2011 and will be one of the most advanced centers for particle therapy with hadrons. CNAO will combine precise dose delivery with highly accurate patient alignment based on stereoscopic X-ray imaging. Sophisticated approaches in image-guided particle therapy (IGPT) augments the radiotherapy machines with imaging capabilities and the latest computer vision technology to increase accuracy of target localization and enable patient alignment accuracies of 0.5 mm and better.
External beam radiotherapy
External beam radiotherapy or teletherapy is the most common form of radiotherapy. The patient sits or lies on a couch and an external source of radiation is pointed at a particular part of the body...
using beams of energetic proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s, neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s, or positive ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s for cancer treatment. The most common type of particle therapy as of 2009 is proton therapy
Proton therapy
Proton therapy is a type of particle therapy which uses a beam of protons to irradiate diseased tissue, most often in the treatment of cancer. The chief advantage of proton therapy is the ability to more precisely localize the radiation dosage when compared with other types of external beam...
. Although a photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
, used in x-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
or gamma ray
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
therapy, can also be considered a particle, photon therapy is not considered here. Additionally, electron therapy
Electron therapy
Electron therapy or Electron Beam Therapy is a kind of external beam radiotherapy where electrons are directed to a tumor site.-Equipment:...
is generally put into its own category. Because of this, particle therapy is sometimes referred to, more correctly, as hadron
Hadron
In particle physics, a hadron is a composite particle made of quarks held together by the strong force...
therapy (that is, therapy with particles that are made of quark
Quark
A quark is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. Due to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never directly...
s).
Muon
Muon
The muon |mu]] used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with a unitary negative electric charge and a spin of ½. Together with the electron, the tau, and the three neutrinos, it is classified as a lepton...
therapy has occasionally been attempted; it is a rare type of particle therapy that does not belong to the previously mentioned categories.
Method
Particle therapy works by aiming energetic ionizing particles at the target tumor. These particles damage the DNADNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
of tissue cells, ultimately causing their death. Because of their reduced ability to repair damaged DNA, cancerous cells are particularly vulnerable to attack.
The figure shows how beams of electrons, X-rays or protons of different energies (expressed in MeV) penetrate human tissue. Electrons have a short range and are therefore only of interest close to the skin (see electron therapy
Electron therapy
Electron therapy or Electron Beam Therapy is a kind of external beam radiotherapy where electrons are directed to a tumor site.-Equipment:...
). Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon because energy is conserved. The term is...
X-rays penetrate more deeply, but the dose
Absorbed dose
Absorbed dose is a measure of the energy deposited in a medium by ionizing radiation per unit mass...
absorbed by the tissue then shows the typical exponential decay with increasing thickness. For protons and heavier ions, on the other hand, the dose increases while the particle penetrates the tissue and loses energy
Stopping power (particle radiation)
In passing through matter, fast charged particles ionize the atoms or molecules which they encounter. Thus, the fast particles gradually lose energy in many small steps. Stopping power is defined as the average energy loss of the particle per unit path length, measured for example in MeV/cm...
continuously. Hence the dose increases with increasing thickness up to the Bragg peak
Bragg Peak
The Bragg peak is a pronounced peak on the Bragg curve which plots the energy loss of ionizing radiation during its travel through matter. For protons, α-rays, and other ion rays, the peak occurs immediately before the particles come to rest...
that occurs near the end of the particle's range
Range (particle radiation)
In passing through matter, charged particles ionize and thus lose energy in many steps, until their energy is zero. The distance to this point is called the range of the particle...
. Beyond the Bragg peak, the dose drops to zero (for protons) or almost zero (for heavier ions).
The advantage of this energy deposition profile is that less energy is deposited into the healthy tissue surrounding the target tissue.
The ions are first accelerated by means of a cyclotron
Cyclotron
In technology, a cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator. In physics, the cyclotron frequency or gyrofrequency is the frequency of a charged particle moving perpendicularly to the direction of a uniform magnetic field, i.e. a magnetic field of constant magnitude and direction...
or synchrotron
Synchrotron
A synchrotron is a particular type of cyclic particle accelerator in which the magnetic field and the electric field are carefully synchronised with the travelling particle beam. The proton synchrotron was originally conceived by Sir Marcus Oliphant...
. The final energy of the emerging particle beam defines the depth of penetration, and hence, the location of the maximum energy deposition. Since it is easy to deflect the beam by means of electro-magnets in a transverse direction, it is possible to employ a raster scan
Raster scan
A raster scan, or raster scanning, is the rectangular pattern of image capture and reconstruction in television. By analogy, the term is used for raster graphics, the pattern of image storage and transmission used in most computer bitmap image systems...
method, i.e., to scan the target area quickly like the electron beam scans a TV tube. If, in addition, the beam energy and hence, the depth of penetration is varied, an entire target volume can be covered in three dimensions, providing an irradiation exactly following the shape of the tumor. This is one of the great advantages compared to conventional x-ray therapy.
At the end of 2008, 28 treatment facilities were in operation worldwide, and over 70000 patients had been treated by means of pion
Pion
In particle physics, a pion is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Pions are the lightest mesons and they play an important role in explaining the low-energy properties of the strong nuclear force....
s, protons and heavier ions worldwide. Most of this therapy has been with protons..
Heavy ion therapy
Heavy ion therapy is the use of particles more massive than protons or neutrons, such as carbonCarbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s. Compared to protons, carbon ions have an advantage: due to the higher density of ionisation at the end of their range, correlated damages of the DNA structure within one cell occur more often so that it becomes more difficult for the cancerous cell to repair
DNA repair
DNA repair refers to a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1...
the damage. This increases the biological efficiency of the dose by a factor between 1.5 and 3.
Compared to protons, carbon ions have the disadvantage that beyond the Bragg peak, the dose does not decrease to zero, since nuclear reactions between the carbon ions and the atoms of the tissue lead to production of lighter ions which have a higher range. Therefore, some damage occurs also beyond the Bragg peak.
By the end of 2008, more than 5000 patients had been treated using carbon ions.
Carbon ion centers in operation
The Particle Therapy Co-Operative Group continuously lists treatment centers in operation and in the planning or construction stage. At present (end of 2008), only two centers using carbon ions are in operation, both in Japan: the HIMAC at ChibaChiba, Chiba
is the capital city of Chiba Prefecture, Japan. It is located approximately 40 km east of the center of Tokyo on Tokyo Bay. Chiba City became a government designated city in 1992. Its population as of 2008 is approximately 960,000....
and the HIBMC at Hyogo. In Germany, treatment at the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung
Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung
The GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research GmbH in the Wixhausen suburb of Darmstadt, Germany is a federally and state co-funded heavy ion research center. The current director of GSI is Horst Stöcker who succeeded Walter F...
(GSI) in Darmstadt
Darmstadt
Darmstadt is a city in the Bundesland of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Rhine Main Area.The sandy soils in the Darmstadt area, ill-suited for agriculture in times before industrial fertilisation, prevented any larger settlement from developing, until the city became the seat...
, which is primarily a physics laboratory, has been discontinued in 2008, but the new HIT in Heidelberg
Heidelberg
-Early history:Between 600,000 and 200,000 years ago, "Heidelberg Man" died at nearby Mauer. His jaw bone was discovered in 1907; with scientific dating, his remains were determined to be the earliest evidence of human life in Europe. In the 5th century BC, a Celtic fortress of refuge and place of...
, which is a dedicated facility, started in November 2009. The CNAO in Pavia, Italy is going to open in 2011 and will be one of the most advanced centers for particle therapy with hadrons. CNAO will combine precise dose delivery with highly accurate patient alignment based on stereoscopic X-ray imaging. Sophisticated approaches in image-guided particle therapy (IGPT) augments the radiotherapy machines with imaging capabilities and the latest computer vision technology to increase accuracy of target localization and enable patient alignment accuracies of 0.5 mm and better.

